int main() {
int a = 0;
int b = 3;
int c = a + b;
double d = 2.5;
return 0;
}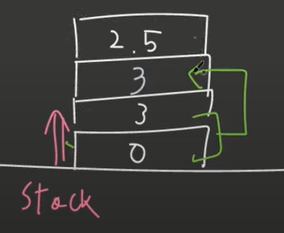
c++에서는 변수명에 어떤 숫자가 있는지 기억하는 것이 아니라
스택 메모리 공간에 top위치에서부터 몇번 째에 무슨 숫자가 있는지 기억한다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 0;
int b = 3;
int c = a + b;
int d = 2.5;
cout << (long)&a << endl;
cout << (long)&b << endl;
cout << (long)&c << endl;
cout << (long)&d << endl;
return 0;
}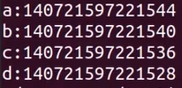
a, b, c는 4bytes
d는 8bytes식으로 type마다 allocation되는 크기가 다르다.
memory allocation 방식은 컴파일러마다 다르지만 unix기반 gcc clang 컴파일러의 경우 하나의 프로세스가 실행되면

위 그림처럼 변수가 들어올 때마다 메모리 주소가 감소하는 방향으로 들어가게 된다.