htop
sudo apt install htop -y , htop
리눅스 프로세스를 보는 명령어(top)보다 더 간편하게 보는 유틸리티
해당 명령어를 통해 core 개수를 확인할 수 있습니다.
Core의 개수마다 thread를 관리하기에 CPU 최고 효율을 뽑아낸다.
Data Decomposition
데이터 단위로 분해 후 Thread Programming, 각 Thread마다 같은 작업 수행 -> core 최고 효율
Ncurses(엔컬즈스)
New Curses의 약어로 CLI로 CUI 같은 APP을 만들고자할 때 사용하는 LIB
sudo apt install libncursesw5-dev로 LIB 설치
gcc ./main.c -o ./main -lncursesw && ./main : 빌드
Ncurses 기본코드
#include <ncurses.h>
int main()
{
initscr(); // ncurses 시작 내부 세팅
printw("Hello wolrd"); // Hello world, printw임을 명심하자
refresh(); // 화면 갱신
getch(); // 키를 눌러야 프로그램이 종료되도록, 안쓰면 자동종료
endwin(); // ncurses 종료
return 0;
}Clear
화면 전체를 지운다.
#include <ncurses.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
initscr();
printw("READY\n");
refresh();
usleep(1000 * 200);
clear(); // READY를 띄운 후 0.2초만에 지워버린다.
printw("GO\n"); // GO는 실행될까?
sleep(3);
clear(); // 화면을 새로고치는 refresh() 전에 clear를 실행해서 GO는 출력되지 않는다.
refresh();
usleep(1000 * 500);
printw("FINISH\n");
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}타이머 구현하기
#include <ncurses.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
initscr();
float count = 0;
while(1)
{
printw("%.2f",count); // 소수 둘째짜리 까지 표현
refresh();
clear();
count += 0.01; // 0.00 ~ 10.00 까지 표현하기 위해
if(count > 10.00) break; // 10초까지의 타미어 구현
usleep(10000); // 0.01초마다 실행
}
clear();
printw("FINISH\n");
refresh();
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
약간의 오차가 발생한다. 10초 타이머인데 표기는 잘되지만 실제 10동안 작동하는게 아닌 14초정도 작동하는
Delay가 발생한다.
sleep함수 내부 구조 Delay와 APP단 개발의 delay가 문제라고 생각할 수 있다.
로딩창
#include <ncurses.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
initscr();
while(1)
{
for(int y=0; y<30; y++) // 로딩창 증가
{
clear();
for(int x=0; x<=y; x++)
{
printw("*");
}
printw("\n");
refresh();
usleep(30*1000);
}
for(int y=29; y>=0; y--) // 로딩창 감소
{
clear();
for(int x = 0; x <= y; x++)
{
printw("*");
}
printw("\n"); // 가시성 좋게 : 증가 및 감소할때 커서가 같이 움직이기 때문에
refresh();
usleep(30*1000);
}
}
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
좌표 옮기기
move(y,x)
#include <ncurses.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
initscr();
// 내 컴퓨터는 좌표가 (57,85)가 좌하단 끝이다. 글자를 적기 위해서는 x값에 여유를 줘야한다. 좌표는 창크기에 따라 달라지니 좌표의 끝은 항상 달라진다.
move(10, 30); // 커서를 y : 10 , x : 30 좌표로 옮긴다.
printw("GAME OVER\n");
refresh();
sleep(2);
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}결과
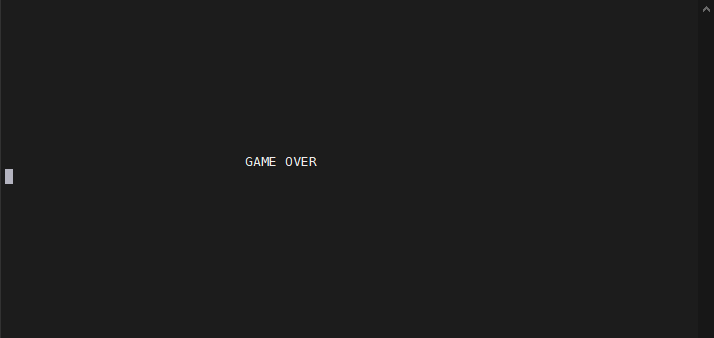
랜덤 함수
정수형 랜덤값을 리턴합니다.
#include <ncurses.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // rand() 함수를 위한 LIB
int main()
{
initscr();
while(1)
{
clear();
printw("%d\n", rand()); // 랜덤수로 큰 수도 나온다.
// rand() % 10 + 3 : 3 ~ 12 => 다양하게 변화가능
printw("%d\n", rand() % 5); // 0 ~ 4
refresh();
usleep(100 * 1000);
}
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
rand( ) 함수 한계점
rand() : 랜덤값은 랜덤 순열의 순서가 고정되어 있다.
#include <ncurses.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // rand() 함수를 위한 LIB
int main()
{
initscr();
for(int i = 0; i< 10; i++) // 0 ~ 9까지 10개 출력하기
{
printw("%d\n", rand() % 10);
}
refresh();
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
| 첫번째 실행 | 두번째 실행 | 세번째 실행 |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
해결책 : srand 함수
srand(랜덤순열ID) : 랜덤값이 각각의 ID의 순열로 생성된다.
#include <ncurses.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // rand() / srand() 함수를 위한 LIB
#include <time.h> // time()을 위한 LIB
int main()
{
initscr();
srand(time(NULL)); // 매초 다른 순열로 랜덤값을 만들어줍니다.
//time(NULL) : 1970년 1월 1일 0시 부터 오늘 시각과의 차를 초를 나타낸 출력하는 함수
for(int i = 0; i< 10; i++)
{
printw("%d\n", rand() % 10);
}
refresh();
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}| 첫번째 실행 | 두번째 실행 | 세번째 실행 |
|---|---|---|
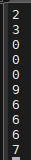 | 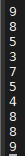 | 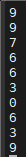 |
입력받기 : scanw
#include <ncurses.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // rand() 함수를 위한 LIB
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
initscr();
int start,end = 0;;
scanw("%d %d",&start,&end); // 3 7
srand(time(NULL));
for(int i = 0; i< 10; i++) // 3 ~ 7을 랜덤하게 출력하는 함수
{
printw("%d\n", rand() % (end-start+1) + start);
}
refresh();
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
ncurses + pthread
gcc ./test.c -o ./test -lncursesw -lpthread && ./test를 통해 빌드
mvprintw
mvprintw(1,3,"###") : move함수 + printw 함수 합친 것
커서제거 함수 : curs_set(0)
코드
#include <pthread.h>
#include <ncurses.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pthread_mutex_t mlock; // mutex를 선언
void *abc() { // thread 함수
int num = 0;
while(1) {
for (int y = 0; y<4; y++) { // (10,20)에서 로딩(#) 증가시키기
pthread_mutex_lock(&mlock); // mutex를 통해 동시성 에러 방지
move(10,20);
for (int x = 0; x<=y; x++) printw("#");
refresh();
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mlock);
usleep(100 * 1000);
}
for (int y = 3; y>=0; y--) { // (10,20)에서 로딩(#) 감소시키기
pthread_mutex_lock(&mlock);
move(10,20);
for (int x = 0; x<=y; x++) printw("#");
for (int x = y + 1; x < 4; x++) printw(" "); // 남아있는 뒷자리 없애주기
refresh();
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mlock);
usleep(100 * 1000);
}
}
}
int main()
{
initscr();
clear();
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, abc, NULL); // thread 생성
int num = 0;
while(1) { // 업카운팅
pthread_mutex_lock(&mlock);
mvprintw(10,10,"%d", num); // move + printw : (10,10) 떨어진 곳에 출력
refresh();
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mlock);
num++;
}
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}