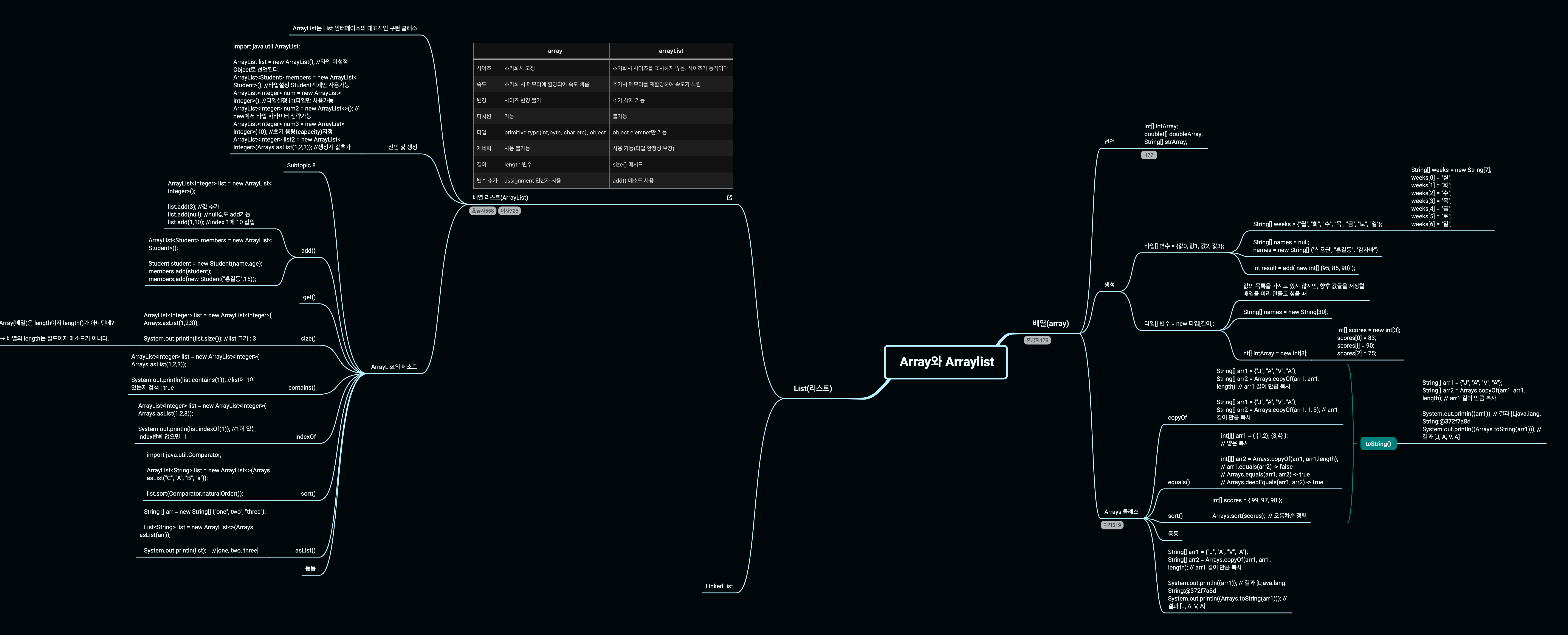
Array와 Arraylist 차이가 잘 이해가 되지 않아 정리
서울에서 김서방 찾기
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/12919
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
String[] a = {"Jane", "Kim"};
System.out.println((solution.solution(a)));
}
}
class Solution {
public String solution(String[] seoul) {
String answer = "";
for (int i = 0; i < seoul.length; i++) {
if ("Kim".matches(seoul[i])){
answer = "김서방은 " + i + "에 있다";
}
}
return answer;
}
}
//seoul은 배열이다. 그 배열의 i번째를 돌려 문자열 kim을 찾는다.
//kim이 있으면 그 위치를 출력한다.속도가 느려서 다른 사람이 푼 정답을 보았다. 그 답은 아래에.
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public String solution(String[] seoul) {
//x에 김서방의 위치를 저장하세요.
int x = Arrays.asList(seoul).indexOf("Kim");
return "김서방은 "+ x + "에 있다";
}
}for문 없이 상당히 깔끔하다.
수박수박수박수박수박수?
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/12922
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
String[] a = {"Jane", "Kim"};
System.out.println((solution.solution(3)));
}
}
class Solution {
public String solution(int n) {
String answer = "";
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0){
answer += "박";
} else {
answer += "수";
}
}
return answer;
}
}
// 짱구 돌리다가 영 모르겠어서 답 대충 훑어보고 힌트얻음.
// 맨 처음에는 array("수", "박")해서 반복하는 거를 하려했다가 어떻게 하는지 모르겠어서 포기함완주하지 못한 선수
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/42576
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
String[] a = {"leo", "kiki", "eden"};
String[] b = {"eden", "kiki"};
System.out.println((solution.solution(a, b)));
}
}
class Solution {
public String solution(String[] participant, String[] completion) {
ArrayList<String> List = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> CompletionList = new ArrayList<>();
List.addAll(Arrays.asList(participant));
List.addAll(Arrays.asList(completion));
String[] NewList = new String[List.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < List.size(); i++) {
NewList[i] = List.get(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < NewList.length; i++) {
if (NewList[i].contains())
}
return answer;
}
}
// 생각보다 간단할 거 같다.
// 두 배열을 합쳐서 2가 아닌 것을 찾으면 될 거 같은데?import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public String solution(String[] participant, String[] completion) {
Arrays.sort(participant);
Arrays.sort(completion);
int i;
for ( i=0; i<completion.length; i++){
if (!participant[i].equals(completion[i])){
return participant[i];
}
}
return participant[i];
}
}여러가지 코드들이 있지만 이 답이 가장 이쁘다. 다만 효율성은 아래의 코드가 좋다.
import java.util.HashMap;
class Solution {
public String solution(String[] participant, String[] completion) {
String answer = "";
HashMap<String, Integer> hm = new HashMap<>();
for (String player : participant) hm.put(player, hm.getOrDefault(player, 0) + 1);
for (String player : completion) hm.put(player, hm.get(player) - 1);
for (String key : hm.keySet()) {
if (hm.get(key) != 0) {
answer = key;
}
}
return answer;
}
}이상한 문자 만들기
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/12930
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.solution("try this"));
}
}
class Solution {
public String solution(String s) {
String answer = "";
String[] str = s.split("");
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
if (str[i].equals(" ")){
count = 0;
}
else if (count % 2 == 0){
str[i] = str[i].toUpperCase();
count++;
}
else if ( count % 2 == 1){
str[i] = str[i].toLowerCase();
count++;
}
answer += str[i];
}
return answer;
}
}
// 문자열을 하나하나 분리.
// for을 charAt(i)을 이용
// count =0 변수 생성
// 공백이 나오면 count = 0
// % 2 == 0 이면 toUpper 하고 count + 1
// 아니면 to lower 하고 count + 1
자연수 뒤집어 배열로 만들기
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/12932
// 자연수 n을 받는다.
// 자연수 n에 맞는 길이의 배열a를 생성한다.
// arraylist b를 생성한다.
// 배열 a에 n[i]를 하나씩 넣는다.
// 배열 a를 b로 옮긴다. 단, a[i]를 큰 수에서 작은 수로 옮긴다.import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(solution.solution(12345)));
}
}
class Solution {
public int[] solution(long n) {
String a = "" + n;
// input값을 문자열로 바꿔줌
int[] answer = new int[a.length()];
int count = 0;
while (n > 0) {
// n이 12이면 12%10은 = 2. answer[0]은 2.
answer[count] = (int) (n % 10);
// 12를 10으로 나누면 1.2. 타입이 long이므로 1.
n = n / 10;
count++;
}
return answer;
}
}제일 작은 수 제거하기
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/12935
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] arr) {
int length = arr.length;
ArrayList<Integer> answer = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int[] temp = arr.clone();
Arrays.sort(temp);
int min = temp[0];
//
// if(length == 0) {
// answer.add(-1);
// }
ArrayList<Integer> a = new ArrayList<Integer>(arr.length - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (min != arr[i]){
answer.add(arr[i]);
}
}
int[] result = new int[a.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) {
result[i] = a.get(i);
}
return result;
}
}
// 배열을 받는다
// 배열이 한 개 이하면 -1을 리턴한다
// 길이가 arr-1인 배열을 받는다. 4개를 받으면 3개를, 5개를 받으면 4개를 출력해야 하기 때문이다.
// 배열을 소팅한다. 가장 작은 수가 맨 앞에 있을 것이다.
// 맨 작은 수만 같지 않은 수를 새로운 배열에 추가.
// for문을 돈다. arr[0]이 자릿수 더하기
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/12931
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.solution("123"));
}
}
class Solution {
public String solution(String s) {
int answer = 0;
int int_val = Integer.parseInt(s);
System.out.println(int_val);
int[] int_array = new int[int_val];
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(int_array));
return String.valueOf(answer);
}
}
// s를 받는다.
// s를 하나하나 분해한다.
// int array로 바꾼다.
// for로 해서 하나 하나 더한다.

class Solution {
public int solution(int s) {
int answer = 0;
String n = Integer.toString(s); //int n을 String으로 변환
for(int i=0; i<n.length(); i++){
answer += Integer.parseInt(n.substring(i, i+1));
}
return answer;
}
}이 것이 정답이다. 다만 문자열을 변형하는 것 보다, 나머지 연산자를 사용하여 푸는 습관을 가지자. 나머지 연산자와 친해질 필요가 있다.
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int solution(int n) {
int answer = 0;
while(n > 0) {
answer += n % 10;
n /= 10;
}
return answer;
}
}