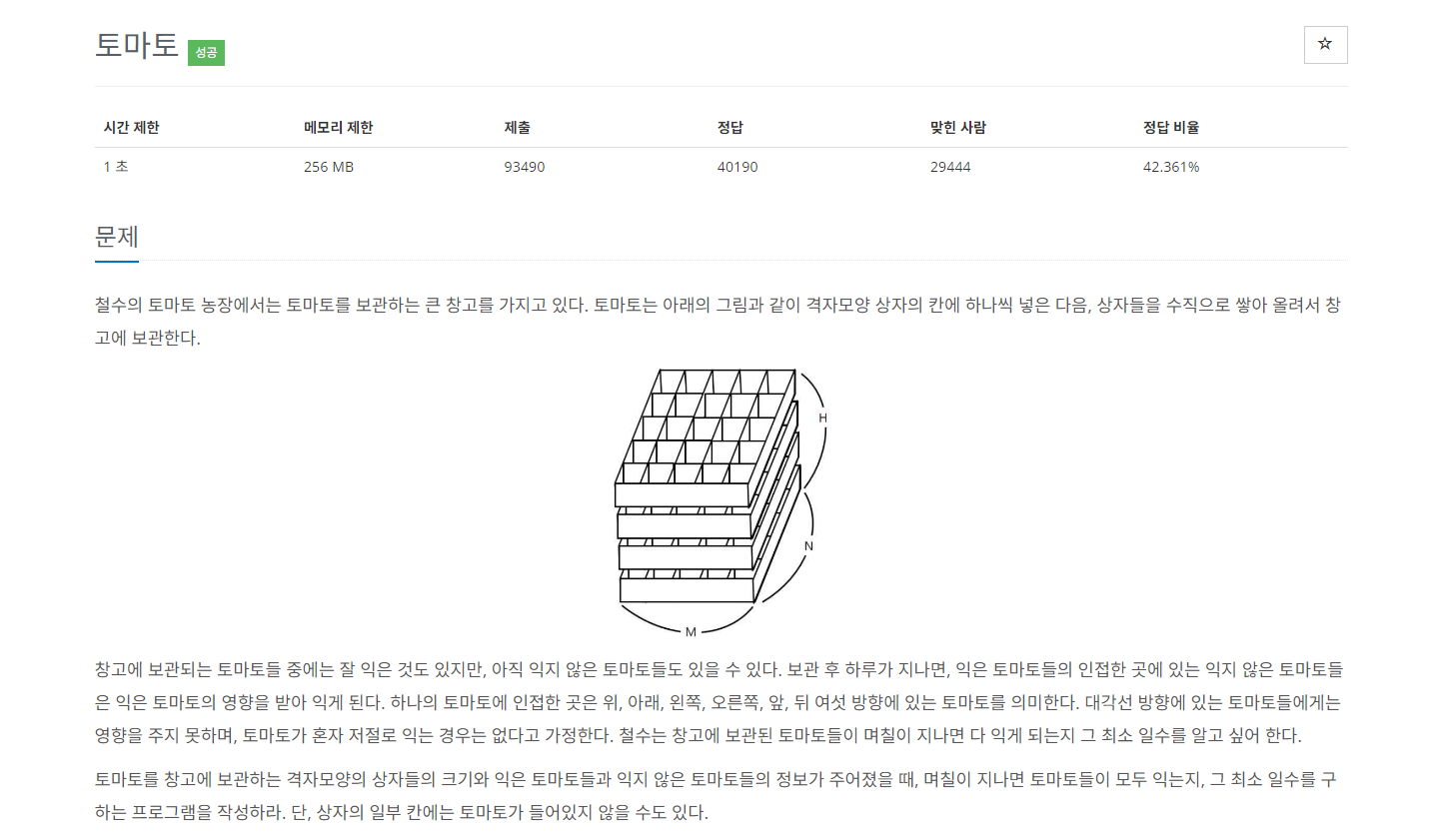
🔴 문제
🟡 Sol
const fs = require('fs');
const path = process.platform === 'linux' ? '/dev/stdin' : 'Wiki\\input.txt';
const [mnh, ...inputs] = fs.readFileSync(path).toString().trim().split('\r\n');
const [m, n, h] = mnh.split(' ').map(Number);
const tomatoBoxes = [];
let tomatoBox = [];
let q = [];
let front = 0;
// 6방향 명시
const dx = [1, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0];
const dy = [0, 0, 1, -1, 0, 0];
const dz = [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, -1];
// 맵 생성
for (let i = 0; i < n * h; i++) {
tomatoBox.push(inputs[i].split(' ').map(Number));
if (tomatoBox.length === n) {
tomatoBoxes.push(tomatoBox);
tomatoBox = [];
}
}
// 시작 좌표 구해주기
for (let i = 0; i < h; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (let k = 0; k < m; k++) {
if (tomatoBoxes[i][j][k] === 1) {
q.push([i, j, k]);
}
}
}
}
// bfs 시작
while (front < q.length) {
const [z, y, x] = q[front++];
for (let i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
const nx = dx[i] + x;
const ny = dy[i] + y;
const nz = dz[i] + z;
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nz < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n || nz >= h) continue;
if (tomatoBoxes[nz][ny][nx] === 0) {
tomatoBoxes[nz][ny][nx] = tomatoBoxes[z][y][x] + 1;
q.push([nz, ny, nx]);
}
}
}
const answer = tomatoBoxes.flat(Infinity);
if (answer.includes(0)) {
console.log(-1);
} else {
console.log(Math.max(...answer) - 1);
}
🟢 풀이
⏰ 소요한 시간 : 2h++
7676번의 토마토 문제의 응용버전이다. 풀이 방법은 동일한데 상하좌우 뿐만아니라 위 아래도 확인해줘야 한다.
먼저 뻗어나갈 6방향을 명시해준다. 보통 bfs는 상하좌우면 봐주면됐는데 z축으로도 봐줘야 하니 총 6번 반복을 돌면 된다.
입력받은 값도 3차원 배열로 가공해야된다.
그 후 시작 좌표를 큐에 모두 넣어준 뒤 front변수로 인덱싱해주면서 bfs 로직을 수행해주면 된다. 마지막 값을 출력할 땐 3차원 배열이니 Infinity 처리를 해주면서 토마토 박스를 펴준다!
