지금까지 배운 집합 데이터 객체에 대해 아는 거라곤 배열 하나 뿐이었다. 데이터를 어떻게 저장을 하느냐에 따라 어떤 식으로 활용할 때 유리한지가 결정된다.
유리함이라 하면, 코드의 성능이 좋음을 의미한다. 즉, 시간이 적게 걸리고(시간복잡도), 메모리 용량을 적게 쓰는 것(공간복잡도)이다. 이러한 성능 좋은 코드를 쓰기 위해 자바에서 주는 자료구조가 바로 Collection이다.
들어가기 전 외워야 하는 족보가 있다.
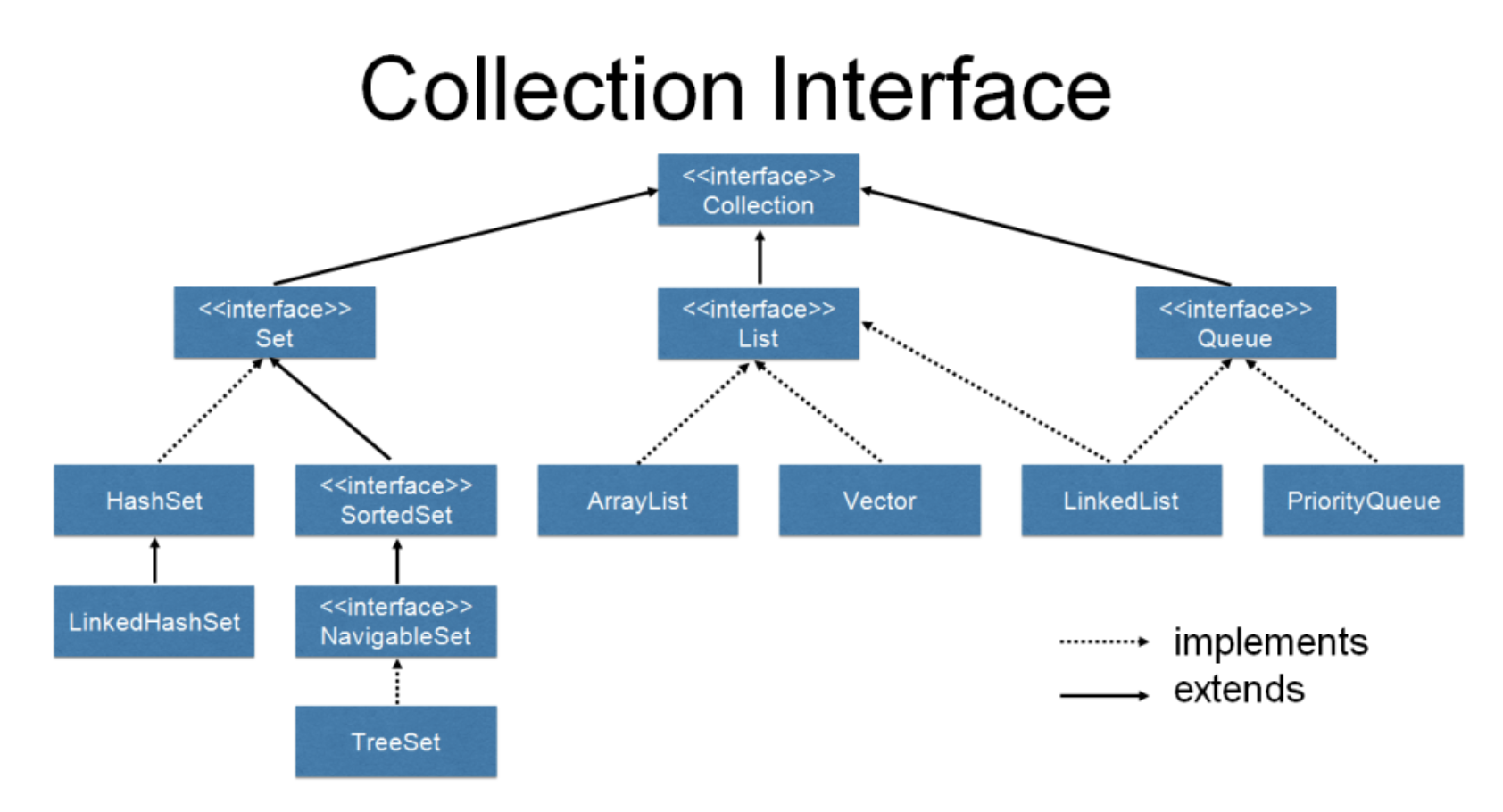
먼저 List에 대해 알아보자.
/*
Collection<E>
|__ List<E>
|__ ArrayList<E>, LinkedList<E>
List 특징(ArrayList와 LinkedList의 공통점)
1. 중복 저장 허용
2. 저장 순서 유지 (인덱스 존재)
ArrayList:
1. 저장 용량을 늘리는 데 많은 시간 소요 - 단점
2. 데이터를 삭제하는 데 많은 연산 - 단점
3. 데이터 참조 매우 빠름 - 장점
LinkedList:
1. 저장 용량을 늘리는 과정이 매우 간단 - 장점
2. 데이터를 삭제하는 과정이 간단 - 장점
3. 데이터 참조가 불편 - 단점
※ Vector<E> <-- ArrayList 와 비슷하나... ArrayList 추천.
※ 데이터 자료구조를 다룰시 각 자료구조에서 데이터에 대한 다음 동작들이 어떻게 되는지 주목하자
- C (Create) 생성
- R (Read) 조회
- U (Update) 수정
- D (Delete) 삭제
*/
일장일단이 있는 것처럼 보이지만, 되도록이면 실무에서는 ArrayList를 쓰자.
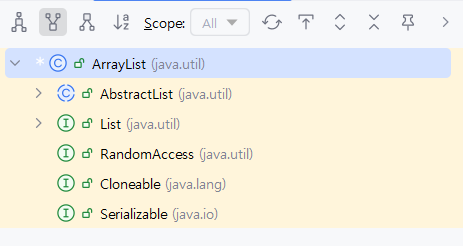
ArrayList에 Ctrl + h 해서 hierachy를 살펴보자.
super hierachy를 선택했을 때 ArrayList의 부모를 확인할 수 있다. List가 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
따라서 ArrayList를 선언할 때, 이렇게 쓸 수 있다.
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();list method 종류
list1.isEmpty();
list1.add();
list1.size();
list1.get();
list1.remove(2); //데이터 삭제: remove(index) method 사용. list1.set(2,333); //데이터 수정: set(index,element) method 사용list1. contains(); //데이터 존재여부ArrayList 출력 방법
1. for
2. Enhanced-for 사용
3. Iterator(반복자) 사용
4. forEach() 사용
//Enhanced-for문
//Enhanced for 사용 가능
for(Integer e:list1){
System.out.println(e);
}
//Iterator(반복자) 사용법
//iterator() 메소드를 사용해서 인스턴스 생성
Iterator<Integer> itr=list1.iterator();
// hasNext(): iterator가 다음 원소를 가지고 있는 지(true/false)
//next(): 현재 iterator 위치의 원소를 값을 리턴하고,
//iterator의 위치를 다음 원소의 위치로 변경
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}//forEach() + functional interface
//Java8 부터 등장
System.out.println("*".repeat(20));
System.out.println("forEach() 를 사용한 출력");
list1.forEach(System.out::println); //method reference 사용다양한 List<> initializer
System.out.println("\n다양한 List<> initializer");
// 참고: https://www.baeldung.com/java-init-list-one-line
{
List<String> list;
// List <- 배열
//immutable list 생성(원래 list는 mutable이 기본)
list =Arrays.asList(new String[]{"반숙","완숙"});
System.out.println(list);
// List <- var args
list = Arrays.asList("부먹","찍먹","막먹");
System.out.println(list);
// Stream 사용 (Java8 이상)
list = Stream.of("시후","최시후")
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
// Factory method (Java9 이상)
// ★ immutable list(unmodifiable list) 가 생성된다.
list = List.of("소금장","기름장","쌈장");
System.out.println(list);
// list.add("된장"); //UnsupportedOperationException
// Double-brace initialization
// 비추
list = new ArrayList(){{
add("최시");
add("시후");
add("최시후");
}};
System.out.println(list);
}