
개요
기존에 클래스에 대한 글을 썼던것에 보충을 좀 해야지..라고 생각해서 오늘 클래스를 좀 더 공부한 다음 내용 보충을 하려고 했는데, 클래스에 대한 글을 안썼었다. 정말 충격적이다. 그래서 처음부터 클래스에 대한 내용을 복습할 겸 작성해본다.
class?
클래스는 OOP(객체 지향 프로그래밍)에서 특정 객체를 생성하기 위해 변수와 메소드를 선언하는 방법이다. 자바스크립트에 클래스가 나타나기 이전에는 기존에 썼던 글 내용인 prototype에 메소드를 할당해서 사용했었다. prototype에 메소드를 선언하는 방법도 있지만 ES6에서 등장한 class를 활용하면 OOP에 익숙한 개발자들은 좀 더 쉽게 접근이 가능하다.
구조
class Person {
constructor(name){
this.name = name;
}
sayHi(){
alert(this.name);
}
}
let user = new User("jay");
user.sayHi() // 경고창과 함께 "jay"가 나타남위처럼 class는 contructor()와 사용자 정의 메소드를 가진다. 위처럼 new User("jay")를 호출하면 객체가 생성되면서 "jay"를 넘겨받은 것과 함께 constructor가 자동으로 실행되면서 this.name에 "jay"가 할당된다.
constructor
constructor는 instance를 생성하고 클래스 필드를 초기화하기 위한 메소드이다. 클래스 내에 한 개만 존재하고, 2개 이상이 존재하면 SyntaxError가 발생한다.
constructor는 생략이 가능한데, 만약 생략하게 된다면 constructor(){}를 클래스내에 포함 것과 동일하게 동작한다.
getter, setter
getter
class Foo {
constructor(arr = []) {
this._arr = arr;
}
get firstElem() {
return this._arr.length ? this._arr[0] : null;
}
}
const foo = new Foo([1, 2]);
// 필드 firstElem에 접근하면 getter가 호출된다.
console.log(foo.firstElem); // 1getter는 클래스 필드에 접근할 때마다 클래스 필드의 값을 조작하는 경우가 필요할 때 사용한다.
사용은 get 키워드를 이용한다. getter는 뭔가를 얻을 때 사용하므로 다시 뭔가를 반환해야 한다.
setter
class Foo {
constructor(arr = []) {
this._arr = arr;
}
get firstElem() {
return this._arr.length ? this._arr[0] : null;
}
set firstElem(elem) {
this._arr = [elem, ...this._arr];
}
}
const foo = new Foo([1, 2]);
foo.firstElem = 100;
console.log(foo.firstElem); // 100setter는 클래스 필드에 값을 할당할 때마다 필드의 값을 조작하는 행위가 필요할 때 사용한다.
사용은 set 키워드를 이용한다. setter는 호출하는 것이 아니라 프로퍼티처럼 값을 할당하는 형식으로 사용해서 할당 시에 메소드가 호출된다.
static
class Foo {
constructor(prop) {
this.prop = prop;
}
static staticMethod() {
return 'staticMethod';
}
prototypeMethod() {
return this.prop;
}
}
console.log(Foo.staticMethod()); // 'staticMethod'
const foo = new Foo(123);
console.log(foo.staticMethod()); // Uncaught TypeError: foo.staticMethod is not a function클래스의 정적(static) 메소드를 정의할 때 static 키워드를 사용한다. 정적 메소드는 클래스의 인스턴스가 아닌 클래스 이름으로 호출한다. 따라서 클래스의 인스턴스를 생성하지 않아도 호출할 수 있다. 위처럼 인스턴스로 호출을 하면 에러가 난다.!
extends, super
class Vehicle {
constructor() {
this.passengers = [];
console.log('Vehicle Created');
}
addPassenger(p) {
this.passengers.push(p);
console.log('Passenger Added');
}
}
class Car extends Vehicle {
constructor() {
super(); // Vehicle 클래스의 constructor를 호출 함
console.log('Car created');
}
deployAirbags() {
console.log('BOOM!');
}
}
const car1 = new Car();
car1.addPassenger('sunny');
car1.deployAirbags();
console.log(car1);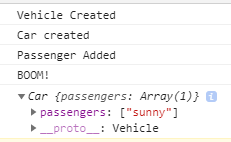
extends는 부모 클래스를 상속받는 자식 클래스를 정의할 떄 사용한다.
super는 부모 클래스를 참조할 때나 부모의 constructor를 호출할 때 사용한다.
