Spring Security
-
Spring 기반의 어플리케이션에서 보안(인증, 인가)을 처리하는 Spring 하위 프레임워크
1) 인증: 로그인 처리
2) 인가: 로그인 한 사용자 별 권한에 따른 처리
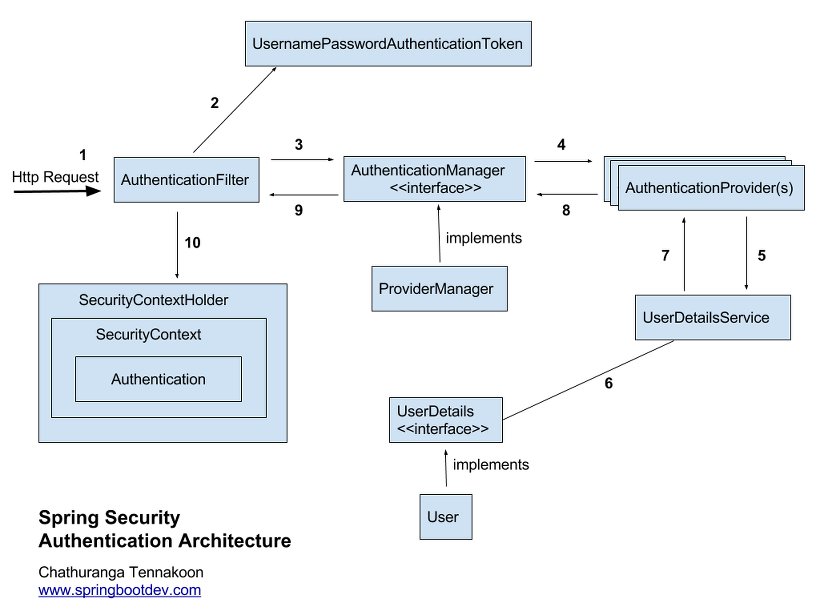
Spring Security 인증 과정
0. 목적
-
Security 인증 과정의 목적은 SecurityContext에 Authentication 객체를 저장하는 것입니다.
-
Authentication는 사용자가 입력한 username, password을 토대로 하여 '인증된 사용자'의 정보를 담고 있는 객체입니다.
1. Http Request (로그인 요청)
-
사용자는 자신의 username과 password를 입력하여 로그인을 요청합니다.
-
요청을 받은 Security는
AuthenticationFilter를 호출합니다. -
정확히는
AuthenticationFilter중 인증을 담당하는UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter를 호출합니다.
2. UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
-
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter은 username과 password를 이용하여UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken객체를 생성합니다. -
현재는 Authentication 객체를 얻지 못했기에 'setAuthentication(false)'인 객체가 생성됩니다.
-
보통 principal은 username, credentials은 password로 지정합니다.
/* Login forms must present two parameters to this filter: a username and password. The default parameter names to use are contained in the static fields * SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY and SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY}. * The parameter names can also be changed by setting the usernameParameter and passwordParameter properties. * This filter by default responds to the URL /login. */ public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter { public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY = "username"; public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY = "password"; private static final AntPathRequestMatcher DEFAULT_ANT_PATH_REQUEST_MATCHER = new AntPathRequestMatcher("/login", "POST"); ...... @Override public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException { if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) { throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod()); } String username = obtainUsername(request); username = (username != null) ? username.trim() : ""; String password = obtainPassword(request); password = (password != null) ? password : ""; UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.unauthenticated(username, password); // Allow subclasses to set the "details" property setDetails(request, authRequest); return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest); }
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken { ...... /* This constructor can be safely used by any code that wishes to create a * UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken, as the isAuthenticated() * will return false. */ public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials) { super(null); this.principal = principal; this.credentials = credentials; setAuthenticated(false); } ...... }
3~5. AuthenticationManager → AuthenticationProvider → UserDetailsService
-
본격적으로
Authentication객체를 생성하기 위한 작업이 시작됩니다. -
앞서 생성한
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken객체는AuthenticationManager와AuthenticationProvider을 거쳐UserDetailsService로 전달됩니다.
public interface AuthenticationManager { /* ...... * Params: authentication - the authentication request object * Returns: a fully authenticated object including credentials */ Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException; }
public interface AuthenticationProvider { /* Params: authentication the authentication request object. * Returns: a fully authenticated object including credentials. May return * null if the AuthenticationProvider is unable to support * authentication of the passed Authentication object. In such a case, * the next AuthenticationProvider that supports the presented * Authentication class will be tried. */ Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException; boolean supports(Class<?> authentication); }
6. UserDetailsService
-
UserDetailsService객체는loadUserByUsername메서드를 통하여 username이 DB에 저장되어 있는지 확인합니다. -
확인이 될 경우 사용자의 username, password, authorities 등의 정보를 field로 갖는
UserDetails객체를 반환합니다.
Authentication 객체를 바로 만들지 않고 UserDetails를 반환하는 이유는 무엇인가?
- Spring Security는 보안을 위해 사용자 정보를 직접 사용하지 않으며, Authentication 객체에 캡슐화하여 저장합니다.
- UserDetailsService가 반환한 UserDetails 객체는 후에 Authentication 객체로 캡슐화 됩니다.
- 추가적으로, UserDetails는 사용자와 관련된 비보안 정보(이메일 주소, 전화번호 등)도 저장할 수 있어서 DB 접근을 줄일 수 있다는 장점이 있습니다.
cf) Provides core user information.
Implementations are not used directly by Spring Security for security purposes. They simply store user information which is later encapsulated into Authentication objects. This allows non-security related user information (such as email addresses, telephone numbers etc) to be stored in a convenient location.
public interface UserDetailsService { UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException; }
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable { Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities(); String getPassword(); String getUsername(); ...... }
7. AuthenticationProvider
AuthenticationProvider은UserDetailsService로부터 받은UserDetails객체를Authentication객체로 캡슐화하여 반환합니다.
8. AuthenticationManager
AuthenticaionProvider과 마찬가지로Authentication객체를 반환합니다.
9. AuthenticationFilter
AuthenticationManager로부터 인증된Authentication을 받았다면SecurityContextHolder를 호출합니다.SecurityContextHolder은 Security 내부 세션 저장소이며, Authentication 객체를 저장합니다.
10. SecurityContext
-
SecurityContextHolder은SecurityContext객체를 호출합니다. -
SecurityContext객체에Authentication객체를 저장하여 인증 과정을 마무리합니다.