.png)
1) String Lib 기초 함수
String 라이브러리 사용을 위해서는 다음과 같이 작성해줘야 한다.
#include <string>String Lib의 최대 장점은 문자열 비교를 쉽게 가능하다는 것이다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string temp = "123";
string a = "123";
string b = "234";
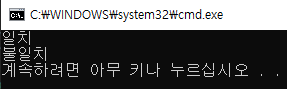
if (temp == a) cout << "일치" << endl;
if (temp != b) cout << "불일치" << endl;
return 0;
}결과
이와 같이 문자열을 숫자 비교하는 거와 같이 == 연산자를 사용하여 비교할 수 있는 것이 큰 장점이다.
또한, String도 문자열이기 때문에 문자 하나하나를 출력할 수도 있다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string temp = "123";
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << temp[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}결과
String의 사이즈또한 쉽게 구할 수 있다.
string temp = "123";
temp.legnth(); // 32) String Lib 심화 함수
find 와 npos 함수
str1.find(str2,pos) : str1 문자열에서 pos위치 부터 str2라는 문자(문자열)을 찾아라!!
결과로는 찾은 위치(Index)를 반환해준다!
만약 str1에서 str2를 찾지 못하였다면, str1.npos와 동일한 값을 반환하게 된다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str1 = "ABCDAB";
string str2 = "AB";
int pos = 0;
while (1) {
// pos(0번 index)부터 "AB"를 찾겠다!
int Gopos = str1.find(str2, pos);
// pos 이후에 "AB"를 찾지 못하면 while문 빠져나오기!
if (Gopos == str1.npos) break;
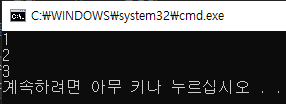
cout << Gopos << endl;
// 한번 찾은 위치 다음부터 찾도록 작성
pos = Gopos + 1;
}
return 0;
}결과
substr : 문자열 자르기
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string temp = "123456789";
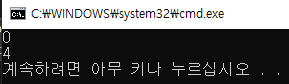
// temp의 2번 index인 3부터 3개 잘라서 자른 부분을 반환
temp.substr(2, 3); // 345
return 0;
}자른 부분을 반환 하는게 아닌 자르고 남은 부분을 반환하고 싶을 때는 erase함수를 사용할 수 있다.
erase : 문자열 지우기
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string temp = "123456789";
// temp의 2번 index인 3부터 3개 자르고 남은 부분 반환
temp.erase(2, 3); // 126789
return 0;
}stoi 와 to_string
string 자료형을 int로 변환하고, int 자료형을 string 자료형으로 변환할 수 있다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string temp = "123";
// 문자열 "123"을 숫자 123으로 변환 후 10 더하기
int tempint = stoi(temp) + 10; // 123 + 10 = 133
// 숫자 133을 문자열 "133"으로 변환 후 문자열 "ABC" 붙이기
to_string(tempint) + "ABC"; // "133ABC"
}