- 강의 : MIT OCW Introduction to Computer Science and Programming in Python - Lecture 1: What is Computation?
컴퓨터는 어떤 일을 하는가
- 기본적으로 초당 수십억 번 이상의 계산을 수행하고 많은 양의 결과를 저장
- 언어에 내장된 계산(더하기 빼기 등)
- 프로그래머로서 정의한 것들
- 컴퓨터는 우리가 컴퓨터에 말한 것만을 할 수 있음
- 빠르게 계산하긴 하지만 우리가 무엇을 할지는 알려줘야함
지식의 종류(Types of Knowledge)
- 서술적 지식(declarative knowledge)
- 팩트에 대한 진술
- 수업이 끝나면 누군가는 상품을 받아갈 것
- 팩트에 대한 진술
- 절차적 지식(imperative knowledge or known as procedural knowledge)
-
how to 에 대한 지식
- 레서피 등
- 출석한 사람들 중 랜덤하게 뽑아서 상품을 준다 등
-
레서피란 무엇인가(특정 작업을 위한 일련의 과정들, 알고리즘이라고 보면 됨)
- sequence of simple steps
- flow of control process that specifies when each step is executed
- a means of determining when to stop
1 + 2 + 3 = an algorithm
-
Computers are machines
- fixed prrogram computer
- 계산기 같이 특정 처리(더하기, 빼기 등)만 할 수 있는 것
- stored program computer
- 일반적으로 생각하는 컴퓨터 같은 것, 일련의 작업 프로세스들을 저장하고 실행하는 것
- 사전에 정의된 primitive instructions 조합이 컴퓨터에 저장되어 있음
- arithmetic and logic (계산, and or 등)
- simple tests (>= == 등)
- moving data (데이터의 이동 등)
- arithmetic and logic (계산, and or 등)
- special program(interpreter)가 순서대로 instruction 실행
- instruction을 계속할지 건너뛸지, 반복할지, 멈출지를 결정
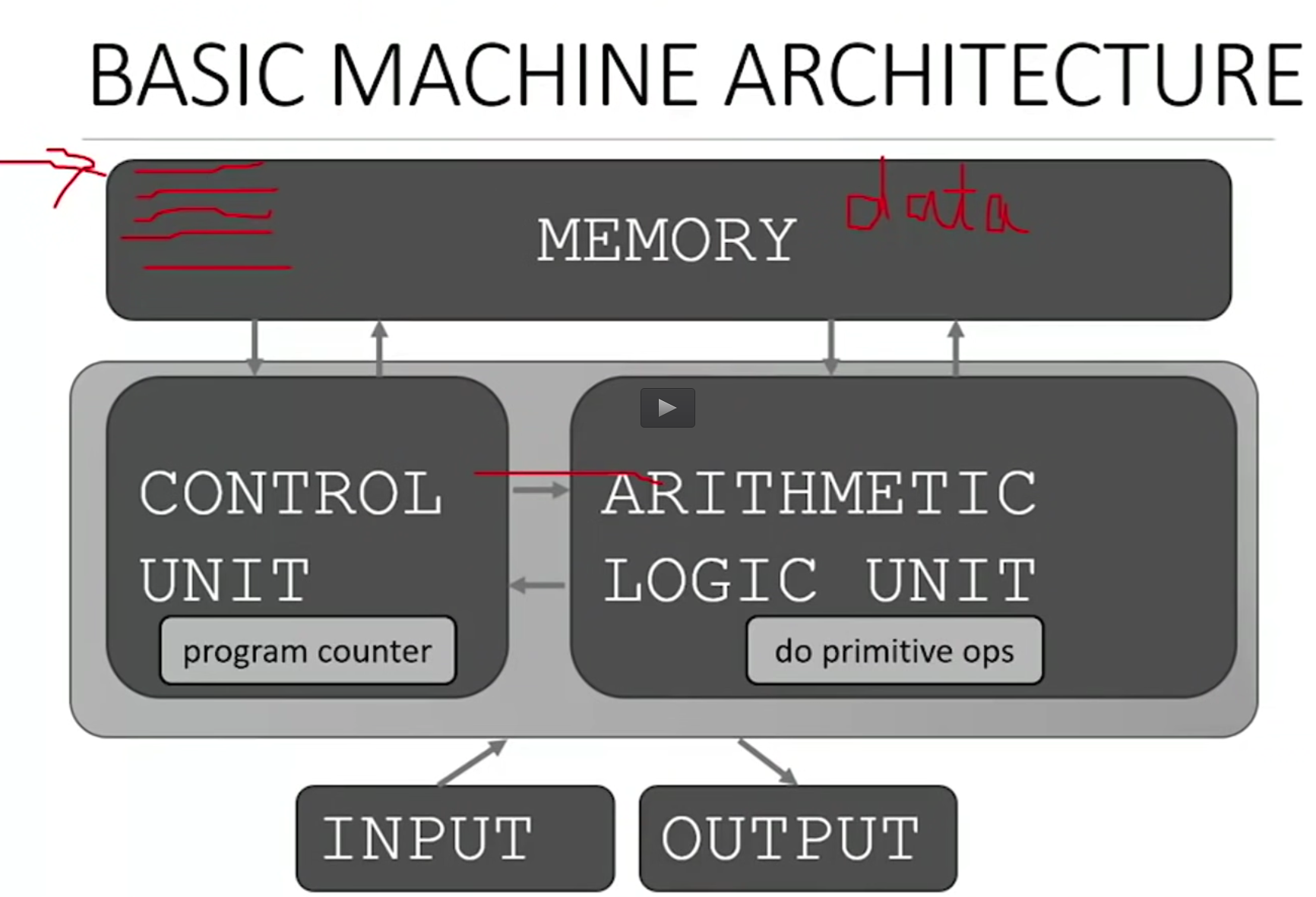
- ARITHMETIC LOGIC UNIT : 원시적인 계산(더하기 빼기) 등을 하고 and or 같은 논리적 연산을 함
- CONTROL UNIT : sequece of instructions 를 읽어내며 instruction 을 실행하도록 ALU 를 통제함
이미지 : 강의자료
참고 자료 : 시스템 프로그래밍:하드웨어 구성
Where Things Go Wrong
- syntactic erros
- 문법적 에러, 일반적이고 쉽게 잡힘
- static semantic errors
- 컴파일 단계에서 확인할 수 있는 에러
- 데이터 타입, scope 등
- 예기치 못한 행동을 일으킬 수 있음
- 참고
- no semantic errors but different meaning than what programmer intended
- semantic 에러는 아닌데 개발자가 의도하지 않은 방식으로 작동하게 된 것
- 프로그램 충돌, 멈춤
- 무한실행
- 원하지 않은 결과 반환 등
Python programs
- a program is a sequece of definitions and commands
- 파이썬 인터프리터에 의해 정의와 명령어가 해석되고 실행됨
- definitions evaluated
- commands executed by Python interpreter in a shell
- inpertreter 가 무언가를 하도록 명령함
- shell 에 바로 타이핑 할 수도 있고 file 로 저장해 shell 에서 읽히게 하거나 evaluated 되게 할 수도 있음
Objects
- programs manipulate data objects
- 파이썬에 있는 모든 것은 object
- objects have a type that defines the kinds of thing programs can do to them
- Ana 는 사람이고, 걸을 수 있고 영어를 한다
- 츄바카는 wookie 고 걸을 수 있고 'mwaaarhrhh' 한다
scalar objects(cannot be subdivided)
수치로만 표현되는(?) object
- int - 정수 ex) 5
- float - 실수 ex)3.27
- bool - boolean ex) True False
- NoneType - specian and has one value, None
- type() - object 의 타입을 볼 수 있음 ex) type(5) >> int
non-scalar objects(have internal structure that can be accessed)
- list etc.
Binding variables and values
- equal sign is an assignment of a value to a variable name(= 으로 변수명에 값을 할당)
pi = 3.14159 - value stored in computer memory
- an assignment binds name to value
- retrieve value associated with name or variable by invoiking the name, by typing pi
- why give names to values of expression? -> to reuse names instead of values, easier to change code later(재사용과 빠른 코드 수정을 위해)
changing bindings
- can re-bind variable names using new assignment statements
- previous value may still stored in memory but lost the handle for it(재할당하면 이전 값은 메모리에 저장은 되어있지만 컨트롤 할 수는 없음. 가비지콜렉터 등으로 처리)
- value for area does not change until you tell the computer to do the calculation again(다시 명령하기 전까지 이전에 할당된 값은 변하지 않음)

강의 총평
- 은연중에 알고 있던 내용들을 정리한 느낌
