Object클래스
- 모든 클래스의 최고 조상
- 오직 11개의 메서드만을 가지고 있음
- noify(), wait() 등은 쓰레드와 관련된 메서드
- equals(), hashCode(), toString()은 적절히 오버라이딩 해야 함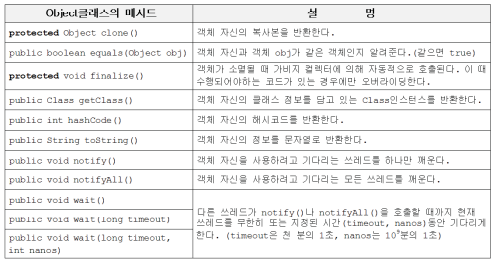
실습 - ch07 / S05.java
표랑 비교해서 적절히 사용할 것
package ch07;
public class S05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 모든 클래스의 최상위 부모
Object object = new Object();
object.getClass();
object.hashCode();
object.toString();
object.equals(null);
// 등이 있다.
// 객체는 직접 상속하지 않아도 Object를 상속 받는다
String str = "홍길동";
str.getClass();
str.hashCode();
str.toString();
str.equals("김첨지");
}
}
String 클래스
String클래스의 특징
- 문자형 배열(char[])과 그에 관련된 메서드들이 정의되어 있음
- String인스턴스의 내용은 바꿀 수 없음


문자열과 기본형간의 변화
- 문자열을 기본형 값으로 변환하는 방법

실습 - ch09 / S01.java
주석과 표와 함께 볼 것
package ch09;
import javax.print.DocFlavor.STRING;
public class S01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = " Show me the money ";
System.out.println("str.length() : " + str.length()); // 19
System.out.println("str.charAt(1) : " + str.charAt(1)); // S
System.out.println("str.substring(6) : " + str.substring(6)); // me the money
// 주민번호 등을 잘라낼 때
// "12345678" -> "1" + "******"
System.out.println("str.substring(6, 11) : " + str.substring(6, 11)); // me th
// 아이디 happy를 캡스록 실수로 눌러서 HAPPY로 했을 때에도
// 비교시 toLowerCase등을 이용해서 처리할 수 있다
System.out.println("str.toLowerCase() : " + str.toLowerCase()); // show me the money
System.out.println("str.toUpperCase() : " + str.toUpperCase()); // SHOW ME THE MONEY
System.out.println("str.indexOf(\"e\") : " + str.indexOf("e")); // 7
System.out.println("str.lastIndexOf(\"e\") : " + str.lastIndexOf("e")); //16
System.out.println("str.contains(\"the\") : " + str.contains("the")); // true
System.out.println("str.startsWith(\"Show\") : " + str.startsWith("Show"));// false
System.out.println("str.endsWith(\"money\") : " + str.endsWith("money")); // false
// 좌우공백제거
System.out.println("str.trim() : " + str.trim()); // show me the money
System.out.println("str.replace(\"e\", \"x\") : " + str.replace("e", "x")); //Show mx thx monxy
System.out.println("str.repeat(2) : " + str.repeat(2)); //Show me the money Show me the money
// split을 하면 기준은 제거
// 공백개수
System.out.println("str.split(\" \").length : " + str.split(" ").length); // 5
System.out.println("str.split(\" \")[0] : " + str.split(" ")[0]); // 없음
System.out.println("str.split(\" \")[1] : " + str.split(" ")[1]); // Show
System.out.println("str.split(\" \")[4] : " + str.split(" ")[4]); // money
String name1 = "홍 길 동";
System.out.println("name1.split(\" \").length : " + name1.split(" ").length); //3
String name2 = "cocacola";
System.out.println("name2.split(\"\").length : " + name2.split("").length); //8
// 값이 없는 빈 문자열 ""만 true
System.out.println("\"\".isEmpty() : " + "".isEmpty()); // true
System.out.println("\" \".isEmpty() : " + " ".isEmpty()); // false
// ""과 " " 둘다 true
System.out.println("\"\".isBlank() : " + "".isBlank()); // true
System.out.println("\" \".isBlank() : " + " ".isBlank()); // true
System.out.println("\" \".isBlank() : " + " ".isBlank()); // true
String bird1 = "오리";
String bird2 = "오리";
System.out.println("(bird1 == bird2) : " + (bird1 == bird2)); // true
String bird3 = "독수리";
System.out.println("(bird3 == \"독수리\") : " + (bird3 == "독수리")); // true
String bird4 = new String("갈매기");
String bird5 = new String("갈매기");
System.out.println("(bird4 == bird5) : " + (bird4 == bird5)); // false
System.out.println("(bird4 == \"갈매기\") : " + (bird4 == "갈매기")); // false
// 객체끼리 ==을 사용하면 주소를 비교하게 된다.
// 객체끼리 equals를 사용하면 주소를 비교해보고 false면
// 내부의 값을 한번 더 확인해서 비교한 뒤 true false를 리턴한다
System.out.println("bird4.equals(bird5) : " + bird4.equals(bird5)); // true
System.out.println("bird4.equals(bird5) : " + bird4.equals(bird5)); // true
// 문자열 / 문자배열
String korean = "가나다라";
String[] split = korean.split("");
// 문자열의 문자(char)를 반복할 때
for (int i = 0; i < korean.length(); i++) {
System.out.println(korean.charAt(i)); //(세로로) 가 나 다 라
}
// 문자열을 문자배열로 바꿔서 반복할 때
// 각 문자에 문자열메소드를 사용하고 싶을 때
for (int i = 0; i < split.length; i++) {
System.out.println(split[i].repeat(2)); //(세로로 - 2열 4행) 가가 나나 다다 라라
}
System.out.println("String.join(\"\", split) : " + String.join("", split)); //가나다라
System.out.println("String.join(\"\", split) : " + String.join("a", split)); //가a나a다a라
}
}
StringBuffer클래스


Math & wrapper클래스
Math클래스
- 수학계산에 유용한 메서드로 구성되어 있음 (모두 Static메서드)

실습 - ch09 / S02.java
표와 함께 볼것
package ch09;
public class S02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 수학 계산용 기능 - 객체가 필요없음
// 인스턴스가 아니라 static
// 0이상 1미만의 랜덤한 doubel
System.out.println("Math.random() : " + Math.random()); //0.20735816721148037
// abs는 숫자의 절대값을 리턴한다
System.out.println("Math.abs(-10) : " + Math.abs(-10)); //10
// round 5를 기준으로 반올림값을 리턴한다
System.out.println("Math.round(1.5) : " + Math.round(1.5)); //2
System.out.println("Math.round(1.4) : " + Math.round(1.4)); //1
// floor 내림값을 double로 리턴한다.
System.out.println("Math.floor(1.5) : " + Math.floor(1.5)); //1.0
System.out.println("Math.floor(1.25) : " + Math.floor(1.25)); //1.0
// ceil 올림값을 double로 리턴한다
System.out.println("Math.ceil(1.5) : " + Math.ceil(1.5)); //2.0
System.out.println("Math.ceil(1.25) : " + Math.ceil(1.25)); //2.0
System.out.println("Math.ceil(1.0) : " + Math.ceil(1.0)); //1.0
// pow 제곱값을 double로 리턴한다
System.out.println("Math.pow(2, 3) : " + Math.pow(2, 3)); //8.0
// sqrt 루트값을 double로 리턴한다
System.out.println("Math.sqrt(4) : " + Math.sqrt(4)); //2.0
System.out.println("Math.PI : " + Math.PI); //3.141592653589793
}
}
wrapper클래스
- 기본형을 클래스로 정의한 것
- 기본형 값도 객체로 다뤄져야 할 때가 있음
- 내부적으로 기본형 변수를 가지고 있음
- 값을 비교하도록 equals()가 오버라이딩되어 있음
실습 - ch00 / Study09.java
주석으로 설명..
package ch00;
public class Study09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 1;
// 기본형 타입을 객체처럼 사용할 수 있다
// 랩퍼 타입 (wrapper)
// 랩퍼 타입은 메소드가 있고 null을 넣을 수 있다
Integer num2 = 1;
System.out.println(num2);
// num1 = null;
num2 = null;
}
}
Number클래스
- 숫자를 멤버변수로 갖는 클래스의 조상(추상클래스)
