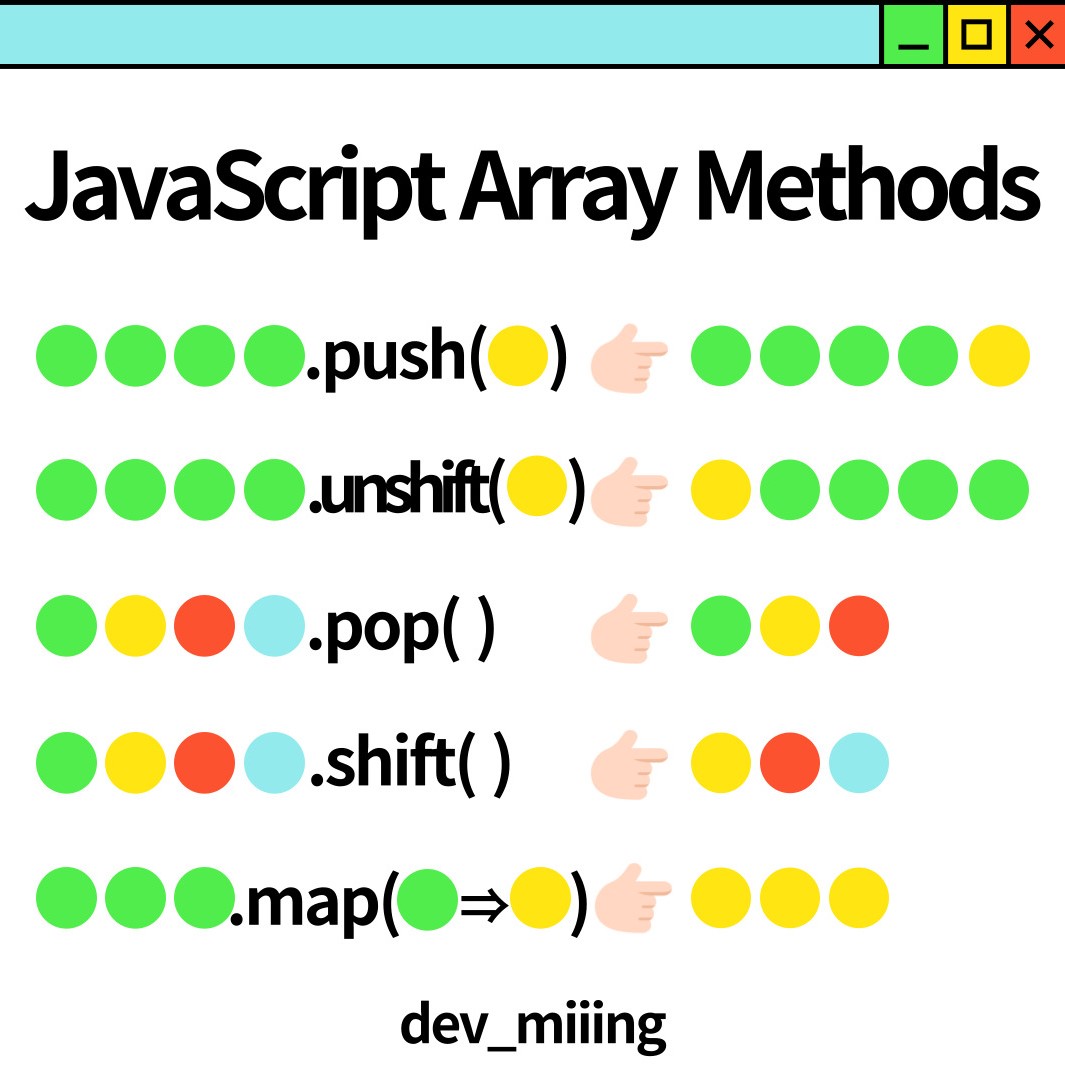
#push
push()
push(element1)
push(element1, element2)
push(element1, element2, / …, / elementN)
▶The element(s) to add to the end of the array.
#unshift
unshift()
unshift(element1)
unshift(element1, element2)
unshift(element1, element2, / …, / elementN)
▶The element(s) to add to the front of the array.
#pop
pop()
▶Parameters : None
Return value : The removed element from the array; 'undefined' if the array is empty
[The pop() method of Array instances removes ✔️the last element✔️ from an array and returns that element. This method changes the length of the array.]
#shift
shift()
▶Parameters : None
Return value : The removed element from the array; undefined if the array is empty
[The shift() method of Array instances removes ✔️the first element✔️ from an array and returns that removed element. This method changes the length of the array.]
#map
map(callbackFn)
map(callbackFn, thisArg)
▶The map() method of Array instances creates a new array populated with the results of calling a provided function on every element in the calling array.
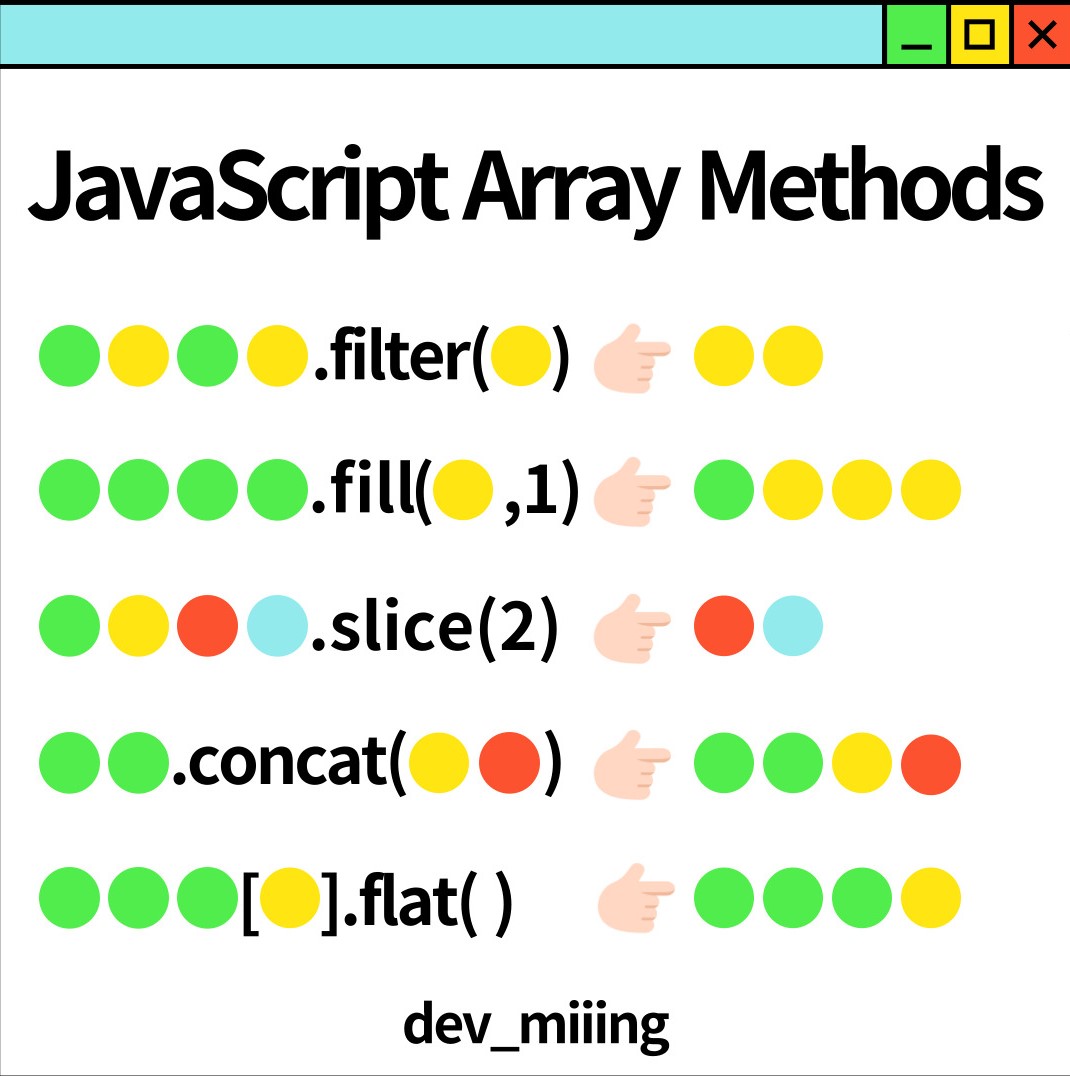
#filter
filter(callbackFn)
filter(callbackFn, thisArg)
▶The filter() method of Array instances creates a shallow copy of a portion of a given array, filtered down to just the elements from the given array that pass the test implemented by the provided function.
#fill
fill(value)
fill(value, start)
fill(value, start, end)
▶The fill() method of Array instances changes all elements within a range of indices in an array to a static value. It returns the modified array.
Value to fill the array with.
Zero-based index at which to start filling, converted to an integer.
#slice
slice()
slice(start)
slice(start, end)
▶The slice() method of Array instances returns a shallow copy of a portion of an array into a new array object selected from start to end (end not included) where start and end represent the index of items in that array. The original array will not be modified.
#concat
concat()
concat(value1)
concat(value1, value2)
concat(value1, value2, / …, / valueN)
▶The concat() method of Array instances is used to merge two or more arrays. This method does not change the existing arrays, but instead returns a new array.
#flat
flat()
flat(depth)
▶The flat() method of Array instances creates a new array with all sub-array elements concatenated into it recursively up to the specified depth.
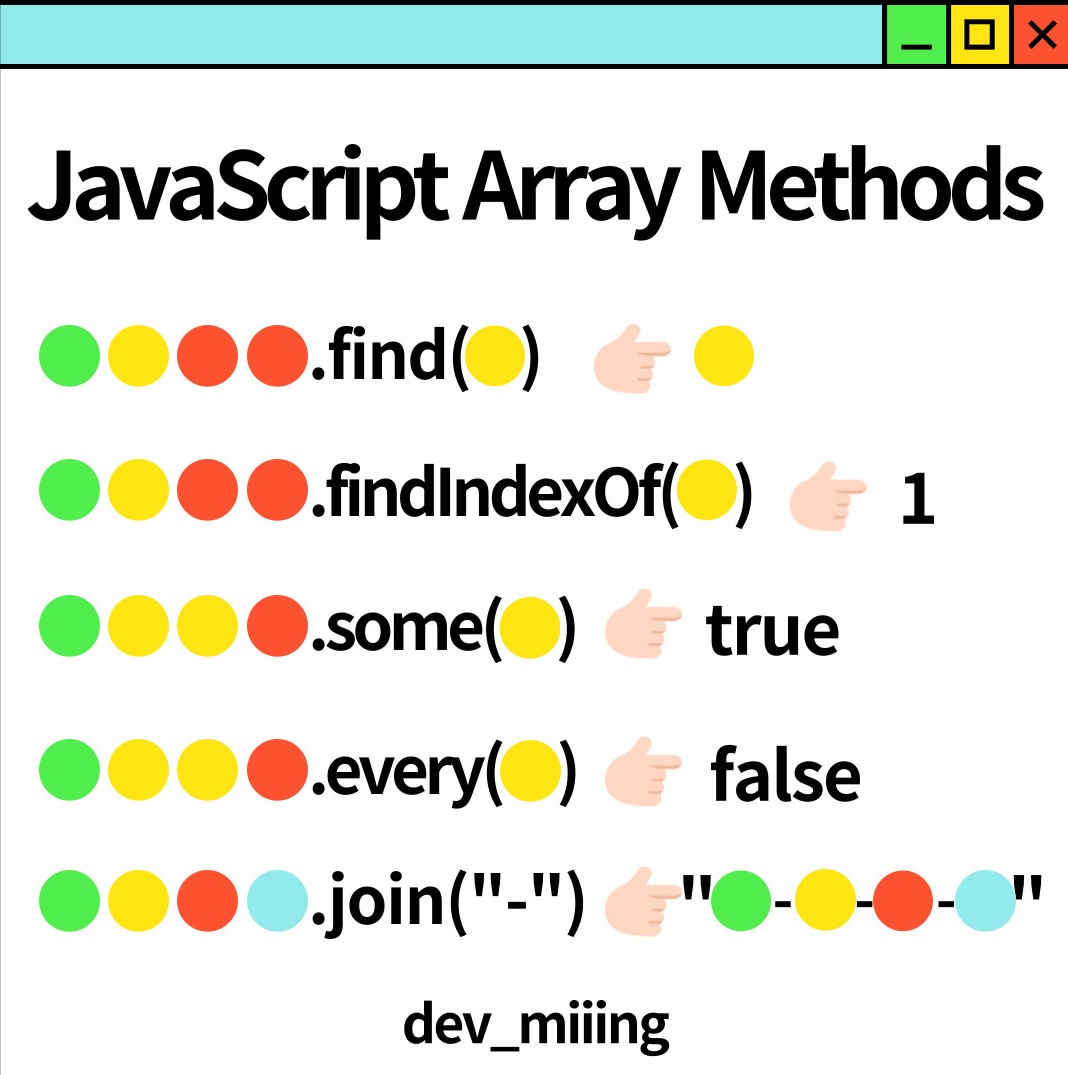
#find
find(callbackFn)
find(callbackFn, thisArg)
▶The find() method of Array instances returns the first element in the provided array that satisfies the provided testing function. If no values satisfy the testing function, undefined is returned.
#findIndexOf
findIndex(callbackFn)
findIndex(callbackFn, thisArg)
▶The findIndex() method of Array instances returns the index of the first element in an array that satisfies the provided testing function. If no elements satisfy the testing function, -1 is returned.
#some
some(callbackFn)
some(callbackFn, thisArg)
▶The some() method of Array instances tests whether ✔️at least one element✔️ in the array passes the test implemented by the provided function. It returns true if, in the array, it finds an element for which the provided function returns true; otherwise it returns false.
#every
every(callbackFn)
every(callbackFn, thisArg)
▶The every() method of Array instances tests whether ✔️all elements✔️ in the array pass the test implemented by the provided function. It returns a Boolean value.
