
힙(Heap)?
우선순위 큐 : FIFO인 큐와 달리 우선 순위가 높은 요소가 먼저 나가는 큐를 우선 순위 큐라고 한다.
우선순위 큐는 자료구조가 아닌 개념이고 힙과 우선 순위 큐는 같지 않다. 단순히 우선순위 큐를 구현하는 방법 중 하나가 힙을 이용하는 것 뿐이다.
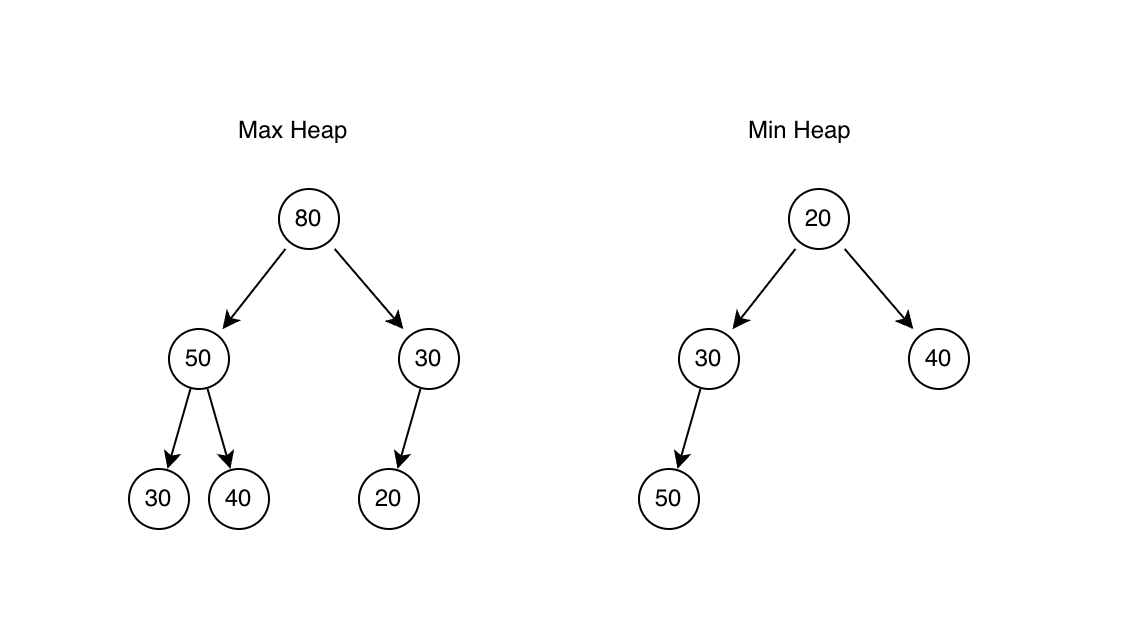
힙은 이진 트리 형태를 가지며 우선순위가 높은 요소가 먼저 나가기 위해 요소가 삽입, 삭제 될 때 바로 졍렬되는 특징이 있다.
힙 특징
- 우선순위가 높ㅇ느 요소가 먼저 나가는 특징을 가진다.
- 루트가 가장 큰 값이 되는 최대 힙(Max Heap)과 루트가 가장 작은 값이 되는 최소 힙(Min Heap)이 있다.
- 자바스크립트에서는 힙을 지원하지 않아 직접 구현해서 사용해야 한다.
힙의 추가와 삭제
힙의 요소 추가
-
요소가 추가될 때는 트리의 가장 마지막 정점에 위치한다.
-
추가 후 부모 정점보다 우선순위가 높다면 부모 정점과 순서를 바꾼다.
-
이 과정을 반복하면 결국 가장 우선순위가 높은 정점이 루트가 된다.
-
완전 이진 트리의 높이는 logN이기에 힙의 요소 추가 알고리즘은 O(logN)의 시간복잡도를 가진다.
힙의 요소 삭제
-
요소 제거는 루트 정점만 가능하다.
-
루트 정점이 제거된 후 가장 마지막 정점이 루트에 위치한다.
-
루트 정점의 두 자식 정점 중 더 우선순위가 높은 정점과 바꾼다.
-
두 자식 정점이 우선순위가 더 낮을 때 까지 반복한다.
-
완전 이진 트리의 높이는 logN이기에 힙의 요소 제거 알고리즘은 O(logN)의 시간 복잡도를 가진다.
최대 힙 구현
class MaxHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [null];
}
getLeftChildIndex(index) {
return index * 2;
}
getRightChildIndex(index) {
return (index * 2) + 1;
}
getParentIndex(index) {
return Math.floor(index / 2);
}
swap(index1, index2) {
const temp = this.heap[index1];
this.heap[index1] = this.heap[index2];
this.heap[index2] = temp;
}
isEmpty() {
return !this.heap[1] ? true : false;
}
push(value) {
if(!value) {
return;
}
this.heap.push(value);
let currentIndex = this.heap.length - 1;
let parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(currentIndex);
while(parentIndex !== 0 && this.heap[parentIndex] < value) {
this.swap(currentIndex, parentIndex);
currentIndex = parentIndex;
parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(currentIndex);
}
}
pop() {
const result = this.heap[1];
let currentIndex = 1;
let leftIndex = 2;
let rightIndex = 3;
if(this.heap.length === 2) {
return this.heap.pop();
}
this.heap[1] = this.heap.pop();
while(this.heap[currentIndex] < this.heap[leftIndex] || this.heap[currentIndex] < this.heap[rightIndex]) {
if(this.heap[leftIndex] > this.heap[rightIndex]) {
this.swap(currentIndex, leftIndex);
currentIndex = leftIndex;
}
else {
this.swap(currentIndex, rightIndex);
currentIndex = rightIndex;
}
leftIndex = this.getLeftChildIndex(currentIndex);
rightIndex = this.getRightChildIndex(currentIndex);
}
return result;
}
}
const maxHeap = new MaxHeap();
maxHeap.push(5);
maxHeap.push(1);
// maxHeap.push(2);
console.log(maxHeap.heap);
console.log(maxHeap.pop());
console.log(maxHeap.heap);
최소 힙 구현
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [null];
}
getLeftChildIndex(index) {
return index * 2;
}
getRightChildIndex(index) {
return (index * 2) + 1;
}
getParentIndex(index) {
return Math.floor(index / 2);
}
swap(index1, index2) {
const temp = this.heap[index1];
this.heap[index1] = this.heap[index2];
this.heap[index2] = temp;
}
isEmpty() {
return !this.heap[1] ? true : false;
}
push(value) {
if(!value) {
return;
}
this.heap.push(value);
let currentIndex = this.heap.length - 1;
let parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(currentIndex);
while(parentIndex !== 0 && this.heap[parentIndex] > value) {
this.swap(currentIndex, parentIndex);
currentIndex = parentIndex;
parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(currentIndex);
}
}
pop() {
const result = this.heap[1];
let currentIndex = 1;
let leftIndex = 2;
let rightIndex = 3;
if(this.heap.length === 2) {
return this.heap.pop();
}
this.heap[1] = this.heap.pop();
while(this.heap[currentIndex] > this.heap[leftIndex] || this.heap[currentIndex] > this.heap[rightIndex]) {
if(this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[rightIndex]) {
this.swap(currentIndex, leftIndex);
currentIndex = leftIndex;
}
else {
this.swap(currentIndex, rightIndex);
currentIndex = rightIndex;
}
leftIndex = this.getLeftChildIndex(currentIndex);
rightIndex = this.getRightChildIndex(currentIndex);
}
return result;
}
}
const minHeap = new MinHeap();
minHeap.push(5);
minHeap.push(1);
// minHeap.push(2);
console.log(minHeap.heap);
console.log(minHeap.pop());
console.log(minHeap.heap);
