
개요
자바스크립트는 prototype 기반 언어이다. 클래스 기반 언어에서는 상속을 사용하지만 프로토타입 기반 언어에서는 어떤 객체를 prototype으로 삼고 이를 복제함으로써 상속과 같은 효과를 얻는다. 아 물론 지금 ES6에서부턴 Class 문법이 추가되어있다.(그렇다고 Class 기반이 되었다것은 아니다ㅎㅎ)
function add (a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function multiply (a, b) {
return a * b;
}
function foo () {
console.log("hello, world");
}
const doSomething = function () {
console.log("do something");
};
console.log(add.prototype);
console.log(multiply.prototype);
console.log(foo.prototype);
console.log(doSomething.prototype);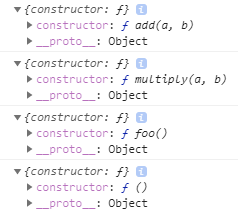
위처럼 생성된 함수마다 자신의 prototype을 가지고 있고 그것은 unique하다.
constructor
constructor는 prototype과 같이 생성되었던 함수를 가리킨다.
proto
__proto__는 dundo proto(던더 프로토)라고 불리는데 모든 객체가 가지고 있는 속성이다.__proto__는 객체가 생성될 때 조상이었던 함수의 prototype을 가리킨다.
const result = Array.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype;
console.log(result);Array의 조상은Object이므로true가 출력된다.
instance
- prototype을 이해하기 위해 instance를 알 필요성이 있다. 생성자 함수가 반환해주는 빈 객체를 instance라고 한다.
function Person (name) {
this.name = name;
}
const jay = new Person("jay");- 위 같은 경우
jay는Person의 instance이다.
function Person (name) {
this.name= name;
}
Person.prototype.age = 32;
const jay = new Person("jay");
console.log(jay.age); // 32- 스크립트의 모든 instance 객체는 해당 객체의 prototype에 존재하는 속성 및 메소드에 접근하여 사용할 수 있다.
- 위의 경우 생성자 함수는
Person이고 instance는jay이다.jay는Person이라는 생성자 함수를 이용해 만들어져서Person.prototype을 이용할 수 있다. 그래서console.log(jay.age)를 하면jay에age프로퍼티가 없어도Person.prototype.age에서 값을 가져와 출력하게 된다.
function Person (name) {
this.name = name;
}
Dog.prototype.kind = "puddle";
const jay = new Person("jay");
console.log(jay.kind) // undefined- 위처럼
jay.kind가undefined로 반환되는 이유는jay는Person의 instance이지Dog의 instance가 아니기 때문이다.
prototype의 관계
function Person (name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.age = 32;
Object.prototype.kind = "animal";
let jay = new Person("jay");
console.log(jay.age); // 32
console.log(jay.kind); // "animal"
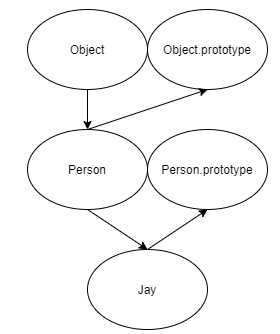
console.log(jay.name); // "jay"- 위 코드의 prototype 관계도를 그려보았다. 이것은 가족과 같은 관계라고 보면 될거 같다.
- 관계도에서
Constructor함수는 남편이 된다.prototype은 아내이다. 그리고 둘의 관계는 1:1이다. - 생성자 함수의 선언이 여러번 이루어지면 그 횟수만큼
prototype의 갯수도 늘어난다. - instance는 생성자 함수의 자식이 된다. 자식에서 당장 필요한 속성을 가지고 있지 않을 때 엄마인
prototype이 필요한 속성을 가지고 있으면 자식에게 상속해 줄수 있다. - 위 코드 같은 경우
jay에겐age가 있지만kind,name이 없어서Person.prototype에게age속성을 빌려왔다. 그런데Person.prototype에게kind는 없어서Person의 엄마인Object.prototype에게kind를 받아와서 할머니가 손주에게 물려준 것이라고 볼수 있다.
상속의 다른 예
function Animal () {
this.eat = function () { console.log("EAT!"); };
}
Animal.prototype.sleep = function () { console.log("sleep"); };
function Human (name) {
Animal.call(this);
this.name = name;
}
Human.prototype = Object.create(Animal.prototype);
Human.prototype.constructor = Human;
const jay = new Human("jay");
const dog = new Animal();
dog.sleep();
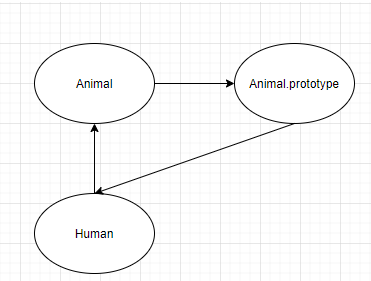
jay.sleep();Animal생성자 함수가 선언됨Animal.prototype.sleep에 "sleep"이라고 출력되는 함수 선언- 생성자 함수
Human은Animal생성자 함수에게 자신의this를call메소드를 통해 전달함(Animal에 속해짐) Human.prototype은Animal.prototype으로부터 상속받는 객체를 생성Human의Constructor는 자기 자신이 됨- 변수
jay는Human생성자 함수로 선언됨 - 변수
dog은Animal생성자 함수로 선언됨 - dog.sleep()은
Animal.prototype.sleep을 통해 "sleep" 출력 - jay.sleep()은
Animal.prototype으로부터 상속받은 "sleep" 출력
예제
1
Array.prototype.hello = 10;
const arr = [];
console.log(arr.hello);arr에는hello속성이 없기 때문에 부모인Array.prototype으로부터 hello를 상속받아10이 출력됨
2
Object.prototype.me = "olleh";
function Person (name) {
this.name = name;
}
const jay = new Person("jay");
console.log(jay.me);- 결과값은 "olleh"가 나온다.
Person에는 me라는 속성이 없어서Person의 constructor인Object에서 me값을jay에게 상속해 주기 때문
출처
코어 자바스크립트
