Broadcastable interface
Radio - action을 받아 BroadcastingStation에게 브로드캐스팅
BroadcastingStation - newState를 받아 Radio들에게 브로드캐스팅
Radio와 BroadcastingStation은 공통적으로 Receiver와 Sender를 갖고있으며 Broadcasting을 수행합니다.
먼저 Broadcasting을 수행할 수 있는 인터페이스를 먼저 만들어줍니다.
// modules/broadcast/interfaces/Broadcastable
export default interface Broadcastable {
broadcast(message: any): void;
}CommunicationDevice class
다음 이 broadcastable 인터페이스를 가지면서 receiver,sender를 갖는 CommunicationDevice를 만들어줍니다.
// modules/broadcast/classes/CommunicationDevice.ts
import Broadcastable from "../interfaces/Broadcastable";
import ChannelAddress from "../types/ChannelAddress";
export default abstract class CommunicationDevice implements Broadcastable {
#sender: BroadcastChannel;
#receiver: BroadcastChannel;
constructor(address: ChannelAddress) {
this.#sender = new BroadcastChannel(address.sender);
this.#receiver = new BroadcastChannel(address.receiver);
this.#receiver.onmessage = this.handleMessage.bind(this);
}
broadcast(message: any): boolean {
this.#sender.postMessage(message);
}
protected abstract handleMessage(evt: MessageEvent) {}
}CommunicationDevice는 sender와 receiver를 갖습니다. broadcast로 sender에게 메세지를 보내고 handleMessage로 receiver가 전달 받은 메세지를 처리합니다. handleMessage는 Device에 따라 다르게 처리할 수 있도록 추상화시켰습니다.
BroadcastChannel은 채널주소를 받고 같은 채널주소의 BroadcastChannel끼리 통신하므로 생성자에서 주소를 받아줍니다.
주소는 ChannelAddress 타입을 따로 생성했습니다.
// modules/broadcast/types/ChannelAddress.ts
type ChannelAddress = {
readonly sender: string;
readonly receiver: string;
};
export default ChannelAddress;Packet,Action 개념 추가
CommunicationDevice를 상속하는 Radio, BroadcastingStation을 구현하기 전에 클래스간의 관계를 그려봅시다.
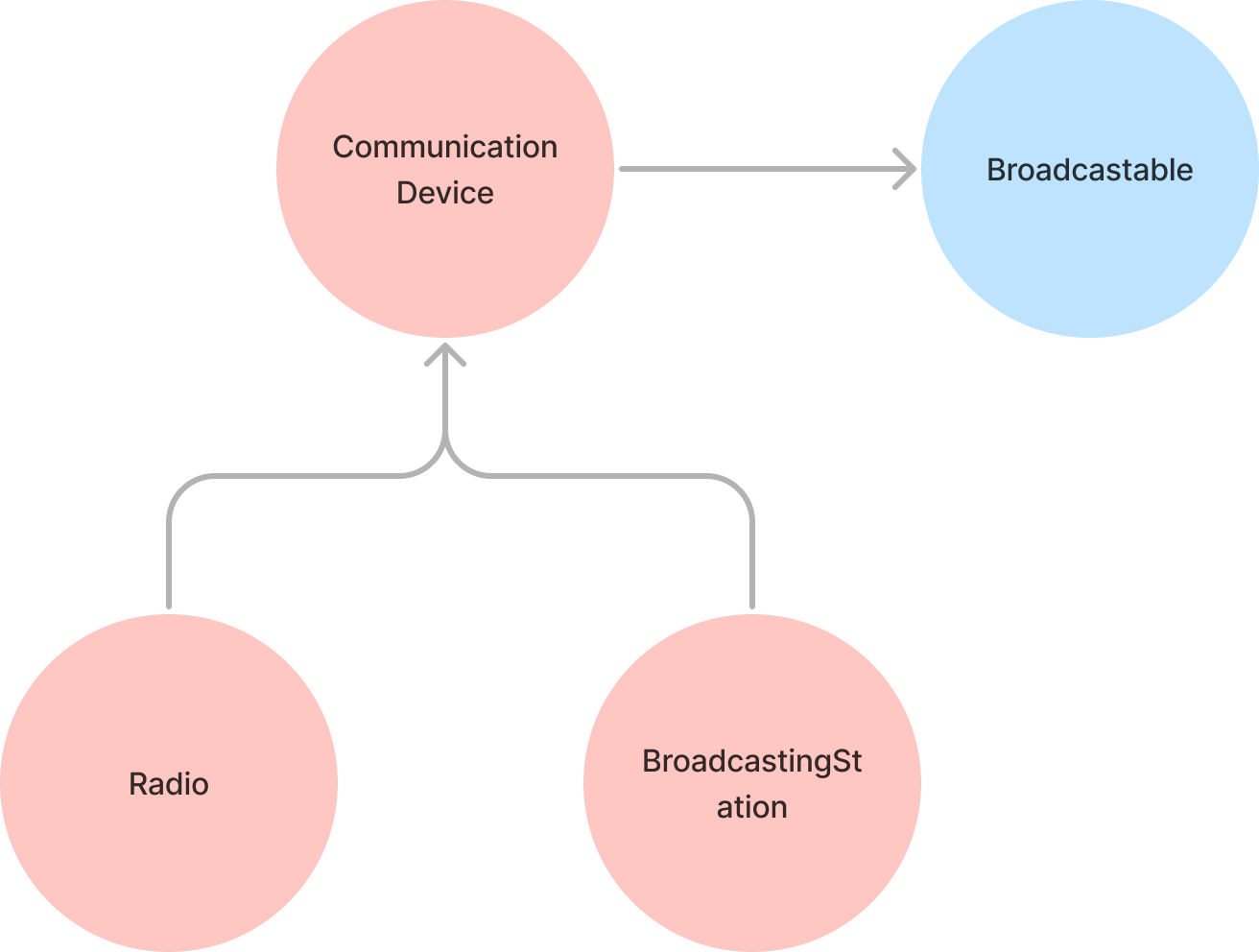
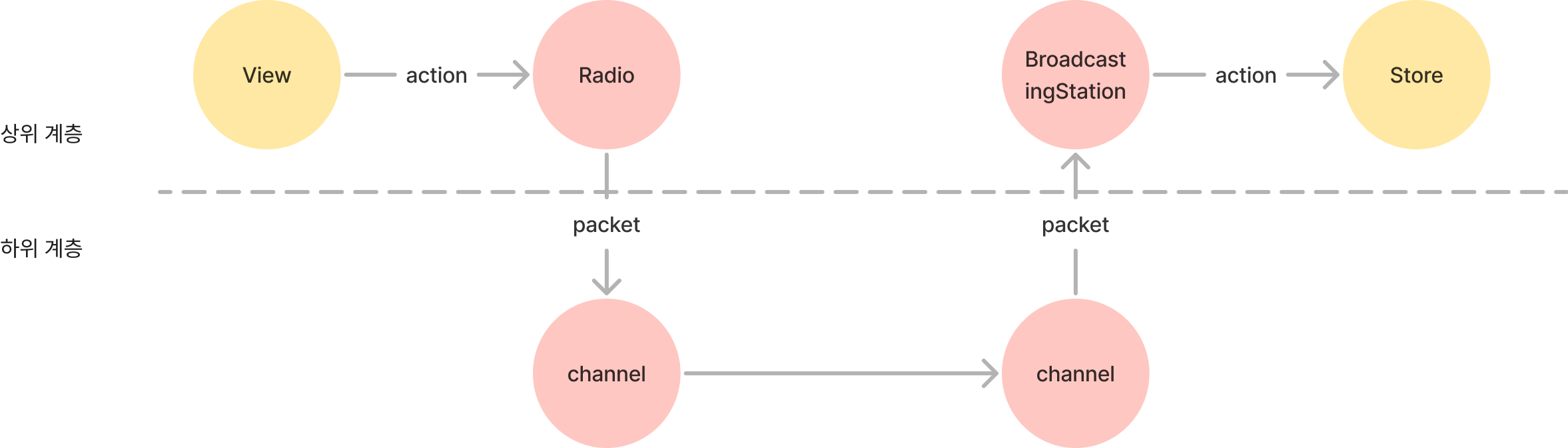
클래스간의 상속 관계는 위와 같아집니다.
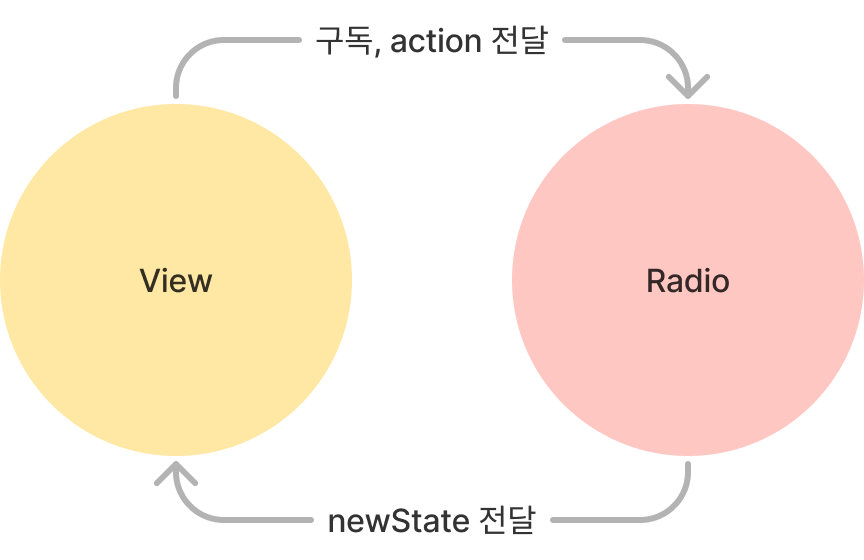
View와 Radio는 위와 같은 관계를 가집니다.
여기서 action은 state를 갱신하기 위한 개념이라, CommunicationDevice에선 관심사 밖의 영역입니다. 따라서 계층을 분리를 위해 Packet과 Action의 개념을 추가합니다.
// modules/broadcast/classes/Action.ts
export default class Action {
type: string;
payload?: any;
constructor(type: string, payload?: any) {
this.type = type;
this.payload = payload;
}
static isAction(target: any) {
if (typeof target.type !== "string") return false;
return true;
}
}// modules/broadcast/classes/Packet.ts
import Action from "./Action";
import PacketHeader from "../types/PacketHeader";
export default class Packet {
header: PacketHeader;
payload?: Action | Message;
constructor(header: PacketHeader, payload?: Action) {
this.header = header;
this.payload = payload;
}
static isPacket(target: any) {
if (!target.header) return false;
if (typeof target.header.type !== "number") return false;
return true;
}
}네트워크에서 SYN,ACK패킷이 나누어져있는 것처럼 header를 추가해 패킷 타입을 추가했습니다.
패킷 타입은 상태 갱신을 요청하는 ACTION과 상태 갱신을 알리는 NEW_STATE 2가지로 구분했습니다.
// modules/broadcast/types/PacketHeader.ts
import PACKET_TYPES from "../constants/PACKET_TYPES";
type PacketType = typeof PACKET_TYPES[number];
type PacketHeader = {
type: PacketType;
};
export default PacketHeader;// modules/broadcast/constants/PACKET_TYPES.ts
export const ACTION = 0;
export const NEW_STATE = 1;
export default [ACTION, NEW_STATE] as const;
패킷 개념 추가에 따라 Broadcastable과 CommunicationDevice이 전송하고 전달받는 단위가 Packet으로 변경됩니다.
// modules/broadcast/interfaces/Broadcastable.ts
import Packet from "../classes/Packet";
export default interface Broadcastable {
broadcast(packet: Packet): void;
}// modules/broadcast/classes/CommunicationDevice.ts
import Broadcastable from "../interfaces/Broadcastable";
import ChannelAddress from "../types/ChannelAddress";
import Packet from "./Packet";
export default abstract class CommunicationDevice implements Broadcastable {
#sender: BroadcastChannel;
#receiver: BroadcastChannel;
constructor(address: ChannelAddress) {
this.#sender = new BroadcastChannel(address.sender);
this.#receiver = new BroadcastChannel(address.receiver);
this.#receiver.onmessage = this.#handleMessage.bind(this);
}
broadcast(packet: Packet): void {
this.#sender.postMessage(packet);
}
#handleMessage(evt: MessageEvent) {
const packet = evt.data;
if (!Packet.isPacket(packet)) return;
this.handlePacket(packet);
}
protected abstract handlePacket(packet: Packet): void;
}Radio class
이제 CommunicationDevice를 상속하는 Radio 클래스를 구현합니다. Radio 클래스는receiver로부터 newState을 받으면 View에서 등록한 리스너를 수행합니다.
따라서 subscribe할 수 있는 구조를 추가합니다.
// modules/broadcast/classes/Radio.ts
import ChannelAddress from "../types/ChannelAddress";
import CommunicationDevice from "./CommunicationDevice";
import Action from "./Action";
import Packet from "./Packet";
import * as PACKET_TYPE from "../constants/PACKET_TYPES";
export default class Radio extends CommunicationDevice {
protected listeners: Function[] = [];
$state: Record<string, any> = {};
constructor(address: ChannelAddress) {
super(address);
}
$subscribe(listener: Function): Function {
this.listeners.push(listener);
/**
* 반환하는 함수는 unsubscriber (구독 취소용)
*/
return () => {
this.listeners = this.listeners.filter((l) => l !== listener);
};
}
broadcastAction(action: Action) {
const packet = new Packet({ type: PACKET_TYPE.ACTION }, action);
this.broadcast(packet);
}
protected handlePacket(packet: Packet): void {
if (packet.header.type === PACKET_TYPE.NEW_STATE) {
this.#updateState(packet.payload as Record<string, any>);
}
}
#updateState(newState: Record<string, any>) {
this.$state = newState;
this.listeners.forEach((l) => l(this.$state));
}
}
이제 다음과 같이 사용하게 됩니다.
// 액션 생성
cosnt someAction = new Action(actionName,payload);
// 라디오 생성
const radio = new Radio({sender:'a',receiver:'b'});
// 라디오 구독
radio.$subscribe((state)=>{
render(state);
});
// 액션 전달
radio.broadcastAction(someAction);BroadcastingStation class
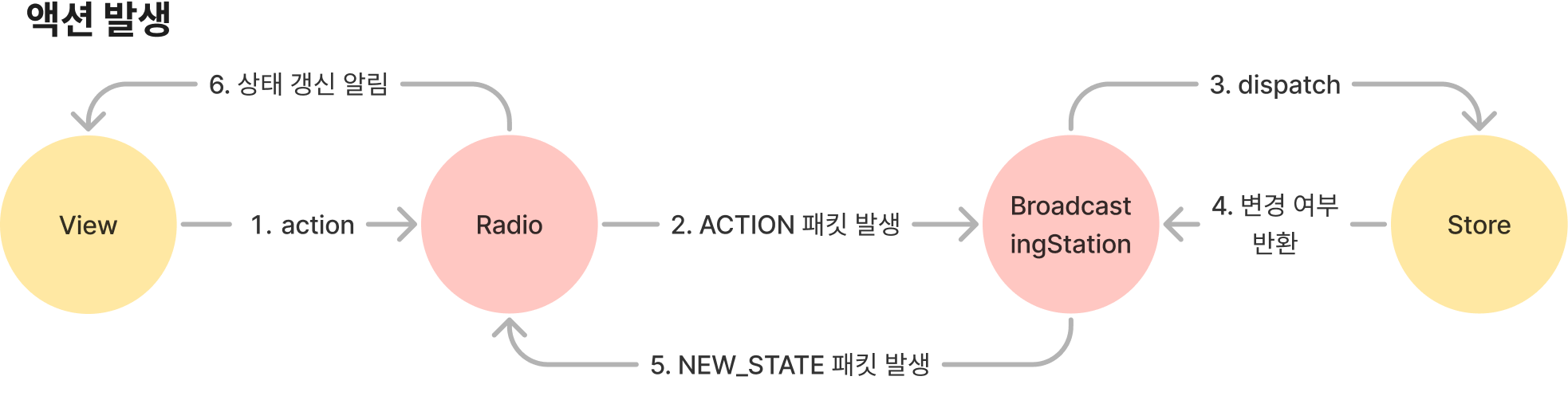
BroadcastingStation은 action을 받아 store를 갱신하고 store가 갱신 되었다면 NEW_STATE 패킷을 전송합니다.
// modules/broadcast/classes/BroadcastingStation.ts
import CommunicationDevice from "./CommunicationDevice";
import createUniqueChannelAddress from "../utils/createUniqueChannelAddress";
import ChannelAddress from "../types/ChannelAddress";
import Message from "../types/Message";
import Action from "./Action";
import Packet from "./Packet";
import * as PACKET_TYPE from "../constants/PACKET_TYPES";
export default class BroadcastingStation extends CommunicationDevice {
#store: Record<string, any>;
#channelAddress: ChannelAddress;
constructor(stationName: string, store: Record<string, any>) {
const channelAddress = createUniqueChannelAddress(stationName);
super(channelAddress);
this.#channelAddress = channelAddress;
this.#store = store;
}
get channelAddress(): ChannelAddress {
return this.#channelAddress;
}
protected handlePacket(packet: Packet) {
if (!Action.isAction(packet.payload)) return;
this.#handleAction(packet.payload as Action);
return;
}
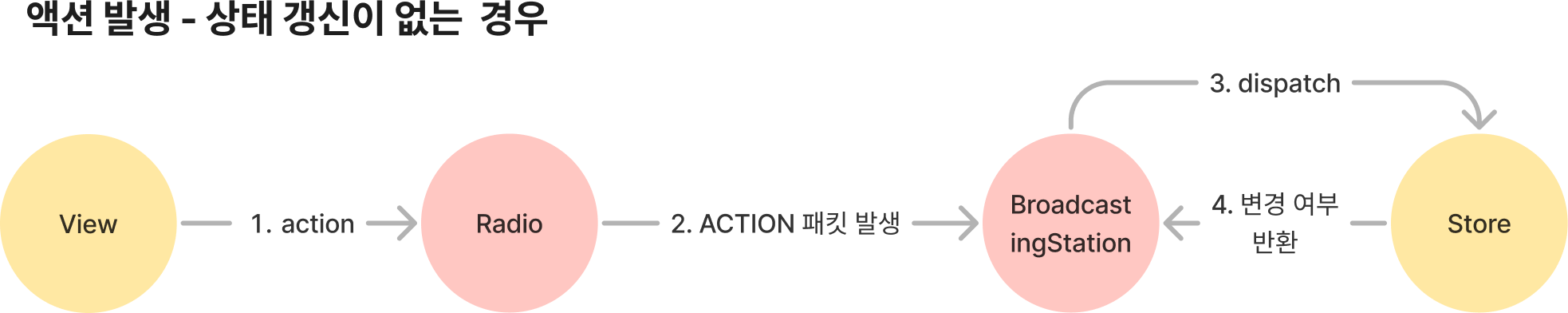
#handleAction(action: Action) {
const isChanged = this.#store.$dispatch(action);
if (!isChanged) return;
const newState: Message = this.#store.$state;
const response = new Packet({ type: PACKET_TYPE.NEW_STATE }, newState);
this.broadcast(response);
}
}BroadcastChannel은 유니크한 receiver,sender 주소를 가져야하고, Radio를 생성할 때 이 주소를 알려줘야하므로 createUniqueChannelAddress라는 별도의 유틸 함수를 사용합니다.
주소는 key + timestamp + postfix로 구성합니다.
timestamp 때문에 고유성이 보장됩니다.
// modules/broadcast/utils/createUniqueChannelAddress.ts
import CHANNEL_ADDRESS_POSTFIX from "../constants/CHANNEL_ADDRESS_POSTFIX";
import ChannelAddress from "../types/ChannelAddress";
export default function createUniqueChannelAddress(
key: string
): ChannelAddress {
const timestamp = Date.now();
return {
sender: key + timestamp + CHANNEL_ADDRESS_POSTFIX.SENDER,
receiver: key + timestamp + CHANNEL_ADDRESS_POSTFIX.RECIVER,
};
}key가 'hello', time은 1000이면 결과는
{
sender: 'hello1000SEND',
receiver: 'hello1000RECV'
}가 됩니다.
DISCOVER,OFFER 패킷 추가
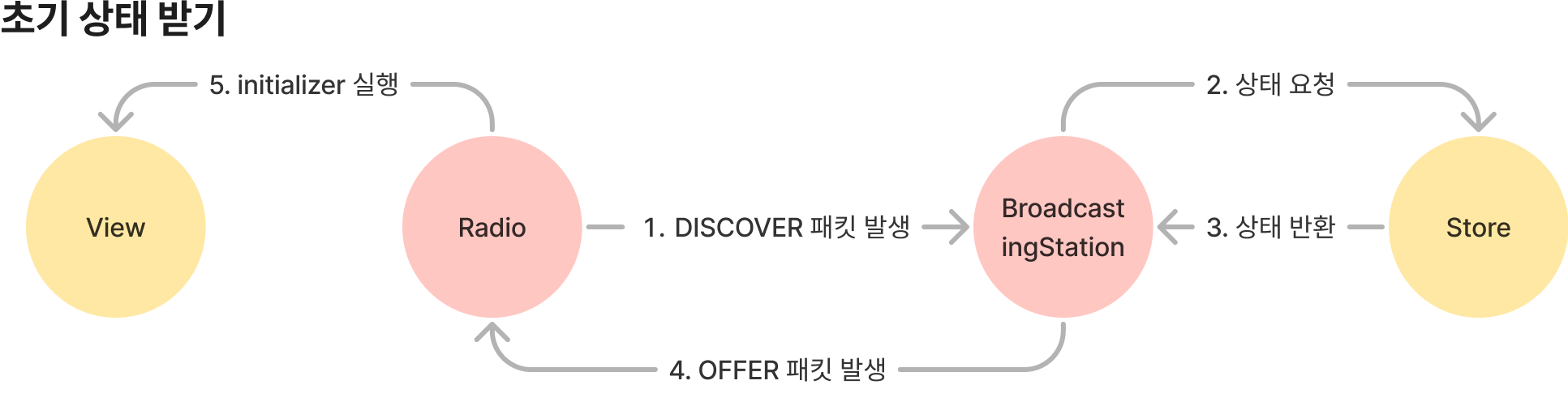
여기서 한가지 문제가 생긴 것이 Radio를 생성하고 BroadcastStation에 Action을 전송해서 새로운 상태값은 받을 수 있지만 처음 상태값은 받을 방법이 없다는 것입니다. 따라서 상태를 초기화해줄 별도의 패킷을 추가하기로 했습니다.
밴치마크한 것은 DHCP (동적 호스트 구성 프로토콜, 동적 ip 부여하는 프로토콜임)의 동작 방식인데, DHCP에선 다음과 같은 로직을 수행합니다.
- 새로운 기기가 망에 DISCOVER 패킷을 브로드캐스트한다.
- DHCP 서버는 DISCOVER 패킷을 받고 부여할 IP가 담긴 OFFER 패킷을 브로드캐스트한다.
이와 같은 구조로 먼저 패킷을 추가합니다.
// modules/broadcast/constants/PACKET_TYPES.ts
export const ACTION = 0;
export const NEW_STATE = 1;
export const DISCOVER = 2;
export const OFFER = 3;
export default [ACTION, NEW_STATE, DISCOVER, OFFER] as const;DISCOVER 패킷은 특수 패킷이고 내용이 없기 때문에 static하게 만들어주기로 했습니다.
// modules/broadcast/classes/Packet.ts
import Action from "./Action";
import PacketHeader from "../types/PacketHeader";
import * as PACKET_TYPE from "../constants/PACKET_TYPES";
export default class Packet {
header: PacketHeader;
payload?: Action;
constructor(header: PacketHeader, payload?: Action) {
this.header = header;
this.payload = payload;
}
static isPacket(target: any) {
if (!target.header) return false;
if (typeof target.header.type !== "number") return false;
return true;
}
/**
* 특수 패킷 추가
*/
static DISCOVER = new Packet({ type: PACKET_TYPE.DISCOVER });
}다음 Radio에 DISCOVER를 보내고 처리하는 로직을 추가합니다.
// modules/broadcast/classes/Radio.ts
import ChannelAddress from "../types/ChannelAddress";
import CommunicationDevice from "./CommunicationDevice";
import Action from "./Action";
import Packet from "./Packet";
import * as PACKET_TYPE from "../constants/PACKET_TYPES";
export default class Radio extends CommunicationDevice {
protected listeners: Function[] = [];
protected initializer: Function;
$state: Record<string, any> = {};
/**
* initializer를 받아 초기 상태를 받으면 어떻게 처리할지 결정합니다.
*/
constructor(address: ChannelAddress, initializer: Function) {
super(address);
this.initializer = initializer;
/**
* Radio가 만들어지면 DISCOVER 패킷을 전송합니다.
*/
this.broadcast(Packet.DISCOVER);
}
$subscribe(listener: Function): Function {
this.listeners.push(listener);
return () => {
this.listeners = this.listeners.filter((l) => l !== listener);
};
}
broadcastAction(action: Action) {
const packet = new Packet({ type: PACKET_TYPE.ACTION }, action);
this.broadcast(packet);
}
protected handlePacket(packet: Packet): void {
/**
* OFFER 패킷을 받은 경우에 대한 처리를 추가합니다.
*/
if (packet.header.type === PACKET_TYPE.OFFER) {
this.#initState(packet.payload as Record<string, any>);
}
if (packet.header.type === PACKET_TYPE.NEW_STATE) {
this.#updateState(packet.payload as Record<string, any>);
}
}
#initState(initialState: Record<string, any>) {
this.$state = initialState;
this.initializer(this.$state);
}
#updateState(newState: Record<string, any>) {
this.$state = newState;
this.listeners.forEach((l) => l(this.$state));
}
}
마지막으로 BroadcastingStation에서도 DISCOVER 패킷을 처리할 수 있게 로직을 추가합니다.
// modules/broadcast/classes/BroadcastingStation.ts
import CommunicationDevice from "./CommunicationDevice";
import createUniqueChannelAddress from "../utils/createUniqueChannelAddress";
import ChannelAddress from "../types/ChannelAddress";
import Action from "./Action";
import Packet from "./Packet";
import * as PACKET_TYPE from "../constants/PACKET_TYPES";
export default class BroadcastingStation extends CommunicationDevice {
#store: Record<string, any>;
#channelAddress: ChannelAddress;
constructor(stationName: string, store: Record<string, any>) {
const channelAddress = createUniqueChannelAddress(stationName);
super(channelAddress);
this.#channelAddress = channelAddress;
this.#store = store;
}
get channelAddress(): ChannelAddress {
return this.#channelAddress;
}
protected handlePacket(packet: Packet) {
/**
* DISCOVER 패킷을 처리할 별도의 로직 추가
*/
switch (packet.header.type) {
case PACKET_TYPE.DISCOVER: {
this.#handleDiscover();
return;
}
default: {
if (!Action.isAction(packet.payload)) return;
this.#handleAction(packet.payload as Action);
return;
}
}
}
/**
* DISCOVER 패킷이 온 경우 스토어의 초기 상태를 브로드캐스트함
*/
#handleDiscover() {
const currentState = this.#store.$state;
const response = new Packet({ type: PACKET_TYPE.OFFER }, currentState);
this.broadcast(response);
}
#handleAction(action: Action) {
const isChanged = this.#store.$dispatch(action);
if (!isChanged) return;
const newState = this.#store.$state;
const response = new Packet({ type: PACKET_TYPE.NEW_STATE }, newState);
this.broadcast(response);
}
}
이제 통신하는 구조를 보면 아래와 같습니다.