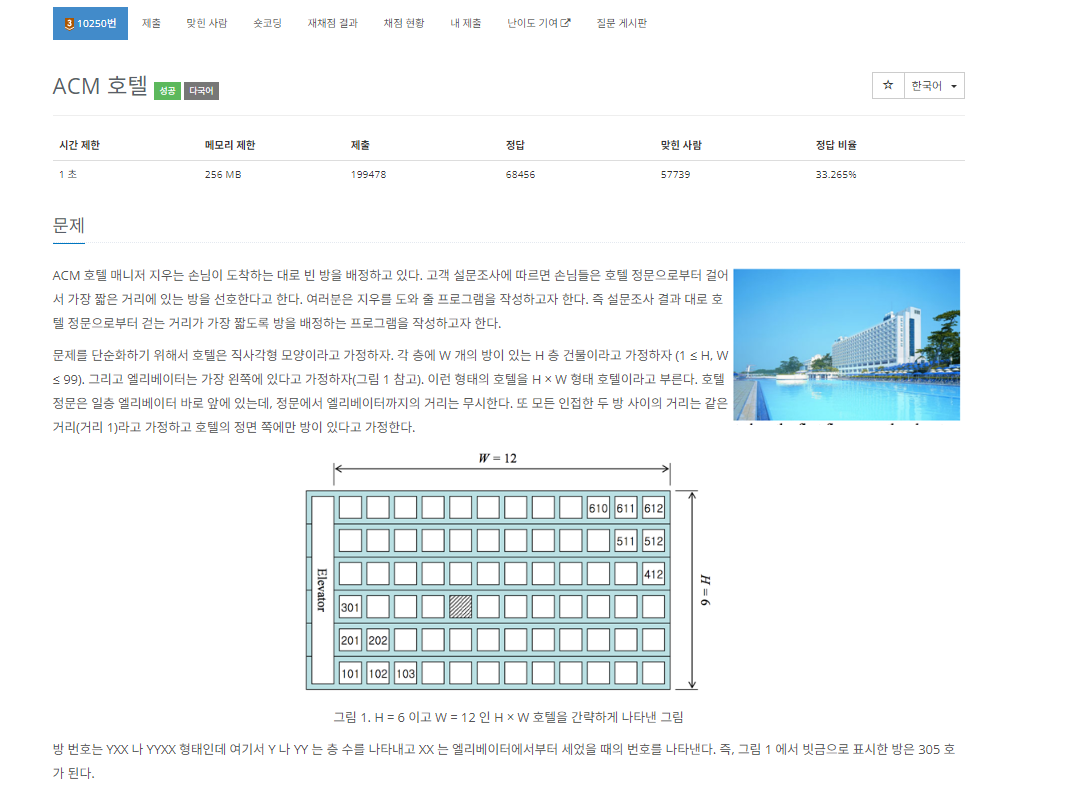
🔴 문제
🟡 Sol
const fs = require('fs');
const path = process.platform === 'linux' ? '/dev/stdin' : 'Wiki\\input.txt';
const [t, ...inputs] = fs.readFileSync(path).toString().trim().split('\n');
for (const input of inputs) {
const [h, w, n] = input.split(' ').map(Number);
const newH = n % h === 0 ? h : n % h;
const newW = newH === h ? Math.floor(n / h) : Math.ceil(n / h);
console.log(
newH.toString() + (newW < 10 ? '0' + newW.toString() : newW.toString())
);
}🟢 풀이
⏰ 소요한 시간 : 15분
테스트 케이스 별로 h, w, n을 분리해준 뒤 몇층(newH), 몇호(newW)인지 구해준다.
newH의 경우 n을 h로 나눈 나머지가 할당되는데 만약 나머지가 0인 경우에는 h층의 끝까지 모두 채운 것이므로 newH의 값이 h가 된다.
newW의 경우 n을 h로 나눈 몫이 할당되는데 마찬가지로 newH === h 인경우 즉 h층의 끝까지 모두 채운 경우는 값을 내림한 값, 그게 아니라면 올림한 값을 할당해준다.
마지막 값을 출력할 때는 0을 붙여서 출력해주는 것... 잊지말자
