😂 문제점
JUnit 를 이론적으로만 공부하는 것은 한계가 있다고 생각이 늘었고 막상 프로젝트의 일부분을 따와서 적용해보려 시도하니 예상하지 못하는 예외가 너무 많이 발생했다.
JUnit를 중점적으로 연습하기 위해 간단하게 새 프로젝트를 생성하고 사용해보자.
프로젝트의 기능은 은행 거래를 간단하게 구현하는 것을 목적으로 두고 있다.
🔧 기본 설정
진행하기 위한 간단한 기본 설정들에 대해서 언급하고 지나가도록 하자.
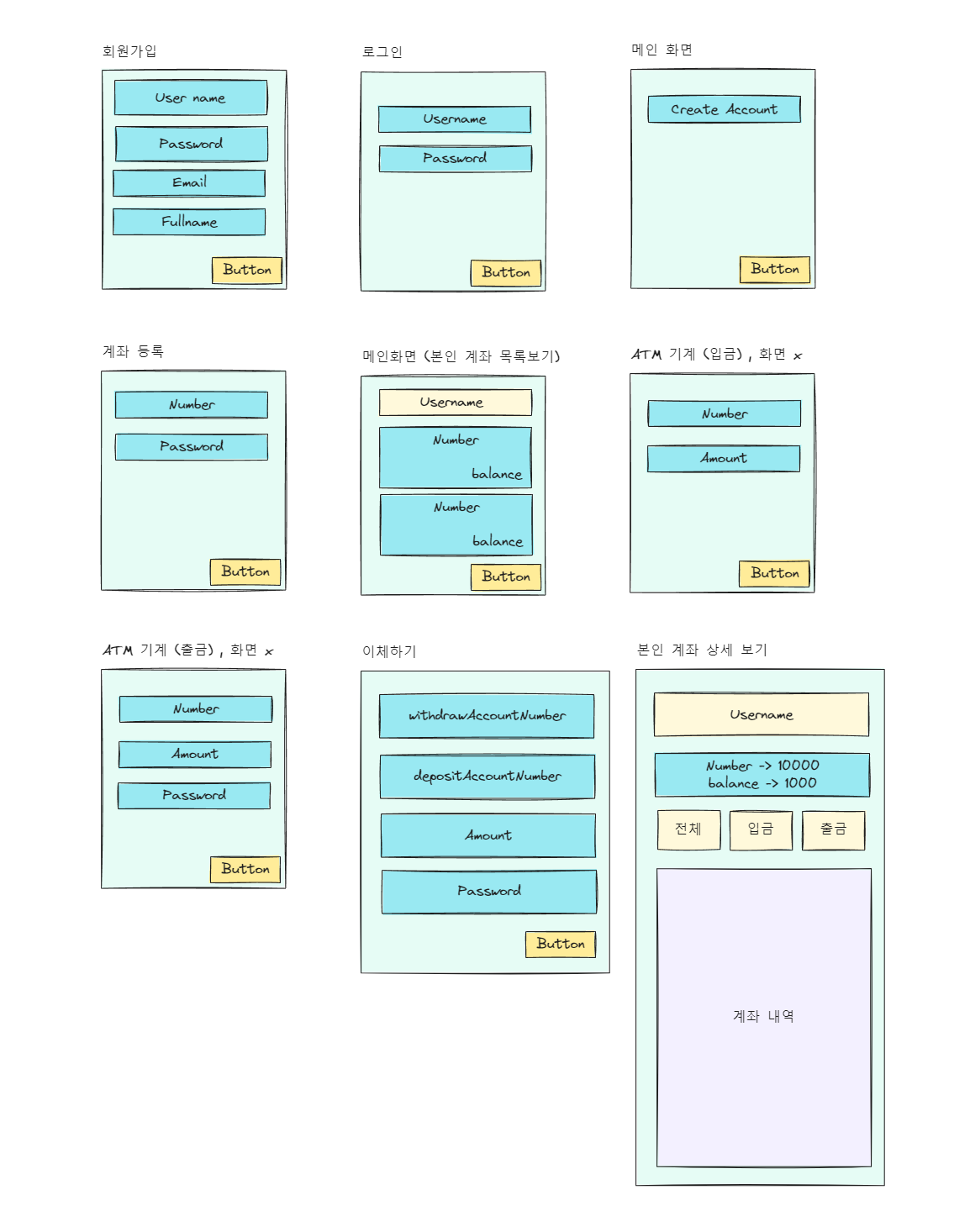
🎨 화면 (UX Design)
📁 Database 설정
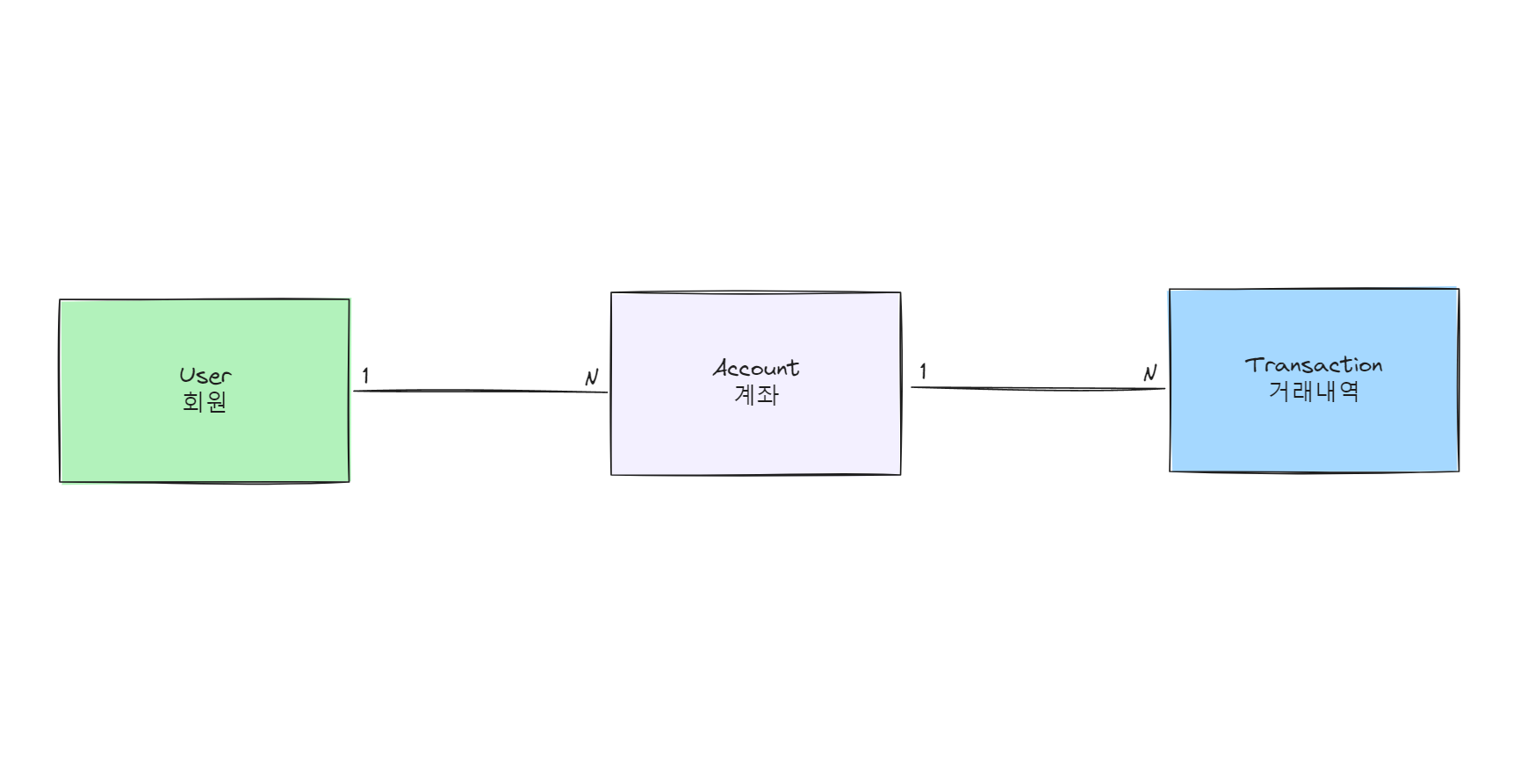
데이터 베이스는 User, Account, Transaction으로 간단하게 진행한다.
⏰ LocalDate 설정
Jpa LocalDateTime 자동으로 LocalDateTime 생성 하는 법
- @EnableJpaAuditing //날짜 기입 어노테이션 , (Main Class 적용)
- @EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class) (Entity Class 적용)
@CreatedDate
@Column(nullable = false)
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
@LastModifiedBy
@Column(nullable = false)
private LocalDateTime updateAt;JUnit 테스트를 편하게 사용하기 위해 시간 Entity를 따로 분리하여 상속해서 사용하지는 않았다.
🧩 User Entity
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.CreatedDate;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.LastModifiedBy;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.support.AuditingEntityListener;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@NoArgsConstructor //스프링이 User 객체 생성할 때 반 생성자로 new를 하기 때문
@Getter
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class) //@CreatedDate , @LastModifiedBy 자동 기입하기 위해 설정
@Table(name = "user_tb")
@Entity
public class User { //extends 시간설정 (상속)
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(unique = true , nullable = false , length = 20)
private String username;
@Column(nullable = false , length = 60) //패스워드 인코딩 시 길이가 증가 하기 때문에 넉넉하게 할당
private String password;
@Column(nullable = false , length = 20)
private String email;
@Column(nullable = false , length = 20)
private String fullname;
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
@Column(nullable = false)
private UserEnum role; //ADMIN , CUSTOMER
@CreatedDate //Insert
@Column(nullable = false)
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
@LastModifiedBy //Insert, Update
@Column(nullable = false)
private LocalDateTime updateAt;
@Builder
public User(Long id, String username, String password, String email, String fullname, UserEnum role, LocalDateTime createdAt, LocalDateTime updateAt) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.email = email;
this.fullname = fullname;
this.role = role;
this.createdAt = createdAt;
this.updateAt = updateAt;
}
}
🧩 Account Entity
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.CreatedDate;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.LastModifiedBy;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.support.AuditingEntityListener;
import shop.mtcoding.bank.domain.user.User;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@NoArgsConstructor //스프링이 User 객체 생성할 때 반 생성자로 new를 하기 때문
@Getter
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class) //@CreatedDate , @LastModifiedBy 자동 기입하기 위해 설정
@Table(name = "account_tb")
@Entity
public class Account {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(unique = true, nullable = false, length = 20)
private Long number; //계좌 번호
@Column(nullable = false, length = 4)
private Long password; //계좌 비밀번호
@Column(nullable = false)
private Long balance; //잔액 (기본값 1000원)
// 항상 ORM 에서 FK의 주인은 Many Entity 쪽 이다.
//account.getUser().아무필드호출() -> Lazy 발동 , 조회
//getUser() 까지도 호출 되지 않는다.
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY) //지연로딩
private User user;
@CreatedDate //Insert
@Column(nullable = false)
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
@LastModifiedBy //Insert, Update
@Column(nullable = false)
private LocalDateTime updateAt;
@Builder
public Account(Long id, Long number, Long password, Long balance, User user, LocalDateTime createdAt, LocalDateTime updateAt) {
this.id = id;
this.number = number;
this.password = password;
this.balance = balance;
this.user = user;
this.createdAt = createdAt;
this.updateAt = updateAt;
}
}
🧩 Transaction Entity
package shop.mtcoding.bank.domain.transaction;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.CreatedDate;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.LastModifiedBy;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.support.AuditingEntityListener;
import shop.mtcoding.bank.domain.account.Account;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@NoArgsConstructor //스프링이 User 객체 생성할 때 반 생성자로 new를 하기 때문
@Getter
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class) //@CreatedDate , @LastModifiedBy 자동 기입하기 위해 설정
@Table(name = "transaction_tb")
@Entity
public class Transaction {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@JoinColumn(foreignKey = @ForeignKey(ConstraintMode.NO_CONSTRAINT))
//논리적으로만 외래키를 맺고 물리적으로는 외래키를 맺지 않음
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
private Account withdrawAccount;
@JoinColumn(foreignKey = @ForeignKey(ConstraintMode.NO_CONSTRAINT))
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
private Account depositAccount;
private Long amount;
//이체나 출금 당시 금액을 남겨 놓기 위함
private Long withdrawAccountBalance;
private Long depositAccountBalance;
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
@Column(nullable = false)
private TransactionEnum gubun;
//계좌가 사라져도 로그는 남아야 한다.
private String sender;
private String receiver;
private String tel;
@CreatedDate //Insert
@Column(nullable = false)
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
@LastModifiedBy //Insert, Update
@Column(nullable = false)
private LocalDateTime updateAt;
@Builder
public Transaction(Long id, Account withdrawAccount, Account depositAccount, Long amount, Long withdrawAccountBalance, Long depositAccountBalance, TransactionEnum gubun, String sender, String receiver, String tel, LocalDateTime createdAt, LocalDateTime updateAt) {
this.id = id;
this.withdrawAccount = withdrawAccount;
this.depositAccount = depositAccount;
this.amount = amount;
this.withdrawAccountBalance = withdrawAccountBalance;
this.depositAccountBalance = depositAccountBalance;
this.gubun = gubun;
this.sender = sender;
this.receiver = receiver;
this.tel = tel;
this.createdAt = createdAt;
this.updateAt = updateAt;
}
}
📝 Security 설정
Security 설정을 하지 않고 8081번 포트에 접속할 경우 Security에서 자체적으로 제공하는 로그인 화면에 가려진다.
Security에서 기본적으로 적용되는 조건을 풀고 임의로 커스텀 하기 위해 추가적인 설정 값이 필요하다.
📑 SecurityConfig
기본적으로 Springboot Security의 Default 설정들만 작성하고 추후 수정하면서 진행 하도록 할 것 이다.
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
import org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfigurationSource;
import org.springframework.web.cors.UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource;
import shop.mtcoding.bank.domain.user.UserEnum;
@Configuration //설정파일 Bean 등록
public class SecurityConfig {
private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
//로그 찍어내기 위함
@Bean //IoC 컨테이너에 BCryptPasswordEncoder() 객체가 등록됨.
public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
log.debug("디버그 : BCryptPasswordEncoder 빈 등록됨");
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
//JWT 필터 등록 추가 구현 필요
//JWT 서버 생성, Session 사용 안함
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.headers().frameOptions().disable(); //iframe 허용 안함
http.csrf().disable(); // enable 상태 이면 post맨 작동 안함
http.cors().configurationSource(configurationSource()); //교차 플랫폼 접근 허용
//jSessionId를 서버에서 관리하지 않음
http.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS);
//react, 앱 , Security에서 제공하는 기본 로그인 방식을 사용하지 않음
http.formLogin().disable();
//httpBasic은 브라우저가 팝업창을 이용해서 사용자 인증을 진행 한다. , disable 설정
http.httpBasic().disable();
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/s/**").authenticated() //s가 붙은 API는 인증 해야 한다.
// 최근 공식문서에는 ROLE_ 붙이지 않아도 된다.
.antMatchers("/api/admin/**").hasRole("" + UserEnum.ADMIN)
.anyRequest().permitAll(); // 나머지 요청은 허용
return http.build();
}
public CorsConfigurationSource configurationSource(){
CorsConfiguration configuration = new CorsConfiguration();
configuration.addAllowedHeader("*");
configuration.addAllowedMethod("*"); //GET, POST, PUT, DELETE (Javascript 요청 허용)
configuration.addAllowedOriginPattern("*"); //모든 IP 주소 허용 (프론트 엔드 IP만 허용 react)
configuration.setAllowCredentials(true); // 클라이언트 쿠키 요청 허용
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", configuration);
return source;
}
}
📌 CSRF
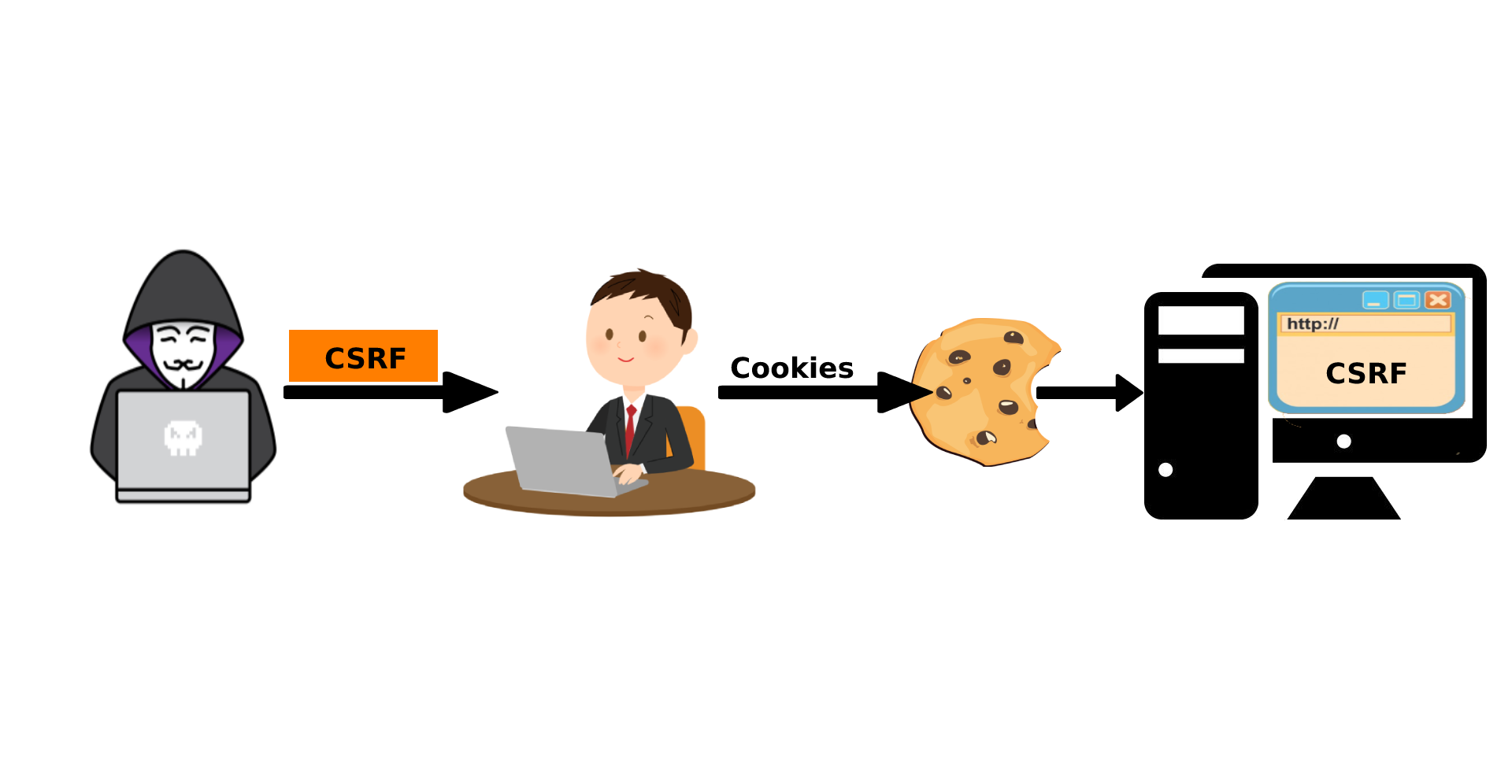
CSRF는 Cross Site Request Forgery(사이트 간 요청 위조)의 줄임말로 웹 취약점 중 하나이다.
공격자가 희생자의 권한을 도용하여 특정 웹 사이트의 기능을 실행하게 할 수 있으며 이는 희생자의 의도와는 무관하게 이루어진다.
Config 에서는 Postman을 통해서 진행 하기 때문에 열어두었다.
📌 CORS
예전 프로젝트를 진행할때 react와 springboot로 클라이언트와 서버를 구축 했었다.
API 요청 시 cors error가 발생했는데 이는 두 출처가 일치하지 않아 발생하는 것이다.
public CorsConfigurationSource configurationSource(){
CorsConfiguration configuration = new CorsConfiguration();
configuration.addAllowedHeader("*");
configuration.addAllowedMethod("*"); //GET, POST, PUT, DELETE (Javascript 요청 허용)
configuration.addAllowedOriginPattern("*"); //모든 IP 주소 허용 (프론트 엔드 IP만 허용 react)
configuration.setAllowCredentials(true); // 클라이언트 쿠키 요청 허용
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", configuration);
return source;
}
이번 프로젝트에서도 대부분의 Javascript 요청을 허용하고 진행 할 것이다.
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaAuditing;
@EnableJpaAuditing //날짜 기입 어노테이션
@SpringBootApplication
public class BankApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(BankApplication.class, args);
String[] iocNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : iocNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
Bean이 정상적으로 작동 되는지 확인하기 위해 Main Class 에 위와 같이 수정 한 후 실행 한다.
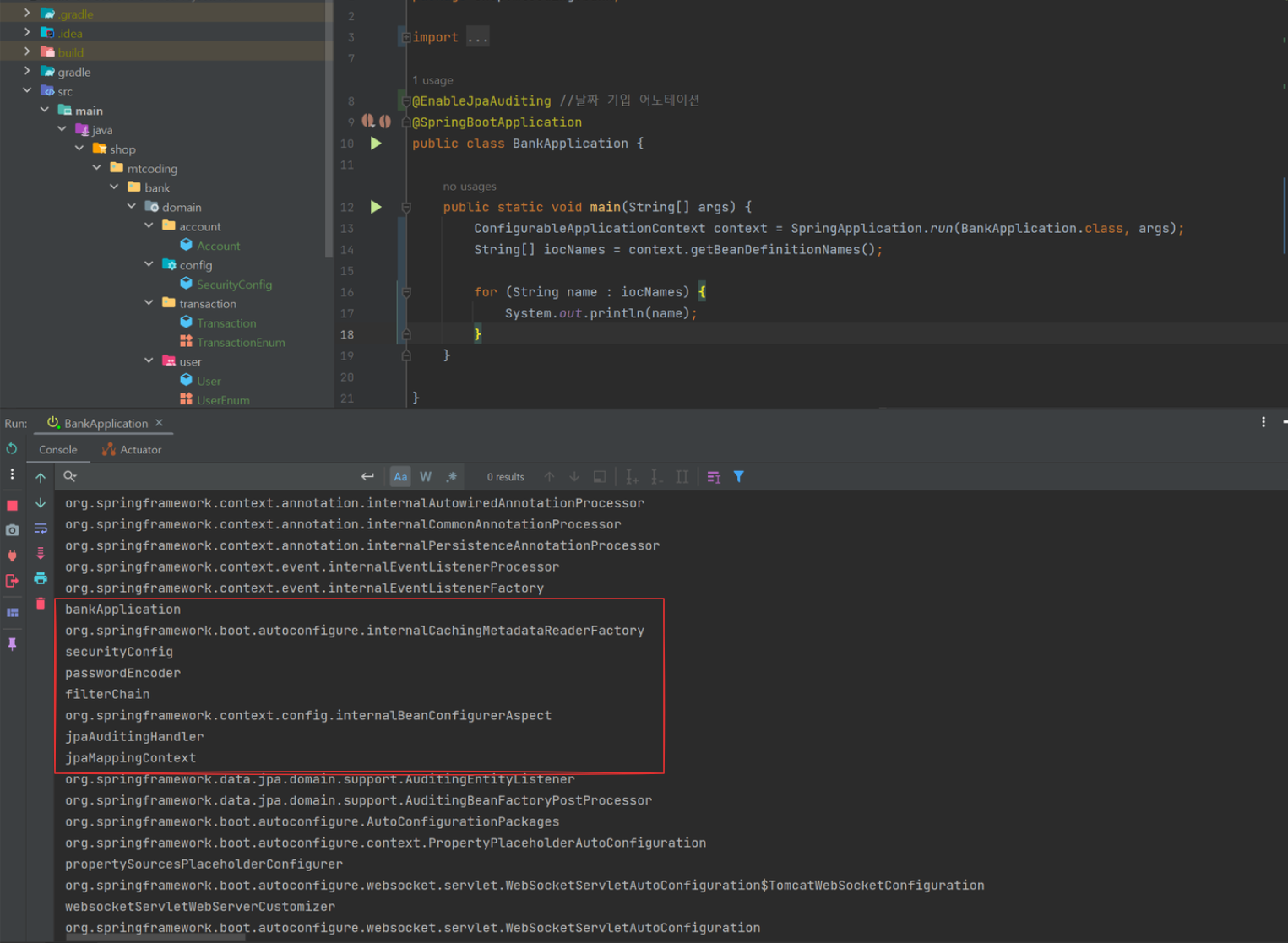
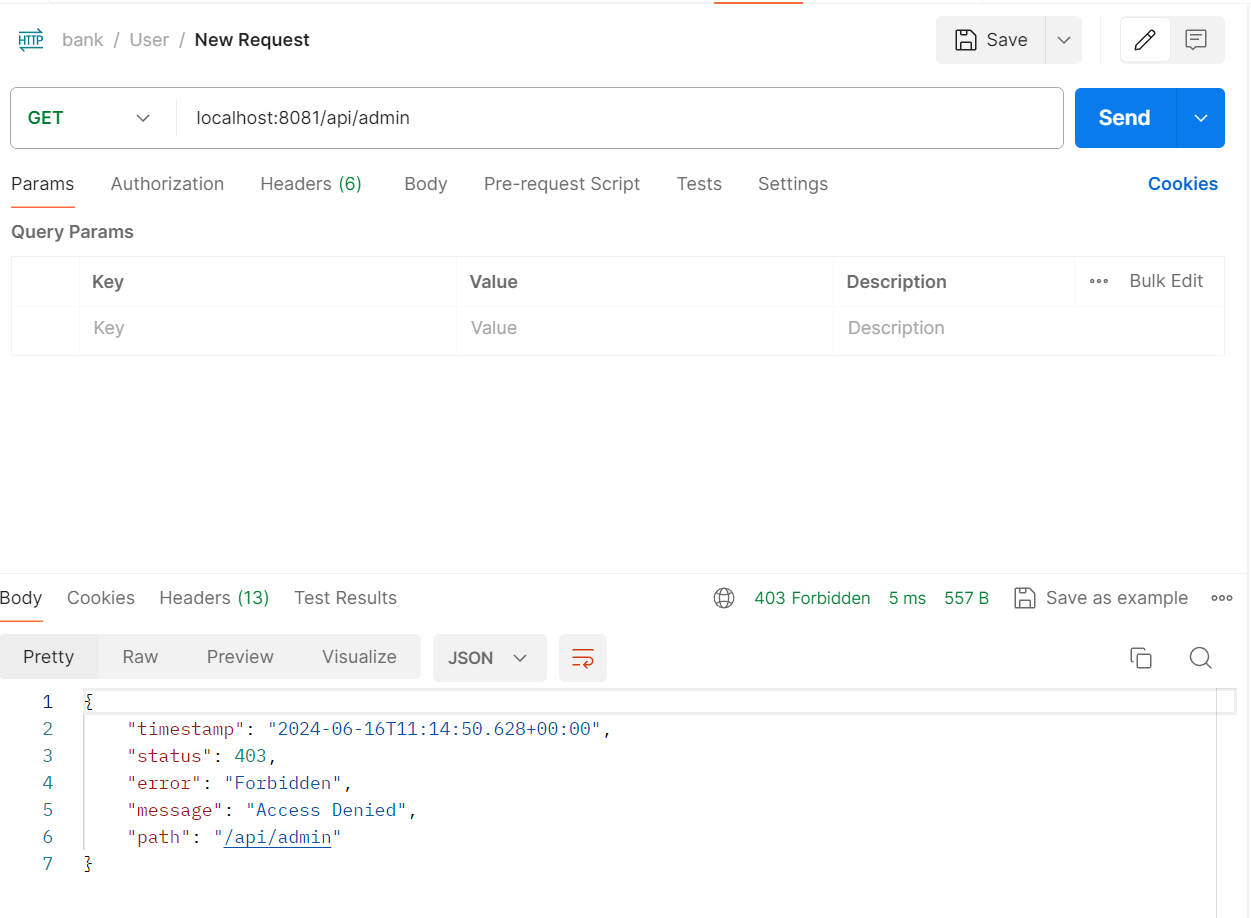
새롭게 8081번 포트에 접속을 한다면
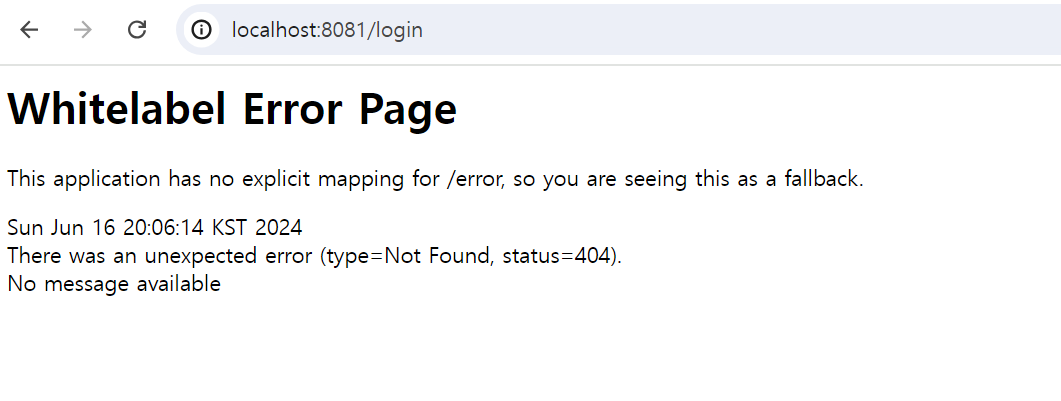
위와 같이 404 Not Found가 발생하는데 이는 클라이언트 화면을 만들지 않았기에 정상적인 Error Message 이다.
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/s/**").authenticated() //s가 붙은 API는 인증 해야 한다.
// 최근 공식문서에는 ROLE_ 붙이지 않아도 된다.
.antMatchers("/api/admin/**").hasRole("" + UserEnum.ADMIN)
.anyRequest().permitAll(); // 나머지 요청은 허용
접근 권한을 설정한 admin api 요청도 정상적으로 제한 되는것을 볼 수 있다.