@ComponentScan
Spring이 특정 패키지 내에서 @Component, @Service, @Repository, @Controller 같은 Annotation이 붙은 클래스를 자동으로 검색하고, 이를 Bean으로 등록하는 기능이다. 개발자가 Bean을 직접 등록하지 않고도 Spring이 자동으로 관리할 객체들을 찾는다.
-
ComponentScan의 역할
- Chef가 요리할 재료를 자동으로 식료품 저장고에서 찾아오는 과정, Chef는 스스로 필요한 재료를 찾아 요리에 사용한다.
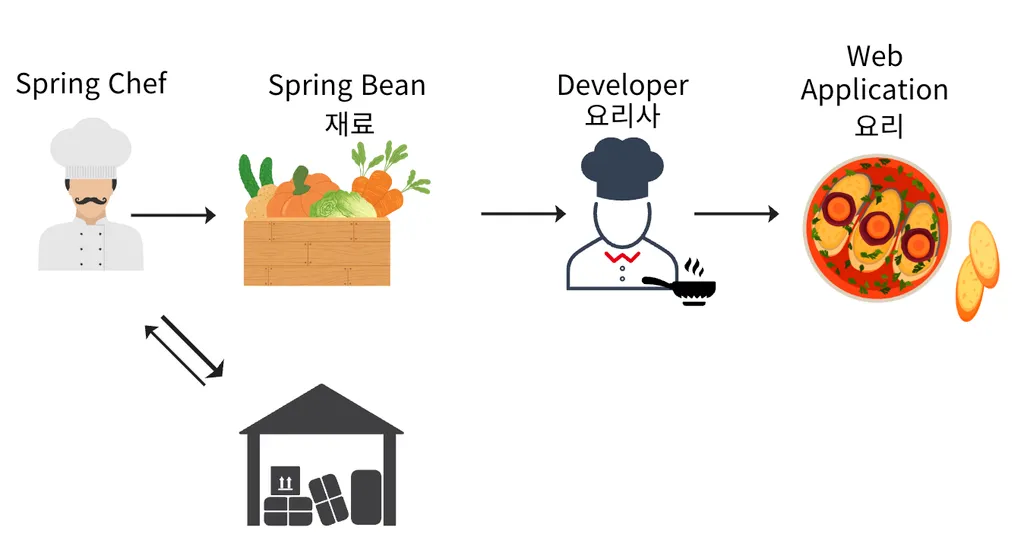
요리사(개발자)가 직접 재료(Bean)를 찾아서 가져올 필요가 없다. -
@ComponentScan
- 특정 패키지 내에
@ComponentAnnotation이 붙은 클래스를 자동으로 찾아서 Spring Bean으로 등록한다.- Annotation을 이용해 Bean을 등록할 수 있어 코드가 간결해지고 유지보수가 쉬워진다.
- 스캐닝 범위는 주로 애플리케이션의 루트(최상위) 패키지에서 시작된다.
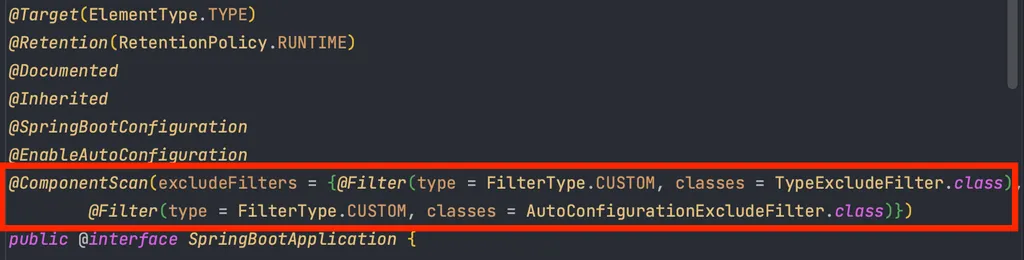
- @SpringBootApplication
- SpringBoot로 프로젝트를 생성하면
main()메서드가 있는 클래스 상단에@SpringBootApplicationAnnotation 이 존재한다.
- SpringBoot로 프로젝트를 생성하면
- 특정 패키지 내에
- @ComponentScan의 동작 순서
- Spring Application이 실행되면
@ComponentScan이 지정된 패키지를 탐색한다. - 해당 패키지에서
@Component또는 Annotation이 붙은 클래스를 찾습니다. - 찾은 클래스를 Spring 컨테이너에 빈으로 등록합니다.
- 등록된 빈은 의존성 주입(DI)과 같은 방식으로 다른 빈과 연결됩니다.
- Spring Application이 실행되면
@Configuration, @Bean
Spring Bean을 등록하는 방법에는 수동, 자동 두가지가 존재한다.
- Spring Bean 등록 방법
- Spring Bean은 Bean의 이름으로 등록된다.
- 자동 Bean 등록(@ComponentScan, @Component)
@Component이 있는 클래스의 앞글자만 소문자로 변경하여 Bean 이름으로 등록한다.
- Spring Bean은 Bean의 이름으로 등록된다.
// myService 라는 이름의 Spring Bean
@Component
public class MyService {
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Spring Bean 으로 동작");
}
}@ComponentScan을 통해@Component로 설정된 클래스를 찾는다.
- 수동 Bean 등록(@Configuration, @Bean)
@Configuration이 있는 클래스를 Bean으로 등록하고 해당 클래스를 파싱해서@Bean이 있는 메서드를 찾아 Bean을 생성한다. 이때 해당 메서드의 이름으로 Bean의 이름이 설정된다.
// 인터페이스
public interface TestService {
void doSomething();
}
// 인터페이스 구현체
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@Override
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Test Service 메서드 호출");
}
}
// 수동으로 빈 등록
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
// TestService 타입의 Spring Bean 등록
@Bean
public TestService testService() {
// TestServiceImpl을 Bean으로 등록
return new TestServiceImpl();
}
}
// Spring Bean으로 등록이 되었는지 확인
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Spring ApplicationContext 생성 및 설정 클래스(AppConfig) 등록
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// 등록된 TestService 빈 가져오기
TestService service = context.getBean(TestService.class);
// 빈 메서드 호출
service.doSomething();
}
}수동으로 Bean을 등록할 때는 항상 @Configuration과 함께 사용해야 Bean이 싱글톤으로 관리된다. CGLIB 라이브러리와 연관이 있다.
Bean 충돌
Bean 등록 방법에는 수동, 자동 두가지가 존재하고 Bean은 각각의 이름으로 생성된다. 이때 이름이 같은 Bean이 설정되고자 한다면 충돌이 발생한다.
- 같은 이름의 Bean 등록
- 자동 Bean 등록 VS 자동 Bean 등록
public interface ConflictService {
void test();
}
// Bean의 이름을 service로 설정
@Component("service")
public class ConflictServiceV1 implements ConflictService {
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("Conflict V1");
}
}
// Bean의 이름을 service로 설정
@Component("service")
public class ConflictServiceV2 implements ConflictService {
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("Conflict V2");
}
}
// componentScan의 범위를 conflict 패키지 하위로 설정
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example.springconcept.conflict")
public class ConflictApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConflictApp.class);
// Service 빈을 가져와서 실행
ConflictService service = context.getBean(ConflictService.class);
service.test();
}
}ConflictingBeanDefinitionException 발생
- 수동 Bean 등록 VS 자동 Bean 등록
// conflictService 이름으로 Bean 생성
@Component
public class ConflictService implements MyService {
@Override
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("ConflictService 메서드 호출");
}
}
public class ConflictServiceV2 implements MyService {
@Override
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("ConflictServiceV2 메서드 호출");
}
}
// 수동으로 Bean 등록
@Configuration
public class ConflictAppConfig {
// conflictService 이름으로 Bean 생성
@Bean(name = "conflictService")
MyService myService() {
return new ConflictServiceV2();
}
}
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example.springconcept.conflict2")
public class ConflictApp2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConflictApp2.class);
// Service 빈을 가져와서 실행
MyService service = context.getBean(MyService.class);
service.doSomething();
}
}
-
수동 Bean 등록이 자동 Bean 등록을 오버라이딩해서 우선권을 가진다.
-
의도한 결과라면 다행이지만, 아닌 경우(실수)가 대부분이다. → 버그 발생
-
Spring Boot에서는 수동과 자동 Bean등록의 충돌이 발생하면 오류가 발생한다.
-
설정 변경(application.properties)
// 수동, 자동 Bean을 동시에 등록할 때 이름이 같으면 수동 Bean이 오버라이딩
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
// 기본값
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=false