Spring Container
Spring으로 구성된 애플리케이션에서 객체(Bean)를 생성, 관리, 소멸하는 역할을 담당한다. 애플리케이션 시작 시, 설정 파일이나 Annotation을 읽어 Bean을 생성하고 주입하는 모든 과정을 컨트롤한다.
- java의 객체 생성
- 사용하는 클래스에서 직접 생성한다.
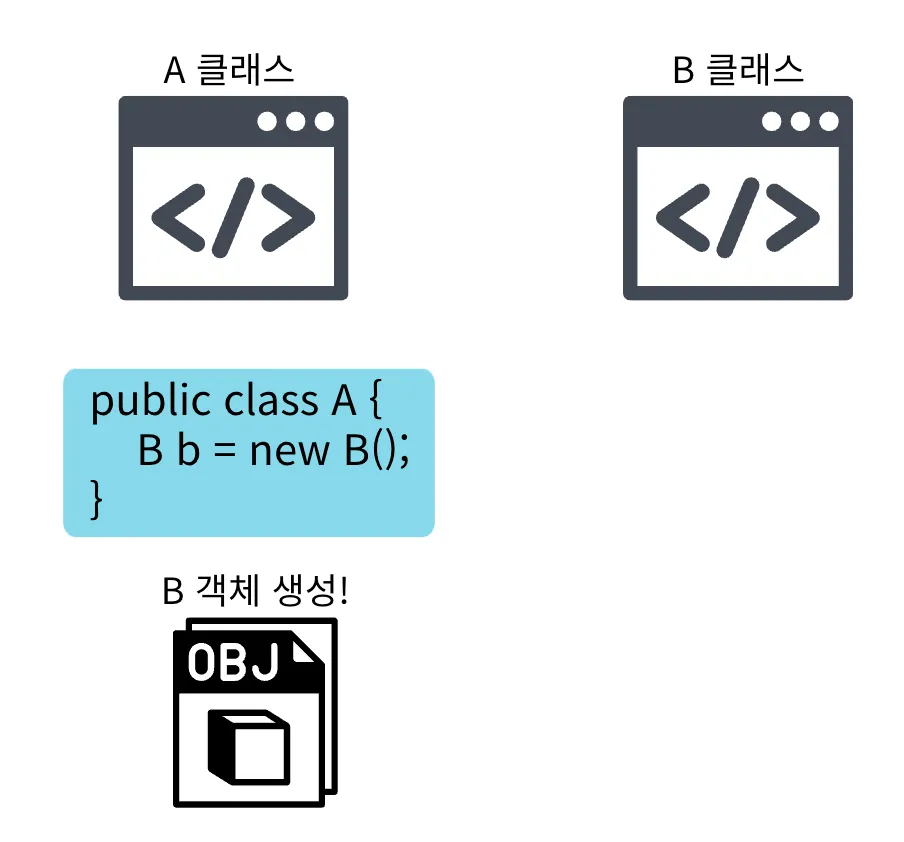
- 사용하는 클래스에서 직접 생성한다.
- Spring Container의 역할
- 객체(Bean)를 생성 및 관리하고 의존성을 주입하는 역할을 담당한다.
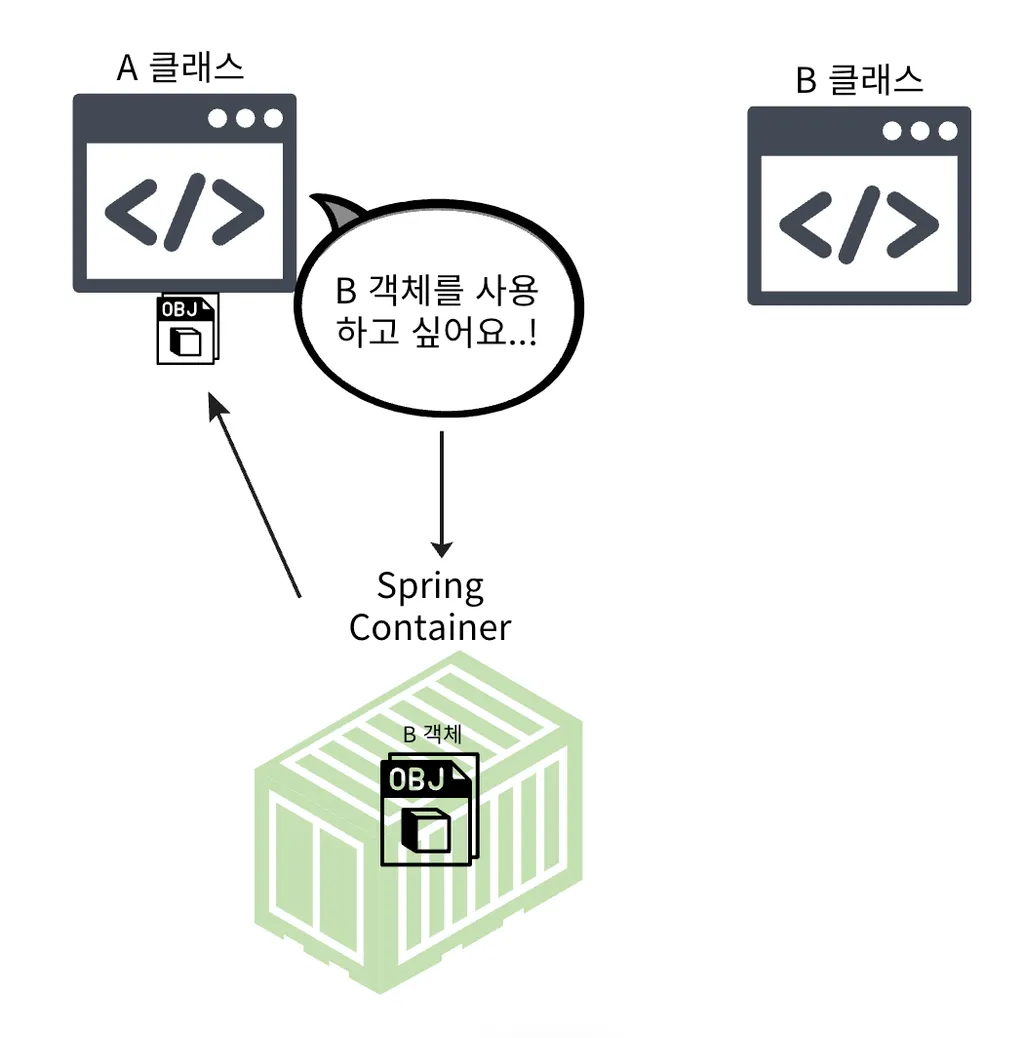
- 객체(Bean)를 생성 및 관리하고 의존성을 주입하는 역할을 담당한다.
- 주방의 Chef
- 재료 선택, 요리, 완성까지 모든 것을 관리한다.

- 재료 선택, 요리, 완성까지 모든 것을 관리한다.
- 객체를 직접 생성하는 경우, 객체 간의 의존성 및 결합도가 높아진다.
- OCP, DIP 위반
- Spring Container를 사용하면 인터페이스에만 의존하는 설계가 가능해진다.
- OCP, DIP 준수
- Spring Container의 종류
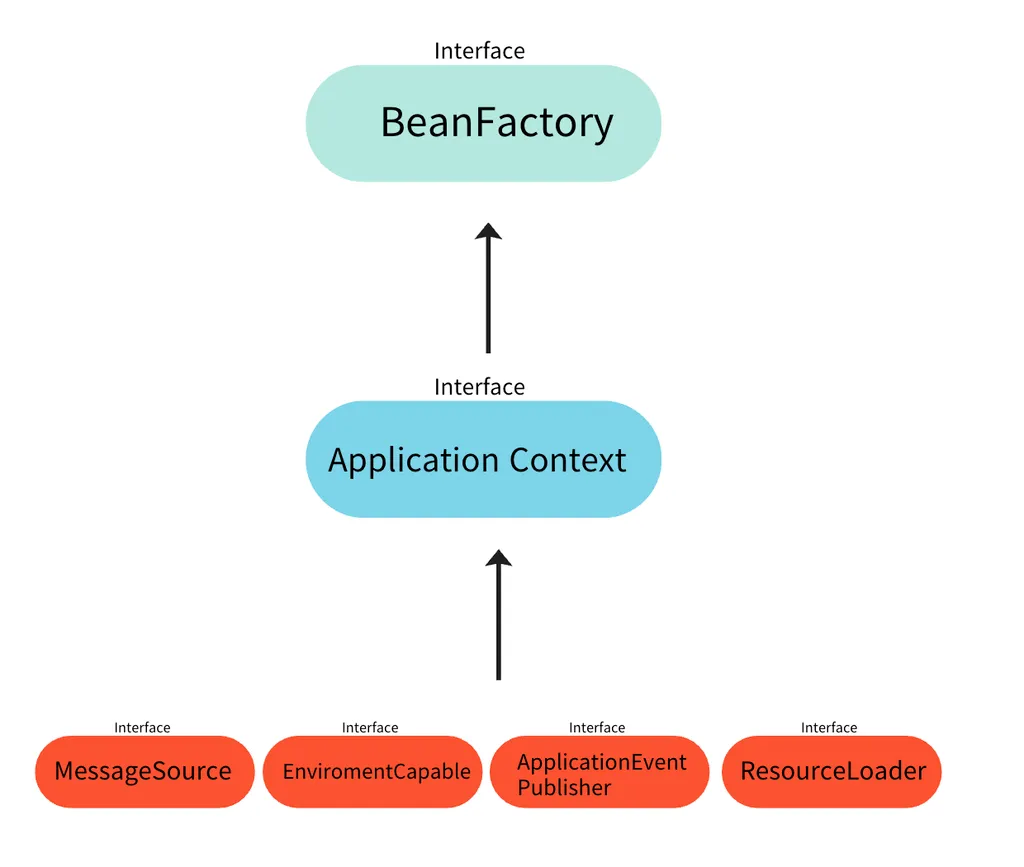
- BeanFactory
- Spring Container의 최상위 인터페이스
- Spring Bean을 관리하고 조회한다.
- ApplicationContext
- BeanFactory의 확장된 형태(implements)
- Application 개발에 필요한 다양한 기능을 추가적으로 제공한다.
-
국제화, 환경변수 분리, 이벤트, 리소스 조회
일반적으로 ApplicationContext를 사용하기 때문에 ApplicationContext를 Spring Container라 표현한다.
-
Spring Bean
Spring 컨테이너가 관리하는 객체를 의미한다. 자바 객체 자체는 특별하지 않지만, Spring이 이 객체를 관리하는 순간부터 Bean이 된다. Spring은 Bean을 생성, 초기화, 의존성 주입 등을 통해 관리한다.
-
Spring Bean이란?
- Spring Container가 생성하고 관리하는 Java 객체
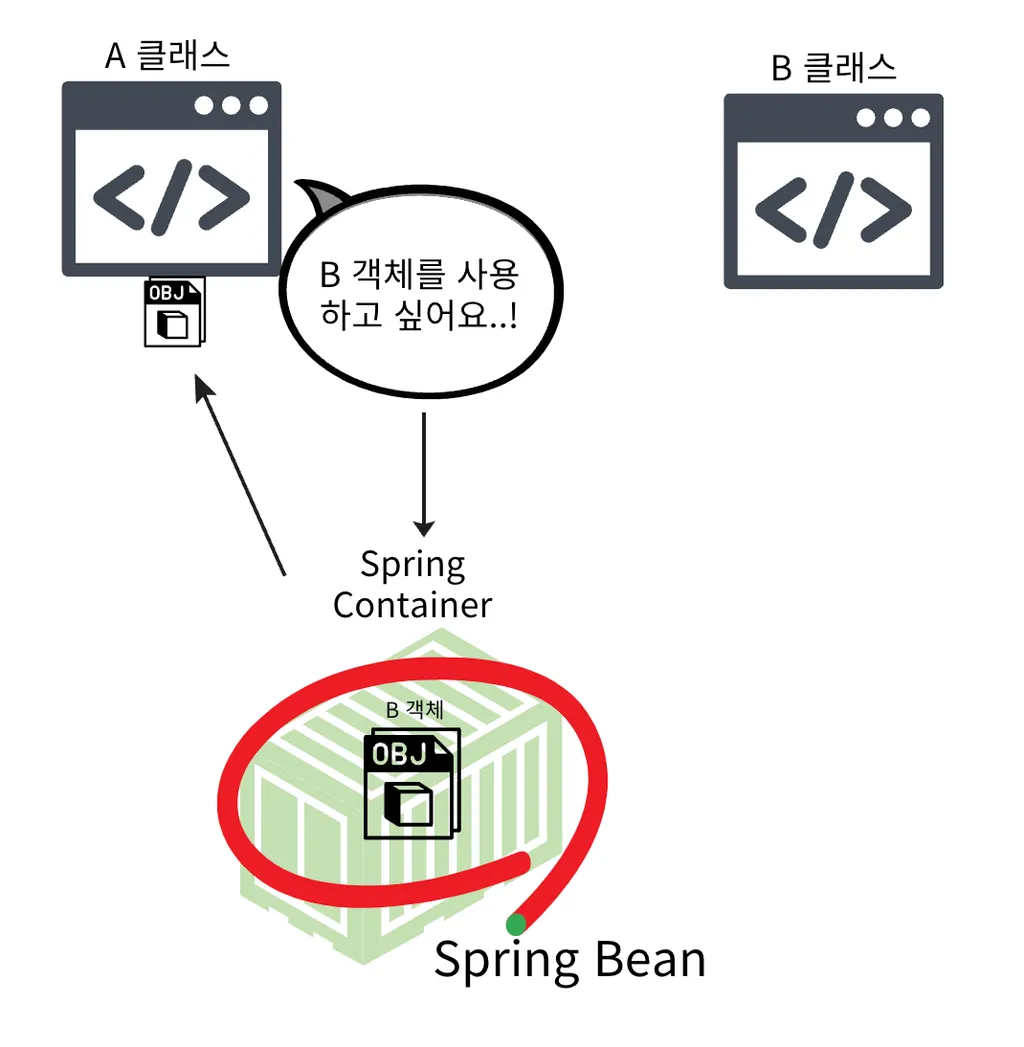
- Spring Container가 생성하고 관리하는 Java 객체
-
Bean은 new 키워드 대신 사용하는 것이다.
-
Spring Container가 제어한다.
-
Spring Bean의 역할
- Chef인 Spring Container가 요리할 음식에 사용될 재료(Bean)
- 요리(Application)의 핵심을 이루는 재료(Bean)

- 요리(Application)의 핵심을 이루는 재료(Bean)
- Chef인 Spring Container가 요리할 음식에 사용될 재료(Bean)
-
Spring Bean의 특징
1. Spring 컨테이너에 의해 생성되고 관리된다.
2. 기본적으로 Singleton으로 설정된다.
3. 의존성 주입(DI)을 통해 다른 객체들과 의존 관계를 맺을 수 있다.
4. 생성, 초기화, 사용, 소멸의 생명주기를 가진다.Bean 등록 방법XML, Java Annotation, Java 설정파일 등을 통해 Bean으로 등록할 수 있다.
XML
<!-- myBean이라는 이름의 Bean 정의 --> <bean id="myBean" class="com.example.MyBean" />
public class MyApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Spring 컨테이너에서 Bean을 가져옴
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
MyService myService = context.getBean("myService", MyService.class);
myService.doSomething();
}
}- Annotation
@ComponentScan
// 이 클래스를 Bean으로 등록
// @Controller, @Service, @Repository
@Component
public class MyService {
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Spring Bean 으로 동작");
}
}@Component
public class MyApp {
private final MyService myService;
@Autowired // 의존성 자동 주입
public MyApp(MyService myService) {
this.myService = myService;
}
public void run() {
myService.doSomething();
}
}// com.example 패키지를 스캔하여 Bean 등록
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example")
public class AppConfig {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
MyApp app = context.getBean(MyApp.class);
app.run();
}
}Java 설정파일
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public MyService myService() {
return new MyService();
}
}public class MyApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Spring 컨테이너에서 Bean을 가져옴
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
MyService myService = context.getBean(MyService.class);
myService.doSomething();
}
}