개발을 하다보면 동적 소스 데이터(fetch같은) 혹은 복잡한 유니온 타입 데이터에 대한 런타임 타입 체크를 해야하는 경우가 종종 있습니다.
그럴 때는 타입스크립트가 타입을 추론할 수 있도록 타입을 좁혀주는 것이 필요한데요(이것을 type narrowing이라고 부릅니다) 그럴 때 사용하는 개념이 바로 type guard입니다.
타입스크립트뿐만 아니라 유니온 타입을 지원하는 일부 언어들에서도 런타임에 유니온 타입으로부터 정확한 타입을 결정할 수 있도록 각자의 방식으로 type narrowing을 지원합니다. 예를 들어 Rust에서는 match 표현을 사용해 타입을 좁힙니다(narrow down).
타입가드(이하 type guard)가 뭔데요?
type guard란 런타임에 조건문에서 변수 혹은 매개변수의 타입을 좁힐 수 있도록 하는 타입스크립트 기능이자 개념입니다. (용어는 언어별로 다를지 몰라도 개념 자체는 동일하게 사용됨)
'타입을 좁힌다'라는건 union타입에서 구체적인 타입으로 딱 정한다는 뜻입니다. 그리고 타입을 좁힘으로써 오류를 방지하고 코드가 의도한 대로 동작하도록 보장할 수 있습니다.
타입가드 = 타입을 좁힌다 = union 타입에서 구체적인 타입으로 변환시킨다 = type narrowing
다양한 구현방식이 있는데요, 타입스크립트에서는 typeof 연산자, instanceof 연산자, 비교연산자, 사용자정의 타입가드 함수(type predicate) 등을 사용하는 방식으로 type guard를 구현합니다.
뒤에서 살펴보겠지만 타입스크립트는 type predicate 방식을 권장합니다.
type guard 그거 왜 써요?
type guard를 사용하면 타입을 체크하지 않은 경우 발생할 수 있는 런타임 에러를 방지할 수 있습니다.
특히 애초에 tsconfig으로 noImplicitAny 옵션을 활성화 시키고 코딩을 하는 경우에는 타입으로 any를 지정하는 것이 불가능하다보니 무조건 컴파일에러가 발생하기 때문에 type guard로 narrowing을 해줘야합니다.
언제 쓰는건데요?
type guard는 조건문에서 null과 undefined같은 optional값을 비롯한 원시 타입, 클래스 타입, 객체의 속성들을 검사할 때 사용합니다.
아래는 type predicate 방식을 제외한 타입가드를 사용하는 예시입니다.
//optional을 검사할 때
function printDouble(value: number | null) {
if (value !== null) {
//value는 number 타입으로 narrowing 돼서 곱연산이 가능해진다.
console.log(value * 2);
}
}
//객체의 속성을 검사할 때
type Square = {
type: "square";
size: number;
}
type Rectangle = {
type: "rectangle";
width: number;
height: number;
}
type Shape = Square | Rectangle;
function area(shape: Shape) {
if (shape.type === "square") {
// 비교연산자를 이용한 타입가드.
// 이 경우에 shape의 type은 Square로 narrowing됩니다.
// Square만의 고유 속성인 size에도 접근 가능해집니다.
return shape.size * shape.size;
} else {
// 조건문에서 Square로 좁혀졌기 때문에
// 자동으로 else문의 type은 Rectangle로 추론됩니다.
// Rectangle만의 고유 속성인 width와 height에도 접근 가능해집니다.
return shape.width * shape.height;
}
}
//인스턴스를 검사할 때
//인터페이스 기반
interface Animal {
name: string;
}
interface Dog extends Animal {
bark: () => void;
}
interface Cat extends Animal {
meow: () => void;
}
function makeSound(animal: Dog | Cat) {
// in 연산자를 이용해 Dog 인스턴스인지 검사하는 타입가드
if ('bark' in animal) {
//animal은 Dog type으로 narrowing됩니다.
animal.bark();
} else {
// animal은 Cat type으로 narrowing됩니다.
animal.meow();
}
}
or
//클래스 기반
class Animal {
name: string;
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
bark() {
console.log("Woof!");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
meow() {
console.log("Meow!");
}
}
function makeSound(animal: Dog | Cat) {
// instanceof 연산자를 이용해 Dog 인스턴스인지 검사하는 타입가드
if (animal instanceof Dog) {
// animal은 Dog type으로 narrowing됩니다.
animal.bark();
} else {
// animal은 Cat type으로 narrowing됩니다.
animal.meow();
}
}엥? typeof, instanceof 로도 충분히 narrowing 가능해보여요
맞습니다. typeof, instanceof 같은 연산자들을 사용해서 충분히 런타임 타입 체크가 되지만 몇 가지 제한사항이있습니다.
typeof같은 연산자를 남발하면 코드가 지저분해져 가독성이 안좋아질 수 있습니다.typeof는string,number,boolean과 같은 원시타입과 함수에 대해서만 검사할 수 있습니다.instanceof는 타입스크립트에서 런타임에 인터페이스와 type alias가 존재하지 않기 때문에 인터페이스 또는 type alias의 인스턴스인지 확인하지는 못하고 클래스의 인스턴스인지 확인하는 데에만 사용가능합니다.
물론 상황에 따라 이런 방식들을 사용해도 전혀 문제는 없습니다.
그럼에도 type predicates?
type predicate function이라고도 불리는 사용자정의 타입가드(type predicates)는 boolean값을 반환하고 Return type으로 value is type을 지정해주는 함수를 말합니다.
return값이 true일 경우, 이 블록에서는 value가 해당 타입이라는 것을 타입스크립트가 알 수 있게 됩니다.
아래는 union 타입의 데이터를 fetch하는 예시입니다. 이 경우 type guard없이 toUpperCase()를 호출하고 있는데요, 이 때 value의 type은 (string | number) 타입입니다. number인지 string인지 타입이 좁혀지지 않았기 때문에 호출할 수 없는 것이죠.
type guard를 적용하지 않는 경우(에러가 발생)
type Value = string | number;
let value: Value = await fetchSomething();
console.log(value.toUpperCase()); // 에러 발생.. Property 'toUpperCase' does not exist on type 'Value'.
type guard를 적용하는 경우
//type predicate function
function isString(value: unknown): value is string {
return typeof value === 'string';
}
if (isString(value)) {
//value의 type은 string으로 narrowing됩니다
console.log(value.toUpperCase()); // value는 string이기 때문에 toUpperCase()를 호출가능
}isString 함수가 바로 type predicate입니다.
만약 value에 string값이 할당이 된 상태라면 이 함수를 호출하는 블록에서는 타입스크립트가 value는 string type이라고 추론할 것 입니다.
그리고 아래 예시는 type predicate를 사용하여 type guard를 구현한 경우와 사용하지 않고 type guard를 구현한 경우를 보여주는 코드입니다.
const isRequiredAndNumberAndNotZero = (value: any): value is number => {
return isNumber(value) && isNotZero(value) && isRequired(value);
}
const isRequired = (value: any): value is any => {
return value !== null && value !== undefined;
}
const isNumber = (value: any): value is number => {
return typeof value === "number";
}
const isNotZero = (value: number | string): value is number => {
return Number(value) !== 0;
}
type StringOrNumber = string | number;
const data: StringOrNumber = await fetchData();
//type predicate 사용한 type guard. 아 data는 저런 데이터겠군 하고 바로 유추가능하다.
if(isRequiredAndNumberAndNotZero(data){
console.log(data + 10);
} else {
console.log(data + "십");
}
//type predicate를 사용하지 않은 type guard. 가독성이 좋지 않다....
if(data !== null || data !== undefined){
if(typeof data === "number"){
if(data !== 0){
console.log(data + 10);
}
}
} else {
console.log(data + "십");
}
예제를 보면 알 수 있다시피, type predicate는 사용자가 커스텀하게 다양한 타입을 검증할 수 있기 때문에 typeof나 instanceof 연산자보다 더 유연하게 타입 체크를 할 수 있습니다. 또한 함수의 이름이 타입 체크의 의미를 명확하게 나타내므로, 코드의 가독성을 높일 수 있습니다.
type predicate를 사용하여 type guard를 구현하는 추가예시
function isRequired<T>(value: T | undefined | null): value is T {
return value !== undefined && value !== null;
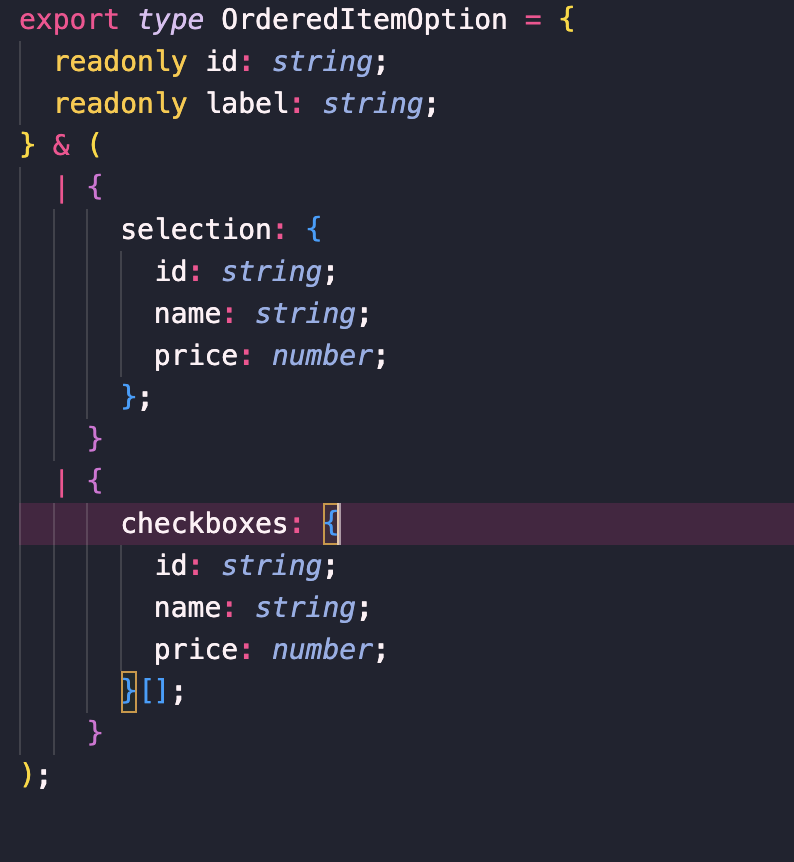
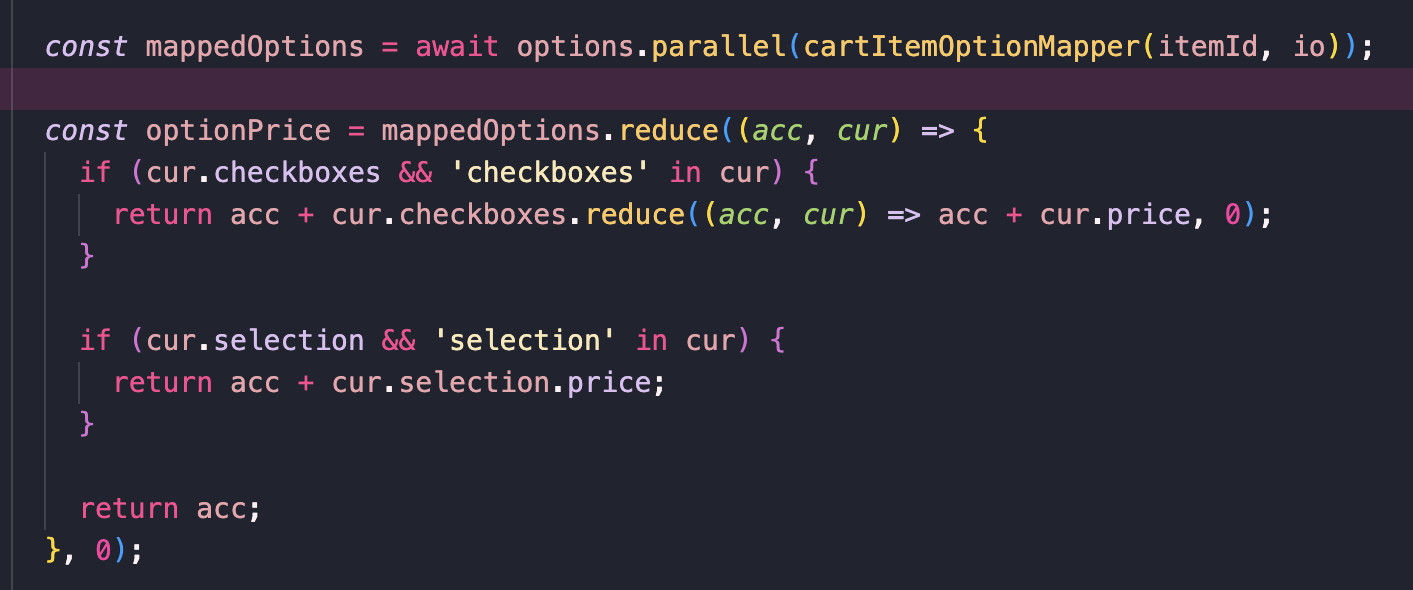
}(실제 type guard를 구현한 주문관련 코드, selection 객체와 checkboxes객체 배열이 union 타입으로 묶여있기 때문에 각각 속성에 접근하기 위해 타입을 좁히는 것을 확인 가능하다.)
type guard 뭐 이런게 있구나하며 정확한 개념은 무엇인지 생각하지 않고 사용하고 있다가 정리를 해봤습니다.



언제쓰는건데요 부분에...
"in"을 사용해 객체의 속성명을 체크해서 타입가드를 사용하는 부분은 맞습니다.
or 다음 부분에 instanceof 의 예제는 틀립니다. interface 로 선언된 타입은 instanceof 로 타입체크를 할 수 없습니다.
글쓴이가 앞서 설명을 잘해주셨음에도 예제를 이렇게 쓰면 안될것 같네요.