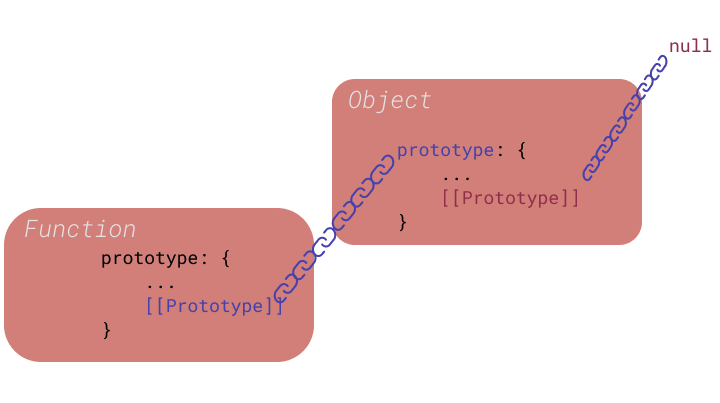
prototype chain 이란?
상위에 있는 proto에 접근할 수 있도록 연결되어 있다.
prototype chain 확인하기
__proto__로 확인할 수 있다.
const array = [];
array.__proto__ // Array
array.__proto__.__proto__ // Object
array.toString() // 이걸 사용할 수 있는 이유는 prototype chain에서 Object에 toString이 있기 때문이다.memory efficient
proto chain 덕분에, 공통으로 사용되는 것에 대한 memory를 줄일 수 있다. (그렇지 않으면, 같은 method를 copy해서 사용해야 한다. 예를 들면, array를 만들때마다 map function이 새로 생성된다고 상상하면 된다.)
Example
big object가 하나이상의 method를 가져쓰기 위해서 prototype chain을 활용할 수 있다.
const dog = {
sound() {
return `${this.name} is barking`
}
}
const brown = {
type: 'dog',
name: 'brown',
color: 'black'
}
brown.__proto__ = dog;
brown.sound(); // brown is barking
dog.isPrototypeOf(brown) // true__proto__
__proto__는 바로 상위에 있는 prototye object를 가리킨다.

실제로 __proto__는 코드상에서 사용하지는 않는다.
__proto__ 대신에 Object.getPrototypeOf(obj)를 사용한다.
const dog = {
sound() {
return `${this.name} is barking`
}
}
const brown = {
type: 'dog',
name: 'brown',
color: 'black'
}
brown.__proto__ = dog;
Object.getPrototypeOf(brown) // {sound: f}prototype
constructor(function)의 이름은 PascalCase를 사용합니다.
// Person은 constructor function이 된다.
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
/* Person 함수는 아래 class와 동일합니다.
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
*/
Person.prototype // { constructor: f Person(name) }
const brown = new Person('brown') // constructor로 instance를 생성합니다.
brown.name // brown
Brown.prototype.sayHi = function() { // sayHi라는 method를 추가합니다.
return 'Hello'
}
brownClone.sayHi() // Helloobject(혹은 instance)에는 prototype을 만들 수 없다.
const brown = {}
console.log(brown.prototype) // undefined
brown.prototype = 'brown'
console.log(brown) // { prototype: 'brown' } 단순히 prototype이라는 이름의 property가 생김function만 prototype property(단순히 prototype이름의 key가 아님)을 가질 수 있다.
Object.prototype이 있기 때문에 헷갈릴 수 있는데, Object자체가 constructor function이다. (아래 typeof의 차이점을 보면 알 수 있다.)
typeof Object // function
typeof Object.prototype // object__proto__와 prototype의 관계
__proto__는 상위 chain의 prototype을 pointing하고 있다.
const array = [];
array.__proto__ === Array.prototype // true
array.__proto__.hasOwnProperty('map') // truearray의 상위 prototype은 Array.prototype이다. 따라서 array.__proto__가 포인팅하는 것은 Array.prototype인 것이다.
hasOwnProperty
object가 특정 property를 갖고 있는지 확인할 수 있다.
const obj = { name: 'cho' }
obj.hasOwnProperty('name'); // trueObject.create
object에 대해서 prototype chain을 만드려면 Object.create로 만들 수 있다.
let human = {
mortal: true,
}
let socrates = Object.create(human)
socrates.age = 80
socrates.mortal
console.log(human.isPrototypeOf(socrates)) // true
console.log(socrates.hasOwnProperty('mortal')) // falsePractice
Date에 lastYear method 추가하기
Date.prototype.lastYear = function() {
return this.getFullYear() - 1; // this는 new Date()의 모든값을 받는다. (lastYear을 invoke한게 new Date()이기 때문)
}
new Date('1900-10-10').lastYear() // 1899map method 만들기#1 (기존 Array에 override)
Array.prototype.map = function() {
const array = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
array.push(this[i] + '🚀') // this는 arr의 모든 값을 받는다. (map을 invoke한게 arr이기 때문)
}
return array;
}
const arr = [1,2,3];
arr.map() // ['1🚀', '2🚀', '3🚀']map method 만들기#2
function MyArray(arr) {
this.arr = arr;
}
MyArray.prototype.map = function (callback) { // 여기서는 arrow function을 쓰지 않아야합니다. (this에 접근하기 위해서)
let newArr = [];
for (let value of this.arr) {
newArr.push(callback(value));
}
return newArr;
}
const myArray = new MyArray([1,2,3]);
console.log(myArray.map(num => num+1))
