Scanner 관련
무한 루프
while (!userChoice.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) {
try {
System.out.println("== 작업을 선택해주세요 ==");
System.out.println("(1) 계산기 | (2) 결과 확인 | (3) 최근 값 하나 제거 | (4) 특정 인덱스 값 변경 | (5) 입력 값보다 큰 저장 값 조회");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1 -> handleCalculation(scanner, calculator);
case 2 -> handlePrintResults(calculator);
case 3 -> handleRemoveFirstResult(calculator);
case 4 -> handleUpdateResult(scanner, calculator);
case 5 -> handleFindResultsGreaterThanInput(scanner, calculator);
default -> System.out.println("목록에 없는 값입니다. 다시 입력해주세요.");
}
} catch (InputMismatchException ime) {
System.out.println("잘못된 입력입니다.");
continue;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ioobe) {
System.out.println("저장된 값이 없거나 잘못된 인덱스 지정입니다.");
continue;
}
scanner.nextLine(); // 개행 문자 제거
System.out.print("작업을 종료하시겠습니까? (exit 입력 시 종료) > ");
userChoice = scanner.nextLine();
}예외 처리를 위해 try-catch를 사용했지만 nextInt() 입력 후 남은 개행 문자로 인해 catch 문을 지나 다시 while 문 안으로 들어오면서 choice 값에 개행 문자가 그대로 들어가 무한 반복되는 문제가 발생
catch에 개행 문자 제거를 위해 nextLine() 추가
while (!userChoice.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) {
try {
System.out.println("== 작업을 선택해주세요 ==");
System.out.println("(1) 계산기 | (2) 결과 확인 | (3) 최근 값 하나 제거 | (4) 특정 인덱스 값 변경 | (5) 입력 값보다 큰 저장 값 조회");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1 -> handleCalculation(scanner, calculator);
case 2 -> handlePrintResults(calculator);
case 3 -> handleRemoveFirstResult(calculator);
case 4 -> handleUpdateResult(scanner, calculator);
case 5 -> handleFindResultsGreaterThanInput(scanner, calculator);
default -> System.out.println("목록에 없는 값입니다. 다시 입력해주세요.");
}
} catch (InputMismatchException ime) {
System.out.println("잘못된 입력입니다.");
scanner.nextLine(); // 개행 문자 제거
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ioobe) {
System.out.println("저장된 값이 없거나 잘못된 인덱스 지정입니다.");
scanner.nextLine(); // 개행 문자 제거
}
scanner.nextLine(); // 개행 문자 제거
System.out.print("작업을 종료하시겠습니까? (exit 입력 시 종료) > ");
userChoice = scanner.nextLine();
}
우선 개행 문자를 제거하기 위해서 각 catch 문 안에 개행 문자 제거를 위한 nextLine()을 두었고, continue를 제거했다.

무한 루프는 해결했지만 catch 문 이후 개행 문자 제거 용도인 nextLine()이 중복 돼서 바로 넘어가지 않고, 엔터를 2번 눌러야 넘어가졌다.
try-catch 문 바깥에 있는
nextLine()을 지우게 되면 catch 문을 지나지 않는 흐름에서 문제가 생기기 때문에 제거할 수 없었다.
continue 추가
continue를 사용하게 되면 continue 이후 내용은 무시하고 다시 while 문으로 돌아가게 된다.

따라서 엔터 한 번으로 다시 while 문의 처음으로 돌아갈 수 있었다.
제네릭 관련
타입 정의
ArithmeticCalculator 클래스에 제네릭을 사용할 때 단순 <T> 를 사용했더니 계산을 하는 메서드 내부에서 컴파일 에러가 나왔다.
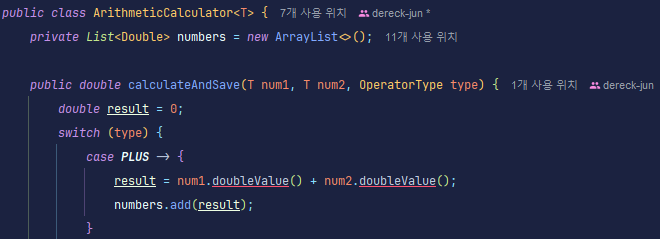
<T extends Number> 사용
<T extends Number>를 사용하면 T의 타입이 Number를 상속한 클래스로 정해진다. 따라서 문제 없이 계산을 진행할 수 있게 되었다.
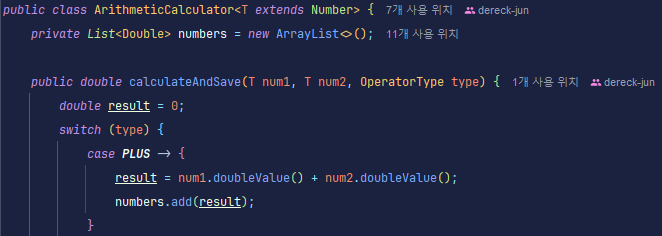
처음엔 제네릭 타입이 아닌 와일드 카드를 사용하려고 했으나 바로 컴파일 에러가 발생해서 제네릭 타입으로 바꾸게 되었다.
Enum 관련
매개변수로 Enum 받기
ArithmeticCalculator<T extends Number> 클래스 내의 calculateAndSave() 메서드에서 switch에 연산자를 char나 String으로 받아서 처리하는 것이 아니라 Enum으로 정의된 값에 따라 계산을 진행하게 하고자 했다.
public enum OperatorType {
PLUS("+"),
MINUS("-"),
MULTIPLY("*"),
DIVIDE("/");
private final String symbol;
OperatorType(String symbol) {
this.symbol = symbol;
}
public String getSymbol() {
return symbol;
}
}public double calculateAndSave(T num1, T num2, OperatorType type) {
double result = 0;
switch (type) {
case PLUS -> {
result = num1.doubleValue() + num2.doubleValue();
numbers.add(result);
}
case MINUS -> {
result = num1.doubleValue() - num2.doubleValue();
numbers.add(result);
}
case MULTIPLY -> {
result = num1.doubleValue() * num2.doubleValue();
numbers.add(result);
}
case DIVIDE -> {
if (num2.doubleValue() == 0) {
throw new ArithmeticException("0 으로 나눌 수 없습니다.");
}
result = num1.doubleValue() / num2.doubleValue();
numbers.add(result);
}
default -> System.out.println("지원하지 않는 연산 기호입니다!");
}
return result;
}하지만 "실행 클래스에서 값을 받고 나서 OperatorType에 맞추려면 분기 처리를 또 해야 되나?" 라는 생각을 하게 됐다. 그리고 나온 결과물은...
if (operator.equalsIgnoreCase("plus") || operator.equals("+")) {
calculator.calculateAndSave(firstNum, secondNum, OperatorType.PLUS);
} else if ( ... ) {
// 위를 반복
}String 값으로 전달된 operator에 따라 Enum 값을 return
values() 메서드를 사용해서 Enum에 정의된 상수를 해당 클래스 타입의 배열 형태로 만들 수 있다는 것을 알았다. 이를 통해 반복문으로 상수에 정의된 symbol과 일치하는 값이 있는지 확인 후 있다면 해당 Enum 상수를 return 하도록 하는 메서드를 만들어서 사용했다.
public static OperatorType fromSymbol(String symbol) {
for (OperatorType type : OperatorType.values()) {
if (type.symbol.equals(symbol)) {
return type;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("지원하지 않는 연산 기호 입니다.");
}또한 Enum 클래스는 인스턴스화 할 수 없고, 사용하는 곳이 main() 내부이므로 메서드를 static으로 만들어서 인스턴스를 생성하지 않고 사용할 수 있도록 했다.

