Sigmoid & TanH
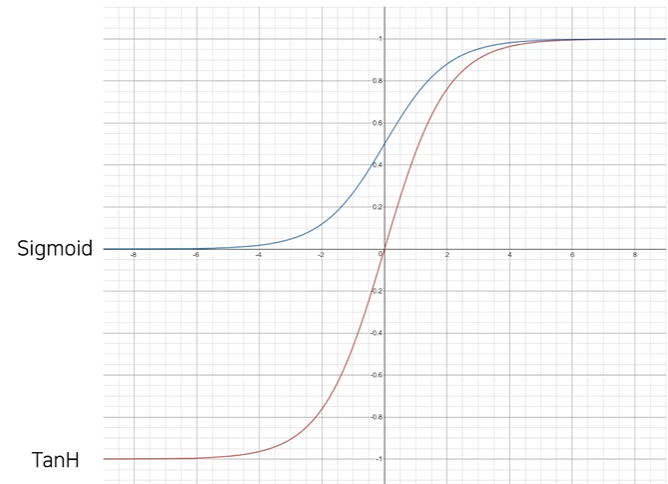
Sigmoid
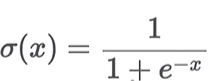
import torch import torch.nn as nn from matplotlib import pyplot as plt # 정규분포 생성 x = torch.sort(torch.randn(100) * 10)[0] # 10을 곱해서 값을 크게 만듬 act = nn.Sigmoid() print(act(x)) # 0~1사이의 값이 나옴 print(torch.sigmoid(x)) plt.plot(x.numpy(), torch.sigmoid(x).numpy()) plt.show()TanH
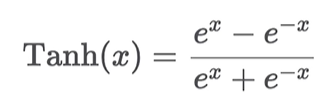
act = nn.Tanh() print(act(x)) # -1 ~ 1 사이의 값이 나옴 print(torch.tang(x)) plt.plot(x.numpy(), torch.tanh(x).numpy()) plt.show()
Logistic Regression
- 이름은 Regression이지만 사실은 이진 분류(binar classification) 문제
- Regression
- Target value : real-value vector
- Classification
- Traget value : categorical value
- Regression
- 기존의 선형회귀(Linear Regression)과 달리, Linear Layer의 결과물에 sigmoid함수를 활용하여 출력값 y'를 계산
- sigmoid의 출력 값은 0에서 1이므로, 확률 값 p(y|x)으로 생각해볼 수 있다.
- Regression의 경우에는 보통 손실함수 MSELoss를 활용하여 파라미터를 최적화
- Classification의 경우에는 BCELoss를 활용하여 파라미터를 최적화하며, Accuracy를 통해 우리는 모델의 성능을 평가할 수 있다.
- BCELoss의 경우에는 확률/통계, 정보 이론과 밀접한 관련이 있다.
structure
- Linear Regression과 비슷한 구조이나, 마지막에 Sigmoid 함수를 통과시킴
- Sigmoid 함수를 사용하기 때문에 1(True)과 0(False) 사이의 값을 반환
- 각 항목에 대하여 0.5 이상이면 True
- 각 항목에 대하여 0.5 이하이면 False
- 출력 벡터의 각 차원별로 하나의 문제
Binary Classification
- sigmoid의 출력 값은 0에서 1
- 따라서 확률 값 p(y|X)으로 생각해볼 수 있음
- 실제 정답이 1이라면, 모델은 확률 값이 최대한 커지도록 학습될 것
Binary Cross Entropy (BCE) Loss Function
- N개의 vector들이 주어졌을 때의 수식
- yi의 값에 따라 수식의 왼쪽 term과 오른쪽 term이 on/off
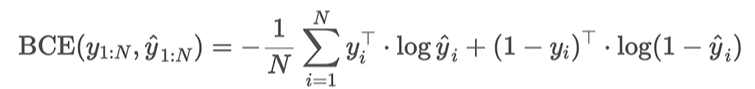
실습
EDA
import pandas as pd import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # sklearn에 있는 데이터셋 사용 from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer cancer = load_breast_cancer() # 데이터프레임으로 변경 df = pd.DataFrame(cancer.data, columns=cancer.feature_names) # targetvalue 컬럼을 추가 df['class'] = cancer.target # Pair plot with mean features sns.pairplot(df[['class'] + list(df.columns[:10])]) plt.show # Pair plot with std features sns.pairplot(df[['class'] + list(df.columns[10:20])]) plt.show # Pair plot with worst features sns.pairplot(df[['class'] + list(df.columns[20:30])]) plt.show cols = ['mean radius', 'mean texture', 'mean smoothness', 'mean compactness', ' mean concave points', 'worst radius', 'worst texture', 'worst smoothness', 'worst compactness', 'worst concave points', 'class'] for c in cols[:-1]: sns.histplot(df, x=c, hue=cols[-1], bins=50, stat='probability') plt.show()
Train Model with PyTorch
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.optim as optim data = torch.from_numpy(df[cols].values).float() # x와 y를 split x = data[:, :-1] y = data[:, -1:] # 학습을 위한 설정 n_epochs = 200000 learning_rate = 1e-2 print_interval = 10000 # 모델 정의 class MyModel(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim): self.input_dim = input_dim self.output_dim = output_dim super().__init__() self.linear = nn.Linear(input_dim, output_dim) self.act = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
# |x| = (batch_size, input_dim)
y = self.act(self.linear(x)) # (n,1)
# |y| = (batch_size, output_dim)
return y모델 선언
model = MyModel(input_dim = x.size(-1),
output_dim = y.size(-1))
crit = nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(),
lr = learning_rate)모델 실행
for i in range(n_epochs):
y_hay = model(x) # 사이즈는 y랑 동일(n,1)
loss = crit(y_hay, y) # 둘이 연산해서 BSELoss 계산optimizer.zero_grad() # gradient 초기화 loss.backward() # loss에 대해 미분 optimizer.step() if (i+1) % print_interval == 0: print("Epoch %d: loss = %.4e' % (i + 1, loss)
결과 확인
correct_cnt = (y ==(y_hat > .5)).sum() # 맞은 갯수 출력 total_cnt = float(y.size(0)) # 총사이즈 print('Accuracy: %.4f' % (correct_cnt / total_cnt)) df = pd.DataFrame(torch.cat([y, y_hat], dim=1).detach().numpy(), columns=['y', 'y_hat']) sns.histplot(df, x='y_hat', hue='y', bins=50, stat='probability') plt.show()
