@RequestParam
URL에서 파라미터 값과 이름을 함께 전달하는 방식으로 주로 HTTP 통신 Method 중 GET 방식의 통신을 할 때 많이 사용한다. @Requestparam을 사용하면 요청 파라미터 값에 아주 쉽고 간편하게 접근(Parameter Binding)할 수 있다.
?뒤에 오는 URL을 Query String, Query Parameter, Request Param이라 한다.
예시코드
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestParamControllerV2 {
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/v1/request-param")
public String requestParamV1 (
@RequestParam("name") String userName,
@RequestParam("age") int userAge
) {
// logic
log.info("name={}", userName);
log.info("age={}", userAge);
return "success";
}
}-
@Controller + @ResponseBody- View를 찾는 것이 아니라 ResponseBody에 응답을 작성한다(=@RestController)
-
@RequestParam- 파라미터 이름으로 바인딩한다.
-
@RequestParam(”속성값”)- 속성값이 파라미터 이름으로 매핑된다.
-
postman
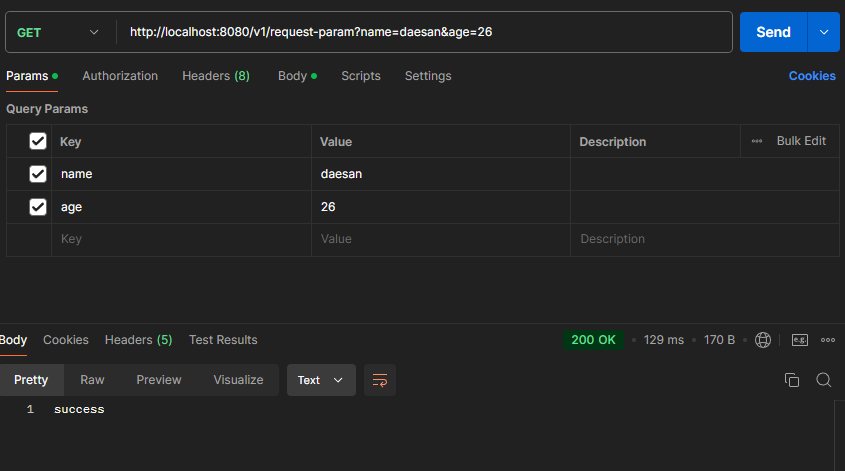
-
출력결과
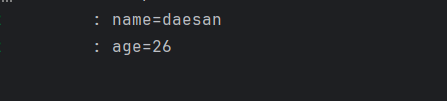
-
“속성값”과 변수명이 같으면 생략이 가능하다.
ex) @RequestParam("name") String name
// GET http://localhost:8080/v2/request-param?name=daesan&age=26
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/v2/request-param")
public String requestParamV2 (
@RequestParam String name,
@RequestParam int age
) {
// logic
log.info("name={}", name);
log.info("age={}", age);
return "success";
}-
Postman
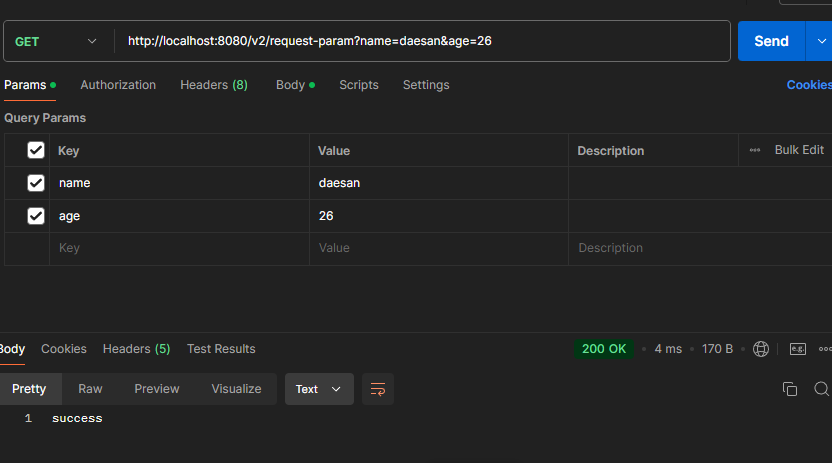
-
출력결과
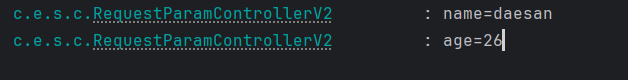
- @RequestParam 사용법
1. 어노테이션, 속성값 모두 생략
- @RequestParam은 생략이 가능하다.
// GET http://localhost:8080/v3/request-param?name=daesan&age=26
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/v3/request-param")
public String requestParamV3 (
String name,
int age
) {
// logic
log.info("name={}", name);
log.info("age={}", age);
return "success";
}- Postman
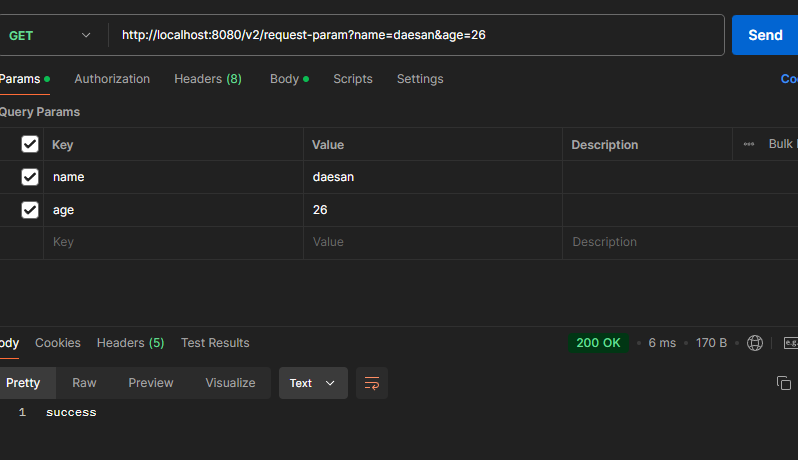
- 출력결과
위의 방식은 팀의 협의가 있지않은 경우 다른개발자들에게 혼동을 줄 수 있으니 최소 @RequestParam String name 속성 값 생략 형태를 사용
2. required 속성 설정
- 파라미터의 필수 값을 설정한다.
- API 스펙을 규정할 때 사용한다.
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/v4/request-param")
public String requestParam (
@RequestParam(required = true) String name, // 필수
@RequestParam(required = false) int age // 필수가 아님
) {
// logic
log.info("name={}", name);
log.info("age={}", age);
return "success";
}- @RequestParam을 사용하면 기본 Default값은 True이다.
- True로 설정된 파라미터 값이 요청에 존재하지 않으면 400 BadRequest(클라이언트 측 에러)
- Exception이 발생하지 않는 경우
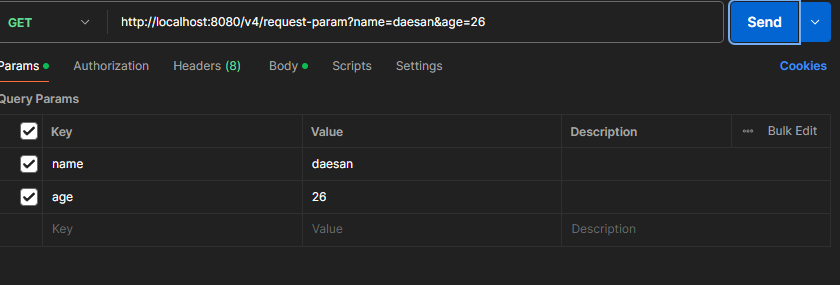
- Exception이 발생하는 경우
ex) http://localhost:8080/v4/request-param?age=26
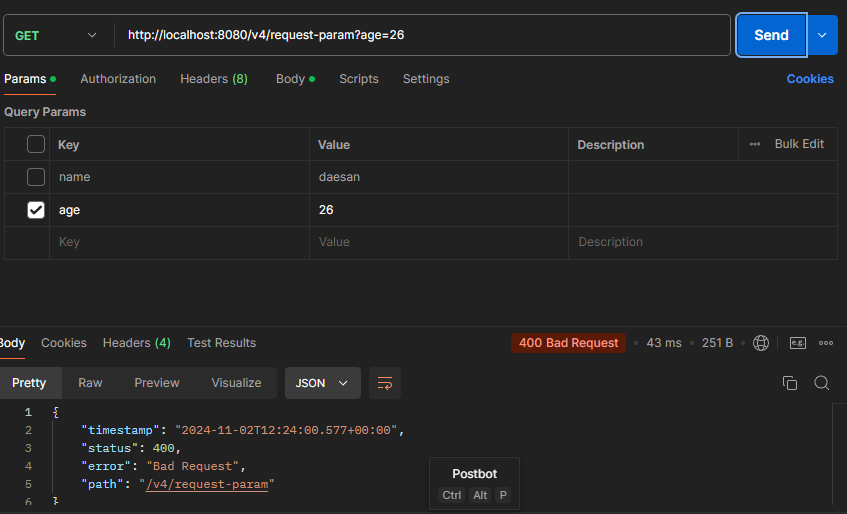
ex) http://localhost:8080/v4/request-param
required = false 설정이 되어있으면 해당 파라미터는 없어도 된다.
주의! http://localhost:8080/v4/request-param?name=daesan 요청한다면?
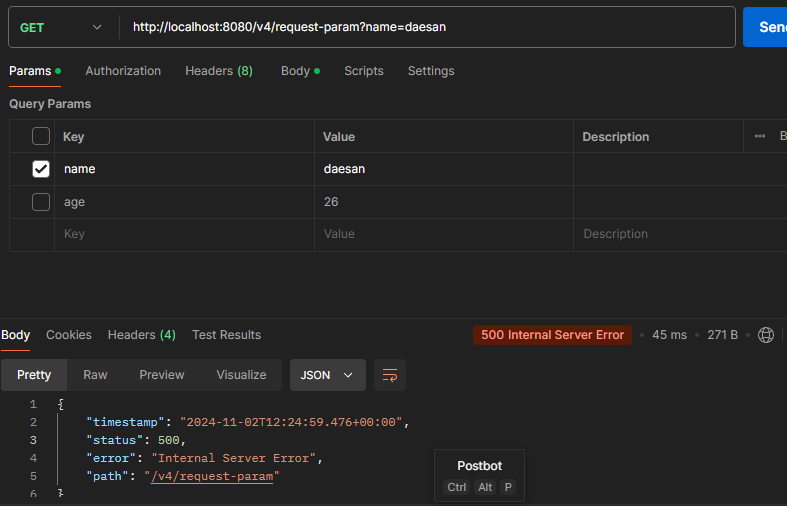
-500에러가 발생한다.
-int Type 에는 null을 넣을 수 없기때문(0이라도 들어가있어야함)
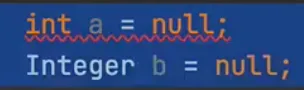
- 따라서 보통 null을 허용하는 Integer로 사용하거나 default 옵션을 사용한다.
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/v4/request-param")
public String requestParam (
@RequestParam(required = true) String name, // 필수
@RequestParam(required = false) Integer age
) {
// logic
log.info("name={}", name);
log.info("age={}", age);
return "success";
}- postman
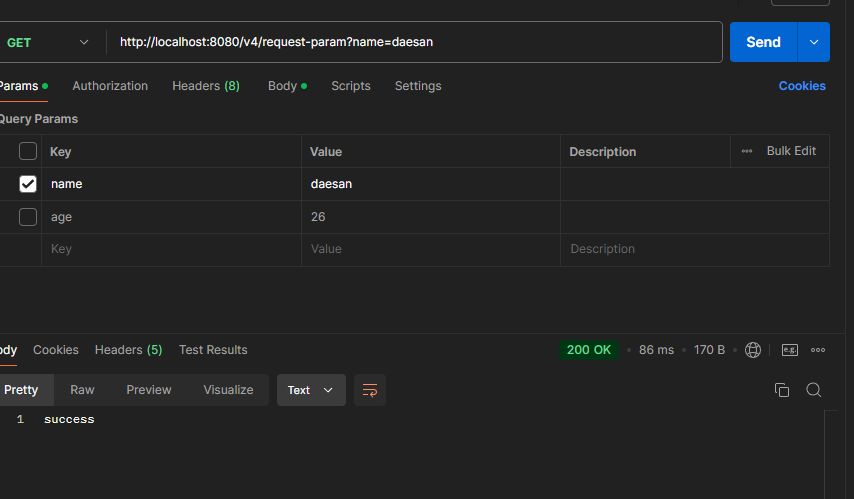
- 출력결과

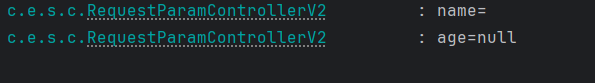
파라미터 Key값만 있고 Value가 없는 경우 http://localhost:8080/request-param?name=
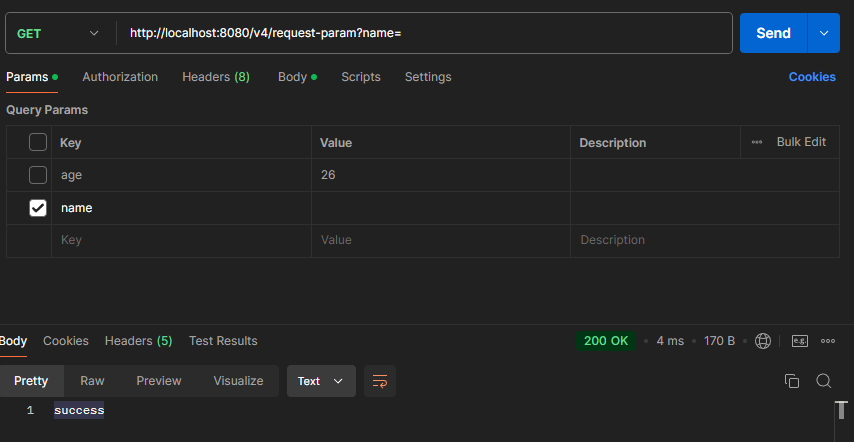
- null과 빈 문자열 “”은 다르다!
- 위 형태는 빈 문자열 “” 로 인식한다, True지만 통과가 되어버린다. 주의해야 한다.
- 출력결과
3. default 속성 적용
- 파라미터의 기본 값을 설정한다.
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/v5/request-param")
public String requestParam (
@RequestParam(required = true, defaultValue = "daesan") String name,
@RequestParam(required = false, defaultValue = "1") int age
) {
// logic
log.info("name={}", name);
log.info("age={}", age);
return "success"
}
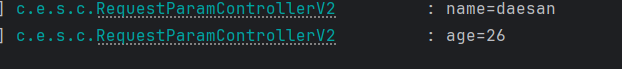
name Parameter 의 값이 없으면 기본적으로 “daesan”으로 설정한다
-postman
-출력결과
default가 daesan으로 설정되어있어 값을 안 넣어도 자동으로 적용되어있는 모습
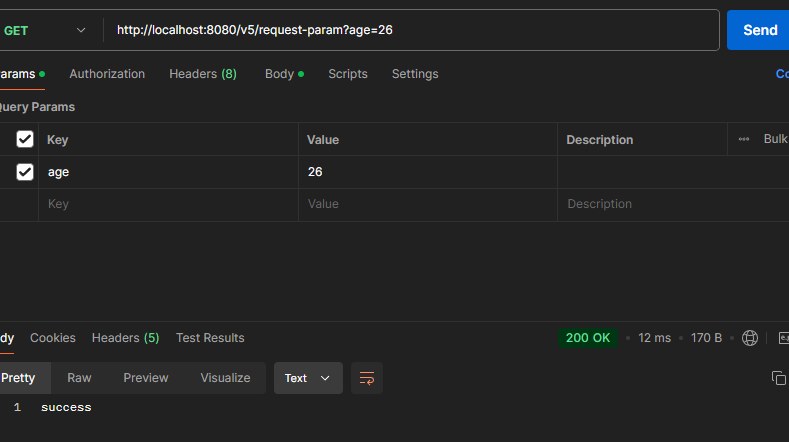
ex) http://localhost:8080/v5/request-param
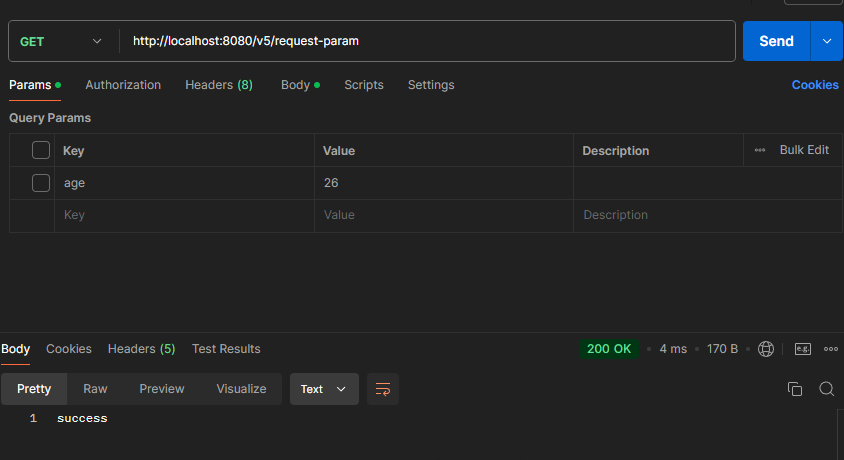

주의! defaultValue 속성을 설정하게 되면 “” 빈 문자열의 경우에도 기본 값이 설정된다.
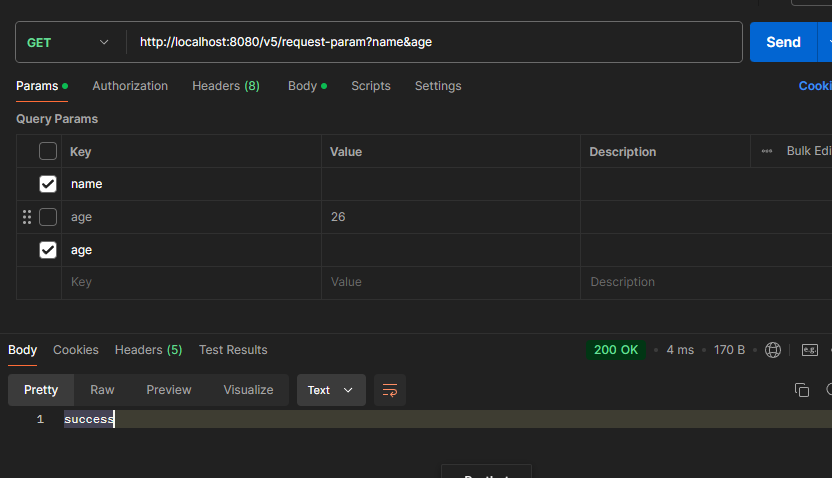
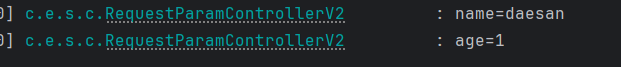
공백을 입력했지만 default 값이 들어온 모습
4. Map사용
Parameter를 Map형태로 조회가 가능하다.
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/v6/request-param")
public String requestParamV6(
@RequestParam Map<String, String> map
) {
// logic
log.info("name={}", map.get("name"));
log.info("age={}", map.get("age"));
return "success";
}- Map 형태(key=value)로 조회가 가능하다
ex) http://localhost:8080/v6/request-param?name=daesan&age=26
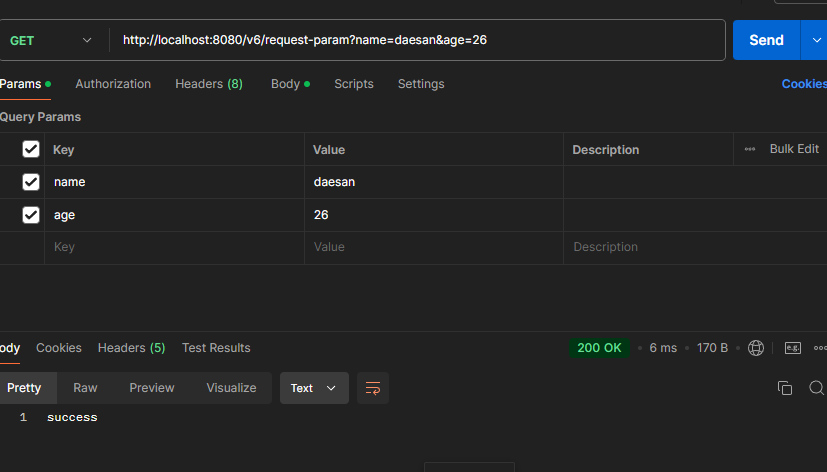
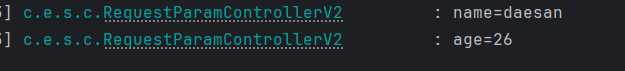
- ultiValueMap 형태(key=[value1, value2])로 조회가 가능하다.
//하나의 키에 여러개의 값이 들어있는 형태
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/v6/request-param")
public String requestParamV6(
@RequestParam MultiValueMap<String, String> map
) {
// logic
log.info("name={}", map.get("name"));
log.info("age={}", map.get("age"));
return "success";
}ex)http://localhost:8080/v6/request-param?age=26&name=daesan&name=naruto&name=sasuke
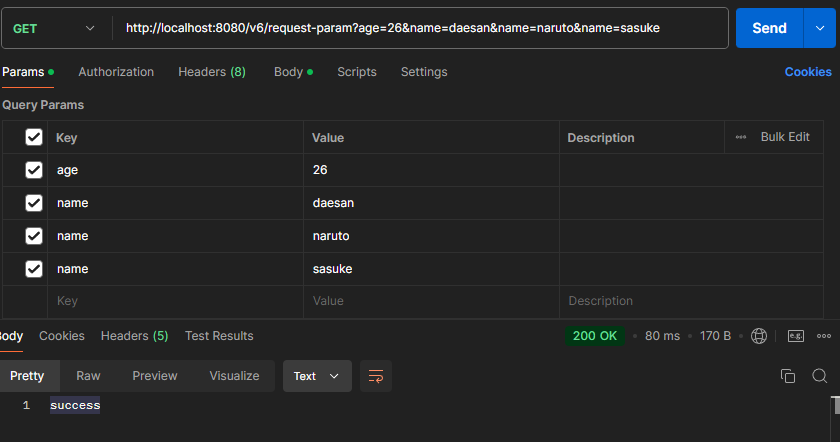
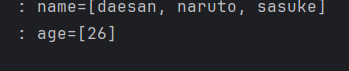
파라미터 Map의 Value가 1개인 경우에는 Map, 여러 개인 경우 MultiValueMap을 사용한다. 하지만 대부분의 파라미터 값은 한 개만 존재한다.
@ModelAttribute
요청 파라미터를 받아 필요한 Object로 바인딩 해준다. 주로 HTML 폼에서 전송된 데이터를 바인딩하고 HTTP Method POST인 경우 사용된다.
1.기존 코드
@Data는 @Getter, @Setter, @ToString, @EqualsAndHashCode, @RequiredArgsConstructer를 자동으로 설정해주는 역할을 한다. 테스트 용도로만 사용하고 실무에서는 잘 사용하지 않는다.
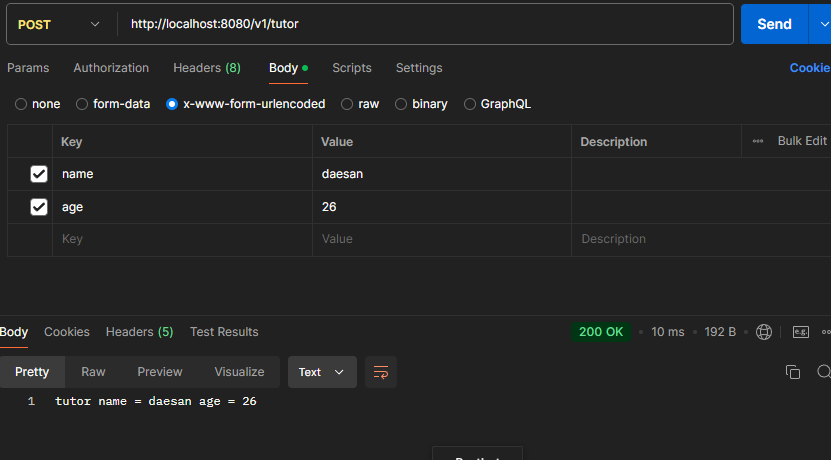
ex) http://localhost:8080/v1/tutor + x-www-form-urlencoded
@Data
public class Tutor {
private String name;
private int age;
}
@Controller
public class ModelAttributeController {
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/v1/tutor")
public String requestParamV1(
@RequestParam String name,
@RequestParam int age
) {
Tutor tutor = new Tutor();
tutor.setName(name);
tutor.setAge(age);
return "tutor name = " + name + " age = " + age;
}
}- @RequestParam 의 Mapping을 사용하게 되면 위와 같은 객체를 생성하는 코드가 포함된다.
@ModelAttribute는 해당 과정을 자동화 한다.
- Postman
POST /v1/tutor
content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
name=daesan&age=26
2.@ModelAttribute 적용
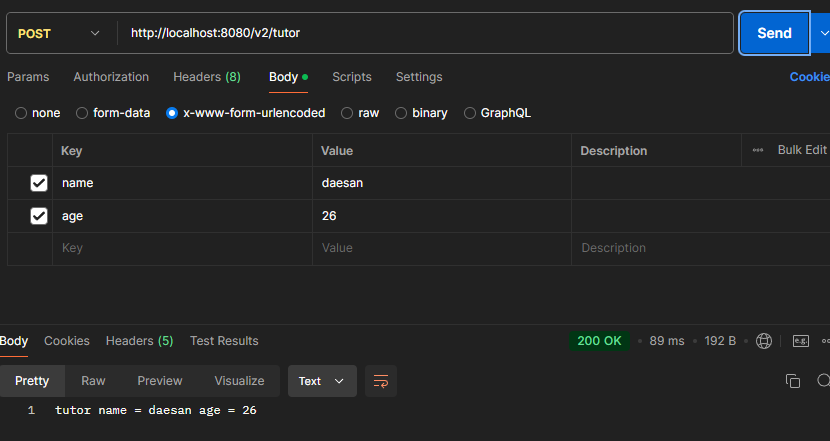
ex) http://localhost:8080/v2/tutor+ x-www-form-urlencoded
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/v2/tutor")
public String modelAttributeV2(
@ModelAttribute Tutor tutor
) {
String name = tutor.getName();
int age = tutor.getAge();
return "tutor name = " + name + " age = " + age;
}- Postman
POST /v2/tutor
content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
name=daesan&age=26
- @ModelAttirubte 동작 순서
- 파라미터에 @ModelAttribute가 있으면 파라미터인 Tutor 객체를 생성한다.
- 요청 파라미터 이름으로 객체 필드의 Setter를 호출해서 바인딩한다.
a. 파라미터 이름이name이면setName(value);메서드를 호출한다.
b. 파라미터 이름과 필드 이름이 반드시 같아야 한다!
- @Data의 Setter가 없다면?
@Getter
public class Tutor {
private String name;
private int age;
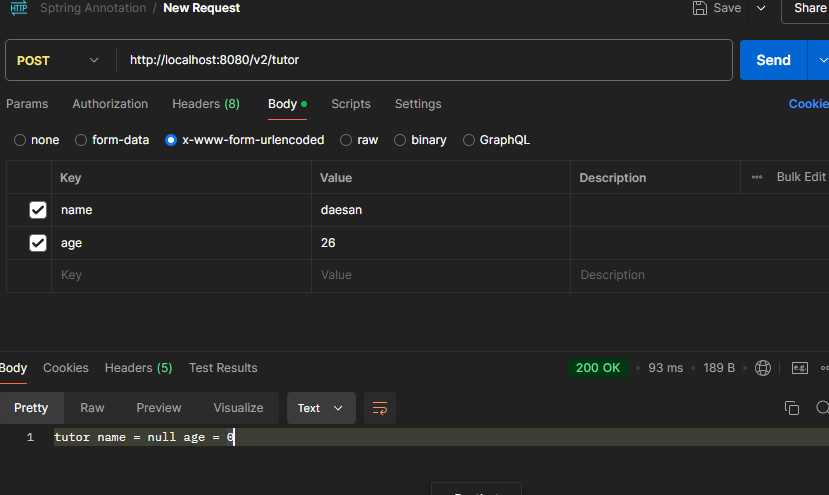
}
-
객체 필드에 값이 set 되지 않는 모습
-
파라미터의 타입이 다른 경우
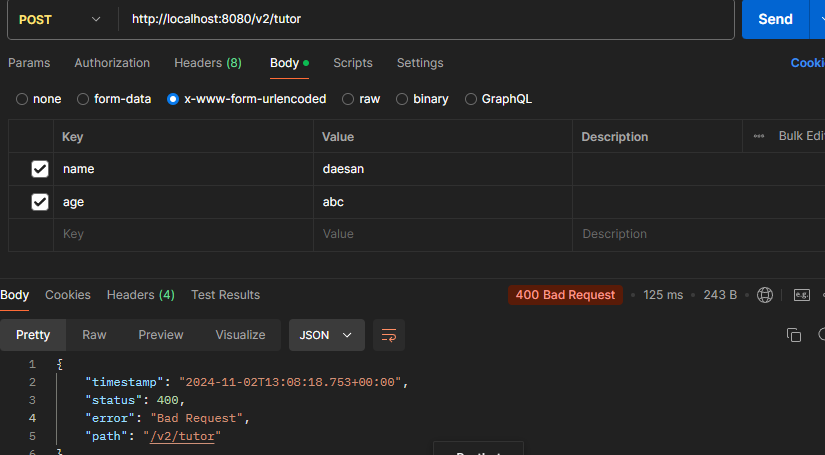
- 만약 요청 파라미터age에int가 아닌String이 전달된다면?
ex) http://localhost:8080/v2/tutor+ x-www-form-urlencoded
POST /v2/tutor
content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
name=daesan&age=abc
2.@ModelAttribute 생략
- @ModelAttribute와 @RequestParam은 모두 생략이 가능하다.
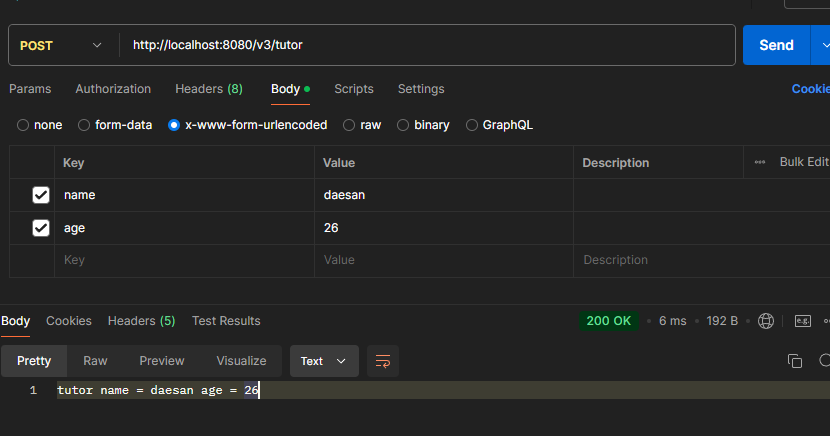
ex) http://localhost:8080/v3/tutor+ x-www-form-urlencoded
POST /v3/tutor
content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
name=daesan&age=26
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/v3/tutor")
public String modelAttributeV3(Tutor tutor) {
String name = tutor.getName();
int age = tutor.getAge();
return "tutor name = " + name + " age = " + age;
}
나머지 경우들(객체)은 모두 @ModelAttribute 와 Mapping한다. V3
