🔴 목차
- Lifelong Learning
- Supervised Lifelong Learning (SLL) vs. Unsupervised Lifelong Learning
- Deep Bayesian Unsupervised Lifelong Learning (DBULL) algorithm
- Introduction
🟠 Lifelong Learning
- Lifelong Learning (LL) refers to the ability to continually learn and solve new problems with incremental available information over time while retaining previous knowledge.
- 이전 지식을 유지하면서 시간이 지남에 따라 점진적으로 사용 가능한 정보를 사용하여 지속적으로 학습하고 새로운 문제를 해결하는 능력을 의미함
🟠 Supervised Lifelong Learning (SLL) vs. Unsupervised Lifelong Learning (ULL)
- 즉, 레이블이 지정된 데이터 스트림을 사용하여 지도 평생 학습
Supervised Lifelong Learning (SLL)에 많은 관심을 가짐SLL는ULL의 레이블이 지정되지 않은 문제를 해결함
🟠 Deep Bayesian Unsupervised Lifelong Learning (DBULL) algorithm
Bayesian framework는 과거의 지식을 통합하고 새로운 데이터를 순차적으로 업데이트함DBULL은 학습하는 동안 레이블이 지정되지 않은 데이터로 과거를 잊지 않고 새로운 클러스터를 점진적으로 발견함
🟡 Introduction
- 본 데이터의 성능을 유지하면서 새로운 데이터에 적응하는 능력을 갖춘 알고리즘을 강화하기 위해 최근 Lifelong Learning (LL)이라는 새로운 기계 학습 패러다임이 주목받음
- LL = continual learning (Thrun and Mitchell (1995)에 의해 처음 제안됨)
- LL은 기존 작업에 대한 성능 저하 없이 동작 가능, 이전에 학습한 지식을 이전하여 과거 지식을 활용하고, 지속적으로 학습하는 패러다임 제공
- ULL의 목표는 환경과 동적으로 상호작용하고 외부 감독이나 지식 없이 레이블이 지정되지 않은 데이터의 변경 사항에 적응하여 새로운 클러스터를 발견하는 것임
- 본 연구의 목적 : 이전 지식을 잊지 않고 각 훈련 단계가 끝날 때 모든 순차적 데이터에서 잘 수행할 수 있는 단일 동적 모델을 개발하는 것
- DBULL 제안 : 베이지안 프레임워크에서 심층 표현을 원활하게 학습하면서 새로운 데이터에 적응하고 새로운 클러스터로 확장할 수 있는 유연한 확률적 생성 모델
- LL의 주요 목표
: 데이터를 완전히 덮어쓴 경우에도 이전 데이터의 성능 저하 없이 스트리밍 방식으로 새 데이터가 도착할 때 지속적으로 우수한 성능을 점진적으로 달성하는 것
:이전에 학습된 정보를 효율적으로 유지하기 위해 지식 보존 계획을 설계
:비지도 학습을 수행하기 위해 수신 데이터로 확장할 수 있는 동적 모델을 설계
:end-to-end 방식으로 좋은 성능을 얻기 위한 알고리즘 설계
🟢 Related work
🌻 Alleviating catastrophic forgetting in lifelong learning
- LL에 대한 연구는 새로운 데이터에 대해 학습할 때 이전 작업의 성능 저하 없이 지속적으로 지식을 학습하는 것을 목표로 함
- LL의 문제점은 파국적 망각(catastrophic forgetting) 또는 파국적 간섭(catastrophic interference)이라는 현상이 자주 발생하는 것
- 충분한 통계를 사용하려는 우리의 제안은 참신하며 충분한 통계의 가산적 속성을 활용하여 새로운 데이터가 도착할 때 증분 업데이트를 허용하면서 이전 데이터를 저장할 필요 없이 과거 지식을 보존할 수 있다는 이점이 있음
🌻 Comparable methods in unsupervised lifelong learning- Rao(2019)는 Continual Unsupervised Representation Learning (CURL)을 제안함
- CURL은 임계값 방법을 사용하여 표현을 학습하고 새로운 클러스터를 발견하는 데 중점을 둠
- CURL의 주요 단점 중 하나는 과도한 클러스터링 문제가 있음
- 본 연구에서는 CURL과 대조되는 방법을 사용 (모델이 경계 없이 자동으로 확장될 수 있도록 하기 전에 비모수 베이지안으로 새로운 확률 프레임워크를 제공)
🌻 Bayesian lifelong learning- Nguyen(2018)은 심층 판별 모델 및 심층 생성 모델을 위한 변형 온라인 추론 프레임워크를 제공하며, 여기서 DNN에서 매개변수의 대략적인 사후 분포를 지속적인 방식으로 연구하였음
- 그러나, 그들의 방법은 데이터의 잠재적인 클러스터링 구조를 찾거나 새로운 데이터에 대한 새로운 클러스터를 감지하는 기능이 없음
- 대조적으로 본 연구에서는 ULL 컨텍스트에서 새로운 종단 간 변형 추론 전략과 함께 즉석에서 잠재 클러스터링 구조 및 새로운 클러스터를 발견하고 표현 학습을 위한 새로운 베이지안 프레임워크를 개발
🌻 Deep generative unsupervised learning methods in a batch setting- 최신 기존 방법은 LL 컨텍스트 대신 독립적이고 동일하게 분산된(i.i.d.) 일괄 학습 모드를 위해 설계되었음
- 그러나, 기존 방법은 새 데이터가 도착하거나 데이터 분포가 변경될 때 잠재적인 새 클러스터를 감지할 수 없음 (LL 설정에 적응할 수 없음)
🌻 Uncertainty quantification in Bayesian deep learning
▶ 요약- 본 연구는 ULL에 대한 완전한 베이지안 프레임워크를 제공하여 격차를 메움
- 이 프레임워크는 표현 학습을 위한 심층 생성 모델을 사용하는 동시에 비모수 베이지안 사전 및 제안된 CERR 기술을 사용하여 즉시 새로운 클러스터 검색을 수행할 수 있는 고유한 기능을 가지고 있음
- 종단 간 베이지안 추론 전략 DBULL을 추가로 개발함
🔵 Model
🌻 Problem formulation
- a good low-dimensional latent representation from to efficiently extract knowledge from the original data
- the clustering structure within the new dataset with the capacity to discover potentially novel clusters without forgetting the previously learned clusters of the seen datasets
- an incremental learning strategy to optimize the cluster learning performance for a new dataset without dramatically degrading the clustering performance in seen datasets
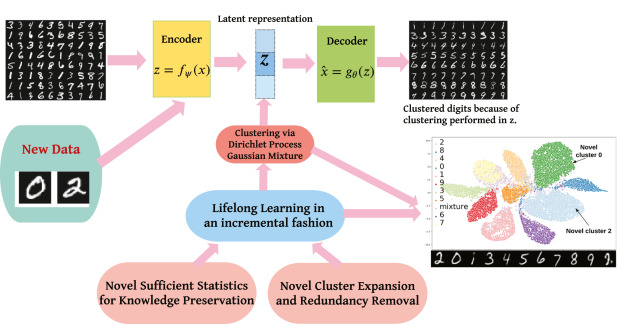
- [그림 1] Flow chart of DBULL
: 설명) DBULL은 인코더를 통해 잠재 표현을 학습하고 Dirichlet 프로세스 가우시안 혼합 모델에서 클러스터링을 수행하고 디코더를 통해 원래 관찰을 재구성
: 설명) 스트리밍 데이터를 처리할 때 incremental fashion으로 Lifelong Learning을 수행하기 위해 지식 보존을 위한 (1) 충분한 통계 및 클러스터 생성 및 (2) 병합을 위한 클러스터 확장 및 중복 제거라는 2가지 새로운 구성 요소를 도입
🟣 Experiments
🌻 Datasets
- 최신 경쟁 방법과의 공정한 비교 및 쉬운 해석을 제공하기 위해
MNIST사용- 복잡한 데이터 세트에 대한 방법을 조사하기 위해 텍스트
Reuters10k와image STL-10사용- [Table 1] DBULL 및 경쟁 방법 용량 비교
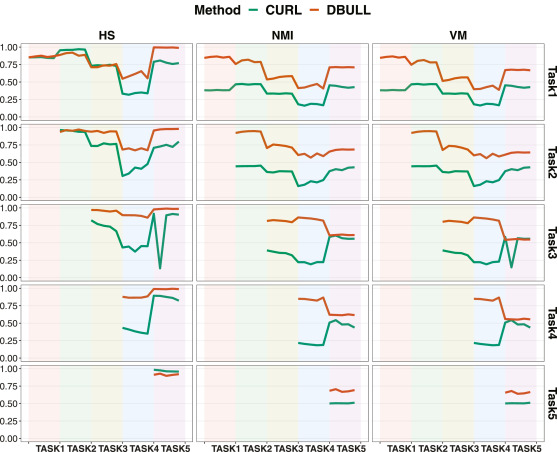
🌻 Discussion on performance- DBULL이 거의 모든 클러스터링 메트릭 측면에서 거의 모든 시나리오에서 이전 작업에 대해 CURL-D보다 성능 저하가 약간 적기 때문에 DBULL이 CURL-D보다 치명적인 망각을 처리하는 데 더 나은 성능을 가지고 있음을 반영함
- [그림 2, 3] Clustering quality performances in terms of ARS and CS measured on each task after sequential training from Task1 to Task2 across every 500 iterations for each task
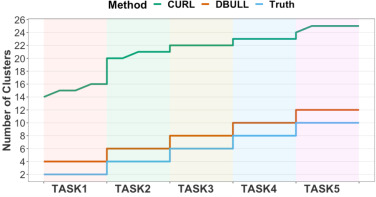
- [그림 4] Number of clusters detected by CURL-D, DBULL after sequentially training from Task3 to Task4 across every 500 iterations for each task compared with the ground truth
- [그림 5] provide visualization of the reconstructed cluster mean from the DP mixture model via our trained decoder of DBULL in Fig 5
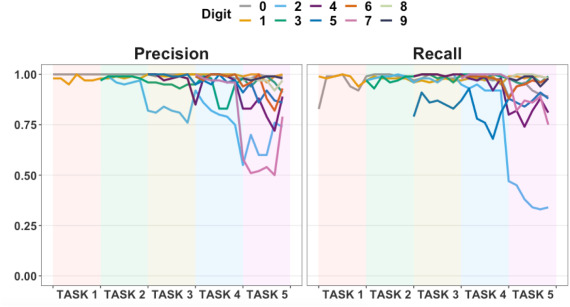
- [그림 6] Besides the overall clustering quality reported, we also provide the precision and recall of DBULL to view the performance for each digit after sequentially training all tasks in Fig 6
🟤 Conclusion
In this work, we introduce our approach DBULL for unsupervised LL problems. DBULL is a novel end-to-end approximate Bayesian inference algorithm, which is able to perform automatic new task discovery via our proposed dynamic model expansion strategy, adapt to changes in the evolving data distributions, and overcome forgetting using our proposed information extraction mechanism via summary sufficient statistics while learning the underlying representation simultaneously. Experiments on MNIST, Reuters10k and STL-10 demonstrate that DBULL has competitive performance compared with state-of-the-art methods in both a batch setting and an unsupervised LL setting. Currently, we do not explore high-resolution tasks for LL. In the future, we plan to investigate more challenging tasks on ImageNet (Deng et al., 2009) in the future. In the field of LL, little attention has been paid to uncertainty quantification. Bayesian neural networks provide a natural choice by including uncertainty through priors on the weights of the neural network and quantifying the uncertainty of the functional mean via posterior predictive distributions. Our work is developed under the Bayesian framework and we hope to extend our work to characterize uncertainty in Bayesian LL. In follow-up work, we also intend to explore additional techniques to alleviate forgetting and develop more advanced methods to continually learn unsupervised representations under various setups such as reinforcement learning domain.
® 논문 : Deep Bayesian Unsupervised Lifelong Learning (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S089360802200034X)