임베디드 OS 개발 프로젝트 CH6-2
Following the last posting, I'll continue to talk about Interrupt controler register.
데이터시트
Distrubutor controller registor
typedef union DistributorCtrl_t
{
uint32_t all;
struct {
uint32_t Enable:1; // 0
uint32_t reserved:31;
} bits;
} DistributorCtrl_t;- Distributor : Among pending registers, it provides the highest priority interrupt to CPU interface.
- This register enables or disables the distributor.
- [31:1]
- reserved - [0]
- b1: enable
- b0: disable
setenable1 register && setenable2 register
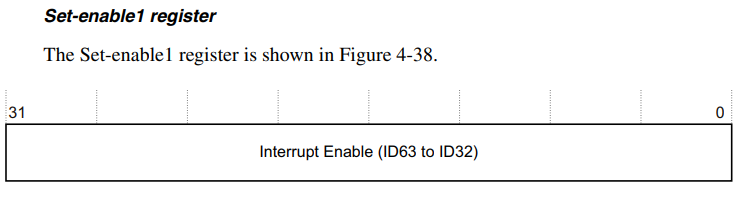
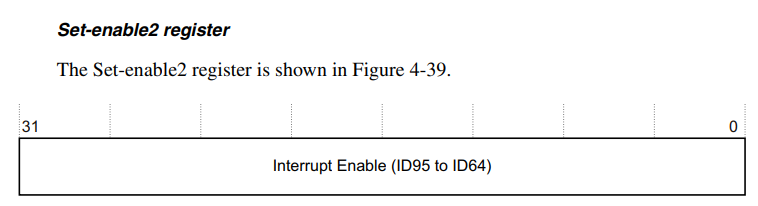
- We will set a bit of the resgieter to enable an interrupt mapped to that bit.
- Total number of bits is 64 and each are mapped to an interrupt respectively.
- The Interrupt number is between 31 and 96.
Code : Interrupt.c
Now I will examine the code.
#include "stdint.h"
#include "memio.h"
#include "Interrupt.h"
#include "HalInterrupt.h"
#include "armcpu.h"
extern volatile GicCput_t* GicCpu;
extern volatile GicDist_t* GicDist;
static InterHdlr_fptr sHandlers[INTERRUPT_HANDLER_NUM];
void Hal_interrupt_init(void){
GicCpu->cpucontrol.bits.Enable =1;
GicDist->distributorctrl.bits.Enable = 1;
GicCpu->prioritymask.bits.Prioritymask = GIC_PRIORITY_MASK_NONE;
for(uint32_t i = 0; i< INTERRUPT_HANDLER_NUM; i++){
sHandlers[i] = NULL;
}
enable_irq();
}
void Hal_interrupt_enable(uint32_t interrupt_num){
if((interrupt_num < GIC_IRQ_START) ||(interrupt_num > GIC_IRQ_END ) )
return;
uint32_t bit_num = interrupt_num - GIC_IRQ_START;
if(bit_num < GIC_IRQ_START){
SET_BIT(GicDist->setenable1, bit_num);
}
else{
bit_num = bit_num - GIC_IRQ_START;
SET_BIT(GicDist->setenable2, bit_num);
}
}
void Hal_interrupt_disable(uint32_t interrupt_num){
if((interrupt_num < GIC_IRQ_START) ||(interrupt_num > GIC_IRQ_END ) )
return;
uint32_t bit_num = interrupt_num - GIC_IRQ_START;
if(bit_num < GIC_IRQ_START){
CLR_BIT(GicDist->setenable1, bit_num);
}
else{
bit_num = bit_num - GIC_IRQ_START;
CLR_BIT(GicDist->setenable2, bit_num);
}
}
void Hal_interrupt_register_handler(InterHdlr_fptr handler, uint32_t interrupt_num){
sHandlers[interrupt_num] = handler;
}
void Hal_interrupt_run_handler(){
uint32_t interrupt_num = GicCpu->interruptack.bits.InterruptID;
if(sHandlers[interrupt_num] != NULL){
sHandlers[interrupt_num]();
}
GicCpu->endofinterrupt.bits.InterruptID = interrupt_num;
}-
It mainly sets registers previously described in this and last posting.
-
'sHandler [ Interrupt_num ]' is a containor of interrupt handlers.
-
'SET_BIT' and 'CLR_BIT' are macro defined in 'memio.h'
#define SET_BIT(p,n) ((p) |= ( 1 << (n))) #define CLR_BIT(p,n) ((p) &= ~( 1 << (n))) -
Therefore, "SET_BIT(GicDist->setenable1, n)" set n th bit 1. And "CLR_BIT" oppositely works.
enable_irq
- There is a function "endble_irq" that is not explained.
- "enable_irq" sets cpsr register for enabling the irq register.
void enable_irq(void){
__asm__ ("PUSH {r0, r1}");
__asm__ ("MRS r0, cpsr");
__asm__ ("BIC r1, r0, #0x80");
__asm__ ("MSR cpsr, r1");
__asm__ ("POP {r0, r1}");
}- Move cpsr register to r0. ("MRS r0, cpsr");
- Set the IRQ enabling bit 1. ("BIC r1, r0, #0x80");
- Update cpsr register. ("MSR cpsr, r1")