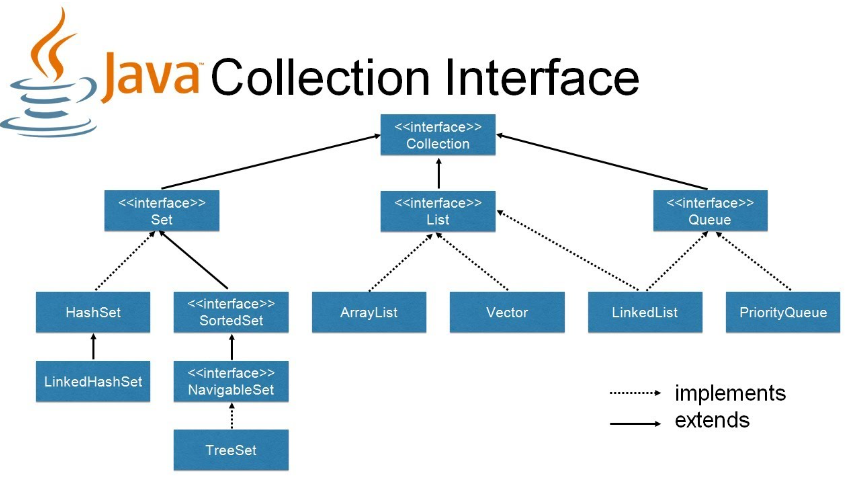
Set 이란?
셋(set: 집합)이란 자료구조 중의 하나로 특정한 값들을 저장하는 추상자료형이다.
객체를 중복해서 저장할 수 없으며, 하나의 null 값만 저장할 수 있다.
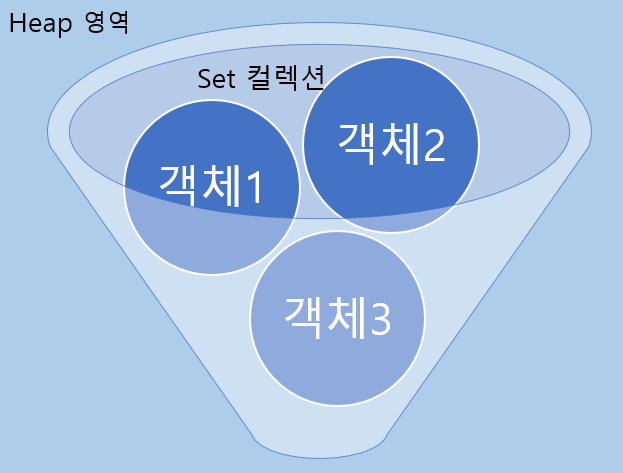
비선형 구조이기 때문에 순서의 개념과 인덱스가 존재하지 않는다.
때문에 값을 추가/삭제하는 경우, Set 내부에 해당 값을 검색하여 해당 기능을 수행해야 한다. 이로 인해 처리 속도가 List 구조에 비해 느리다는 것이 단점이다.
Set 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스
- HashSet: Set을 구현하는 대표 클래스로 데이터를 중복할 수 없고 순서를 보장하지 않는다.
- TreeSet: HashSet 특성 + 오름차순으로 데이터를 정렬한다.
- LinkedHashSet: 데이터를 중복해서 저장할 수 없고, 입력한 순서대로 데이터를 저장한다.
HashSet이란
자바의 컬렉션 프레임워크에서 제공되는 자료구조로, Set 인터페이스의 구현 클래스이다. 때문에 Set의 성질을 그대로 상속받는 다는 것이 특징이다.
HashSet의 성질
- 중복된 값을 허용하지 않는다.
값의 존재 유무를 파악할 때 사용할 수 있다. - List 등과는 다르게 저장한 순서가 보장되지 않는다.
저장 순서를 유지해야 한다면 JDK 1.4부터 제공되는 클래스 LinkedHashSet을 사용해야 한다. - null을 값으로 허용한다.
즉, 정렬되지 않고, 중복되지 않는 데이터를 순서에 상관없이 저장한다. 저장 요청이 왔을 때 기존 저장되어 있는 데이터에 같은 데이터가 있는지를 확인해야 한다.
HashSet 장점
- 효율적이고 빠른 성능: 요소 추가, 제거 및 검색과 같은 기본 작업에 대해 일정한 시간 복잡도를 제공한다.
- 중복되지 않는 요소: 중복 요소를 포함하지 않는다.
- 유연성: 사용자 정의 클래스를 포함하여 모든 유형의 객체를 저장할 수 있다.
- 순서 유지 하지 않음 : 요소가 추가되는 순서를 유지하지 않는다.
중복을 걸러내는 과정
- HashSet은 객체를 저장하기 전에 먼저 객체의 hashCode() 메서드를 호출해서 해시 코드를 얻어낸 다음, 저장되어 있는 객체들의 해시 코드와 비교합니다.
- 만약 같은 해시 코드가 있다면 다시 equals() 메서드로 두 객체를 비교해서 true가 나오면 동일한 객체로 간주하고 중복 저장을 하지 않습니다.
- 문자열을 HashSet에 저장할 경우, 같은 문자열을 갖는 String 객체는 동일한 객체로 간주되고 다른 문자열을 갖는 String 객체는 다른 객체로 간주되는데,
- 그 이유는 String 클래스가 hashCode()와 equals() 메서드를 재정의해서 같은 문자열일 경우 hashCode()의 리턴값이 같고, equals()의 리턴값은 true가 나오도록 했기 때문입니다.
HashSet 사용법 및 메서드
1. HashSet 생성
아래 코드와 같이 사용하여 다양한 방법으로 Hash를 생성할 수 있다.
HashSet<데이터타입> set = new HashSet<데이터 타입(생략 가능)>();
// 타입을 지정 가능
HashSet<String> animals1 = new HashSet<String>();
// 타입을 생략하여 사용 가능 -> 빈 HashSet생성 시 사용
HashSet<String> animals2 = new HashSet<>();
// 초기 용량(Capacity) 설정
HashSet<String> animals3 = new HashSet<>(10);
// animal의 모든 값을 가진 HashSet 생성
HashSet<String> animals4 = new HashSet<>(animals1);
//초기값 지정 가능
HashSet<String> animals5 = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList("tiger", "lion", "fox")); 2. HashSet 요소 값 추가 - add()
생성된 Hash에 add() 메서드를 호출하여 값을 추가할 수 있다.
HashSet<String> animals = new HashSet<>()
animals.add("tiger");
animals.add("lion");
animals.add("fox");만약 입력되는 값이
- HashSet 내부에 존재하지 않는다면 그 값을 HashSet에 추가하고 true 를 반환한다.
- HashSet 내부에 존재한다면 false를 반환한다.
3. HashSet 요소 값 삭제 - remove()
remove(value)와 clear() 메서드를 사용하여 Hash값을 제거할 수 있다.
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>(Arrays.asList(1,2,3));
//값 1 제거
set.remove(2);
//모든 값을 제거
set.clear();만약 삭제하려는 값이
- HashSet 내부에 존재한다면 그 값을 삭제하고 true를 반환한다.
- HashSet 내부에 존재하지 않는 다면, false를 반환한다.
4. HashSet 크기 구하기 - size()
size() 메서드를 사용하여 Hash의 크기를 구할 수 있다.
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>(Arrays.asList(1,2,3));
//set 크기 : 3
System.out.println(set.size());5. HashSet 검색 - contains()
원하는 값에 대해 contains(value) 메서드를 통해 Hash 내부에 존재하는 지 확인할 수 있다.
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>(Arrays.asList(1,2,3));
////set내부에 값 1이 있다면 true 출력, 없다면 false 출력
System.out.println(set.contains(1));6. HashSet 데이터 출력
Set 컬렉션을 그냥 print 처리할 경우 대괄호로 묶여 Set의 전체값이 출력된다.
때문에 하나의 객체를 가져오고 싶을 경우 반복자(Iterator)를 사용해 출력할 수 있다.
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Integer
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(1);
System.out.println(set);
// 결과값 [1, 2, 3]
// String
HashSet<String> set2 = new HashSet<String>();
set2.add("a");
set2.add("b");
set2.add("c");
set2.add("a");
System.out.println(set2);
// 결과값 [a, b, c]
// Integer 출력
Iterator iter = set.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iter.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println("");
// 결과값 1 2 3
// String 출력
Iterator iter2 = set2.iterator();
while(iter2.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iter2.next() + " ");
// 결과값 a b c
}
}
}참고 자료
