컴퓨터 하드웨어의 오작동 또는 고장으로 인해 응용프로그램 실행 오류가 발생하는 것 또는 개발자의 실수로 예기치 못한 오류가 발생하는 것을 에러라고 한다.
이러한 에러 상황을 처리해줌으로써 프로그램이 정상 실행 상태가 되도록 유지하는 것을 예외처리라고 한다.
예외가 발생하는 경우
- 예상치 못한 에러, 대응 불가능한 에러(ex. 데이터센터 화재, 천재지변)
- 대응이 가능한 에러(ex.개발자가 대응할 수 있는 에러)
- 예외가 발생했을 때 상황에서 처리할 수 있는 코드 작성
- (없는 파일) file에 데이터를 쓰고 싶을 경우
- “default_file”
- Database 데이터를 저장 → 시스템 장애 → 실패에 대한 예외 처리
- 예외처리 → 시스템 장애를 막고, 예상치 못한 서비스의 Shutdown을 막을 수 있음
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int result = 10/b; // 예외 발생 가능성이 있는 코드(예외처리 해야함)ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 발생 : 코드 상에서 빨간 밑줄은 없으나, 실행을 시키면 경고 에러가 남(UncheckedException )
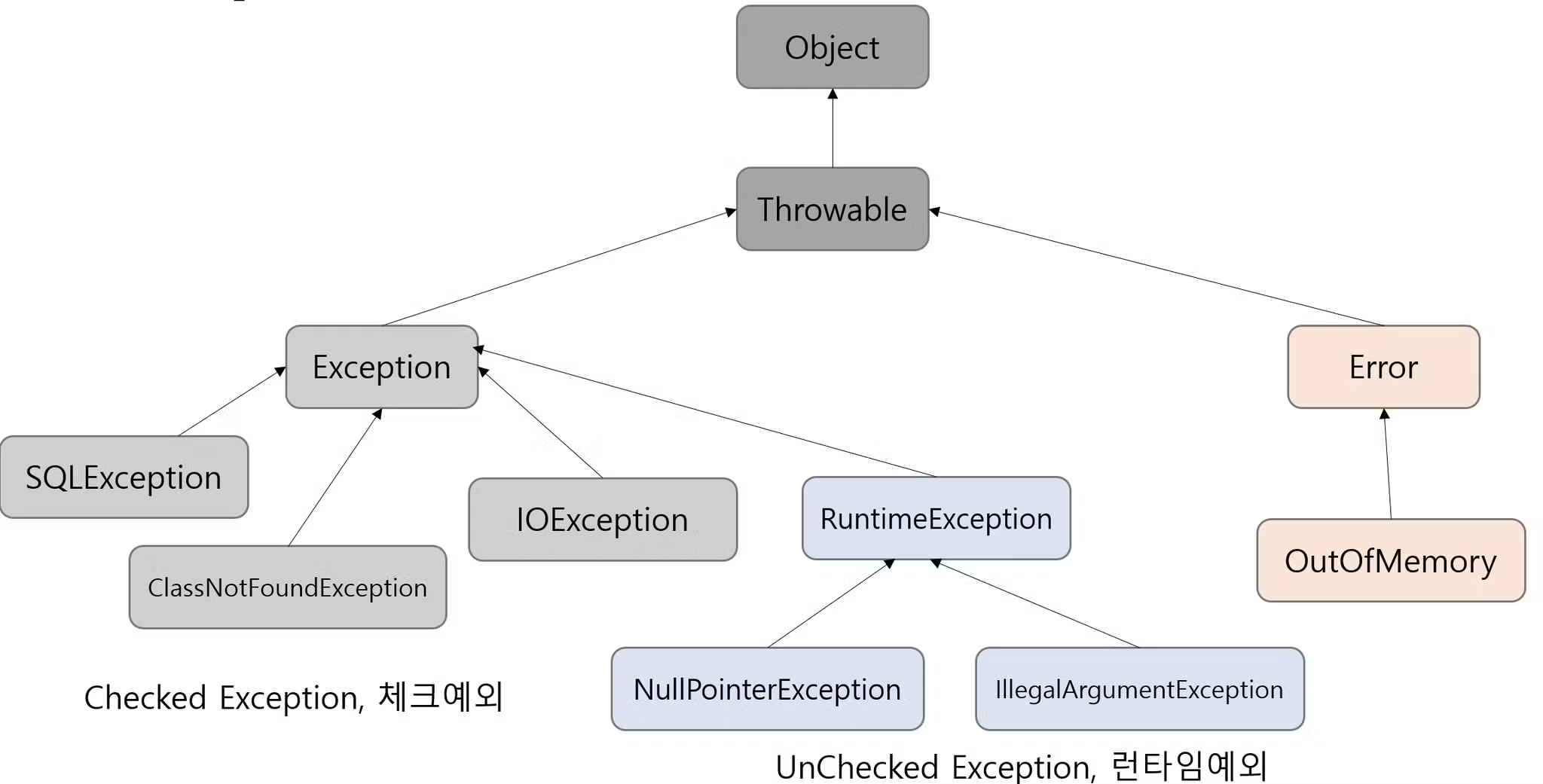
자바 표준 API에서 제공하는 예외
자바에서 정의하는 예외(Exception)
-
CheckedException
- 체크 예외
- 명시적으로 예외 처리를 강제화 O (컴파일러가 빨간 밑줄로 알려줌)
- Exception 클래스를 상속 받고 있음
- Exception 클래스는 Throwable을 상속 받고 있다.
-
UncheckedException
- 런타임예외, 실행예외, RuntimeExcepton
- 명시적으로 예외 처리를 강제화 X
- RuntimeExcepton 클래스를 상속 받고 있음
- RuntimeExcepton 도 Exception 을 상속 받고 있다.
-
FileNotFoundException : CheckedException
-
ArithmeticException : UncheckedException
-
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException : UncheckedException
-
ArithmeticException : UncheckedException
자바는 에러가 발생하면 프로그램을 중단하고 오류 메세지를 보여준다. 이런 경우 예외 처리를 해준다면 프로그램 중단 없이 오류 메세지를 출력하고 다음 프로세스로 넘어가지 않도록 조치해줄 수 있다.
예외 처리를 하는 방법은
- 예외 처리를 당장 해주는 것 (try-catch)
- 호출측으로 넘겨주는 것 (throw)
두 가지가 있다.
예외 처리 try-catch
try {
<수행할 문장 1>; // 예외 발생 가능성 있는 코드
<수행할 문장 2>;
...
} catch (예외1) { // 예외가 발생했을 때 프로그램이 종료되지 않고, catch 안에 정의해둔 실행문을 실행
<수행할 문장 A>;
...
} catch (Exception a) {
<수행할 문장 a>;
...
}try-catch 실습
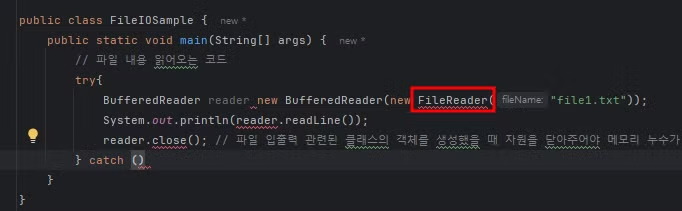
작성 시 빨간 밑줄로 뜨는 경고 표시에 ctrl + 클릭으로 자바 파일 확인
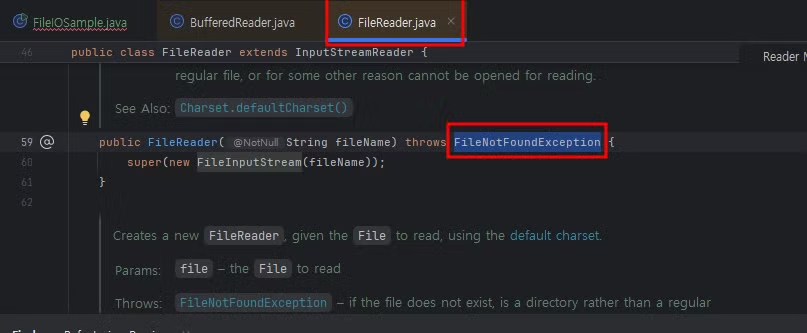
예외 처리가 필요한 구문 확인 후 try-catch문으로 예외처리 해줌
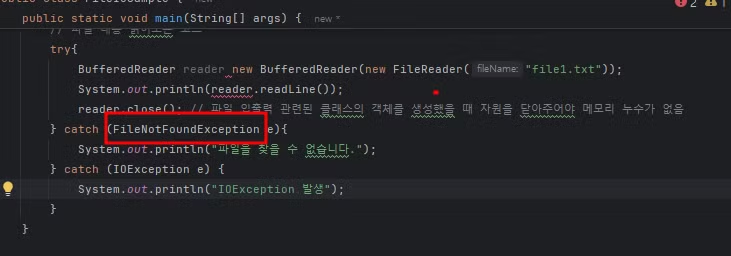
프로젝트 루트 확인 후 FileReader 에 변수를 넣어주는 방식으로 해줄 수 있음
public class FileIOSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 파일 내용 읽어오는 코드
try{
// 파일 경로
String file = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String filename = file + "/example.txt";
System.out.println(filename);
// 컴파일된 파일 기준으로 출력
String path = FileIOSample.class.getResource("").getPath();
System.out.println(path);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
reader.close(); // 파일 입출력 관련된 클래스의 객체를 생성했을 때 자원을 닫아주어야 메모리 누수가 없음
} catch (FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println("파일을 찾을 수 없습니다.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IOException 발생");
}
}
}FileNotFoundException 은 IOException을 상속 받는다.(IOException 이 부모임)
이럴 경우에는IOException 이 FileNotFoundException의 예외까지 처리할 수 있음으로 catch 문을 2개 하지 않아도 된다. → 부모 Exception이 자식 Exception까지 포괄할 수 있다.
다만, FileNotFoundException 일 경우에만 처리해야될 로직이 있을 경우 따로 처리해주는 게 맞다. → 예외 출력문만 남길 때(로깅)는 최상위 exception만 작성하는 경우도 있다.
프로젝트 루트 확인하는 방법
String file = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String filename = file + "/example.txt";
System.out.println(filename);C:\Users\User\IdeaProjects\java-project/example.txt 다중 catch문 작성시 주의사항
상위 예외클래스가 하위 예외 클래스보다 아래쪽에 위치해야한다
try {
(FNFE 발생)
} catch(IOExceptione e) {
예외처리1
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) { // 컴파일 오류
예외처리2
}try {
(FNFE 발생)
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
예외처리1
} catch(IOExceptione e) {
예외처리2
}같은 위상에 있을 경우 다중 캐치문으로 각각 정의를 해주어도 되지만, 각 예외 처리문에서 실행될 내용이 같을 경우 두 개의 Exception을 같이 선언해줄 수 있다.
try {
<수행할 문장 1>;
<수행할 문장 2>;
...
} catch (예외1 | 예외2) { // 둘 중 하나가 예외일 경우 A 수행 (멀티 catch)
<수행할 문장 A>;
...
}public class FileIOSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 파일 내용 읽어오는 코드
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
try{
int result = 5 / b; // ArithmeticException 발생 가능
// 파일명 루트를 기준으로 확인
String file = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String filename = file + "/example.txt";
System.out.println(filename);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
reader.close(); // 파일 입출력 관련된 클래스의 객체를 생성했을 때 자원을 닫아주어야 메모리 누수가 없음
} catch (FileNotFoundException | ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("Exception: " + e);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IOException 발생");
}
}
}
finally
try-catch가 정상 실행되거나, 예외가 발생했을 경우에도 반드시 1번은 실행되는 구문
public class FileIOSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 파일 내용 읽어오는 코드
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
try{
int result = 5 / b; // ArithmeticException 발생 가능
// 파일명 루트를 기준으로 확인
String file = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String filename = file + "/example.txt";
System.out.println(filename);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
reader.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException | ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("Exception: " + e);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IOException 발생");
} finally{
System.out.println("bye"); // 예외 발생해도 실행하고 싶은 코드
}
}
}
Exception: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
bye자바 IO 관련된 것들은 클로징을 반드시 해주어야 되는데, 실행을 하다가 예외로 넘어가게 되어서 자원이 닫히지 않을 가능성이 있음으로, 클로징 작업을 finally 에 해준다.
public class FileIOSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 파일 내용 읽어오는 코드
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
BufferedReader reader = null;
try{
int result = 5 / b; // ArithmeticException 발생 가능
// 파일명 루트를 기준으로 확인
String file = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String filename = file + "/example.txt";
System.out.println(filename);
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
} catch (FileNotFoundException | ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("Exception: " + e);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IOException 발생");
} finally{
try{
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// reader 자원 닫으면서 예외 발생했을 때
}
}
}
}finally 에 생기는 exception을 처리하기 위해 안에 또 try 문을 해주는 경우가 생긴다. 위와 같은 경우 가독성이 떨어지는 문제를 해결하기 위해 자바 7 버전 부터 예외 발생 여부와 상관없이 사용했던 리소스를 자동으로 닫아주는 자동 리소스 닫기 try-with-resource 를 지원해준다.
public class FileIOSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
String file = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String filename = file + "/example.txt";
try(BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename))){
int result = 5 / b; // ArithmeticException 발생 가능
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
} catch (FileNotFoundException | ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("Exception: " + e);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IOException 발생");
}
}
}BufferedReader 선언했던 부분을 try 구문에 넣어준다.
BufferedReader reader = null;
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));try(BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename))){
//실행문
}throws
던지는 것, 메서드를 호출한 쪽에서 컴파일 오류가 발생함
이 방법은 당장 처리해 주지 않고 호출측한테 예외처리를 넘기는 것
public class FileIOSample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileIOSample3 fileIOSample3 = new FileIOSample3();
fileIOSample3.readFile();
}
public void readFile() throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(""));
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
reader.close();
}
}위 코드에서는 예외 처리를 던졌기 때문에 fileIOSample3.readFile(); 에서 컴파일 오류가 발생한다.
public class FileIOSample3 {
public static void main(String[] args){
FileIOSample3 fileIOSample3 = new FileIOSample3();
try{
fileIOSample3.readFile();
} catch(IOException e){
System.out.println("IOException 예외 발생 시 예외 처리")
}
}
public void readFile() throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(""));
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
reader.close();
}
}예외 처리를 던지기만 하는 코드가 발생하는 것은 잘못 작성된 코드이고, 제일 베스트는 예외 발생이 일어날 수 있는 구문에서 try-catch를 해주는 것이 좋다.
public class FileIOSample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileIOSample3 fileIOSample3 = new FileIOSample3();
fileIOSample3.readFile();
}
public void readFile() throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(""));
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
reader.close();
}
public void handleFile() throws IOException {
readFile();
}
}public class FileIOSample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileIOSample3 fileIOSample3 = new FileIOSample3();
}
public void readFile() {
try{
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(""));
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
reader.close();
} catch(Exception e){
// 예외 처리 발생
}
}
}사용자 정의 예외(checked Exception)
각각 상속 받아서 정의할 수 있다. 사용자 정의 예외를 만들어주는 이유는 자바에서 만들어주지 않는 예외를 내가 만들어서 던져주고 싶을 때 , 외부에서 이 처리에 대한 것을 강제화 하고 싶을 때 사용한다.
// 사용자 정의 예외(checked Exception)
public class BalanceInsufficientException extends Exception{
public BalanceInsufficientException(){
}
public BalanceInsufficientException(String message){
super("Balance insufficient: " + message);
}
}사용자 정의 예외 발생 시키기
throw를 사용하여 예외를 던져준다.
void method() throws BalanceInsufficientException{
// 수동으로 사용자 정의 예외 발생시키기 (만약 런타임이라면? 에러 발생하지 않음)
throw new BalanceInsufficientException("잔고 부족 에러 메세지");
}public void withdraw(int money) throws BalanceInsufficientException { // 사용자 정의 예외 떠넘기기
if (balance < money) {
throw new BalanceInsufficientException("잔고가 부족합니다. " + (balance - money) + " 부족함"); // 사용자 정의 예외 발생
}
balance -= money;
}호출측이 인지할 수 있고, 호출 측에서 처리해줄 수 있다. 사용자 정의 예외를 던짐으로써 호출측에서의 처리를 강제화 시킬 수 있다.
throw: 예외를 일부러 발생 시키는 용도로 사용함throws: 메서드의 시그니처, 생성자의 뒤에 붙고, 던지고 싶은 exception을 붙혀준다. → 던지는 목적으로 사용함, 메서드가 예외를 던질 수 있음을 선언함