JS Essentials
목차
- Truthy vs Falsy
- 배열
- Closures 클로저
- Closures in a Loop
- Json 파싱
- Json 문자열 만들기
- 구조 분해 할당
1. Operator
Truthy vs Falsy
true가 되는값 vs false가 되는값
| falsy값 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| false | 키워드 false |
| 0 | Number zero.(0.0, 0x0 등등 또한 해당된다) |
| -0 | Number Negative zero.(-0.0, -0x0 등등 또한 해당된다) |
| 0n | BigInt zero. (0x0n 도 포함) BigInt negative zero는 없음에 유의하자(0n의 negative는 0n이다.) |
| "", '' | 빈 문자열 값 |
| null | 어떠한 값도 없는 상태 |
| undefined | |
| NaN | Not a Number |
| document.all | ? |
| 연산자 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| l l | 가장 먼저 나오는 truthy 값을 return , 없으면 false return |
| && | 가장 먼저 나오는 falsy 값을 return, 없으면 true return |
| ?? | l l 연산자와 역할은 같지만 null만 falsy값으로 쓸 수 있음 |
NaN과 Infinity는 비교연산자 사용x
isNan(), isInfinity() 사용
배열
buffer = 우체통
배열 메소드
- 배열 지울땐 >> arr.splice(i),arr.splice(i,n,x)사용, i에서 n개를 지우고 x를 넣어줘
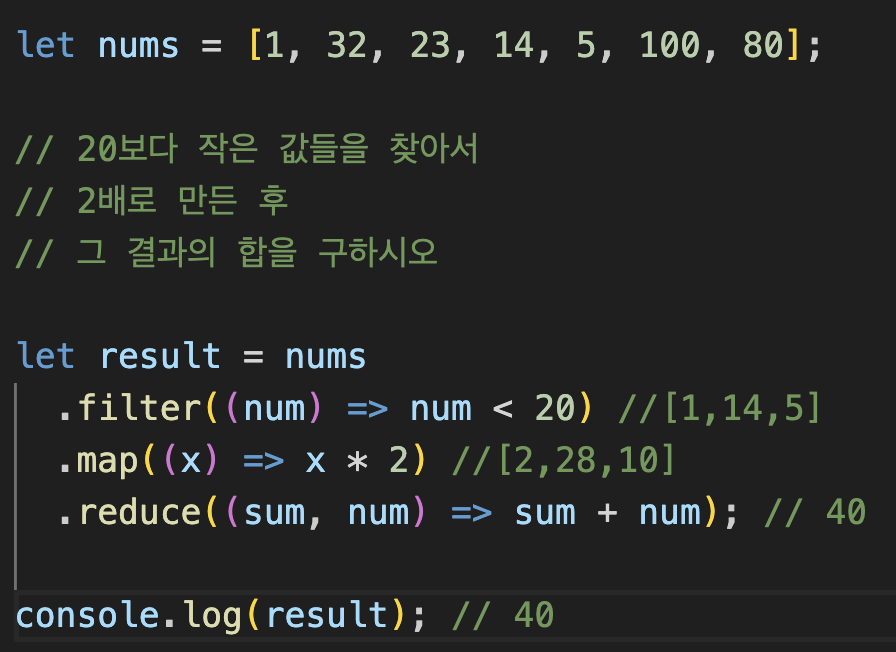
arr.find(조건문)>> 조건에 만족하는 첫번째 값을 저장 (검색)arr.filter(조건문)>> 조건에 만족하는 값을 모두저장 (필터링)arr.map>> 인자값을 다른형태로 만들어낼때 사용 (변환)arr.reduce>> 합,평균,갯수 등을 구할때 사용(집계)
ex)
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let init = 0;
let result = arr.reduce((acc, current) => acc + current, init);
console.log(result); //15- 함수를 쓰는이유?? >> 꼬리물기가능

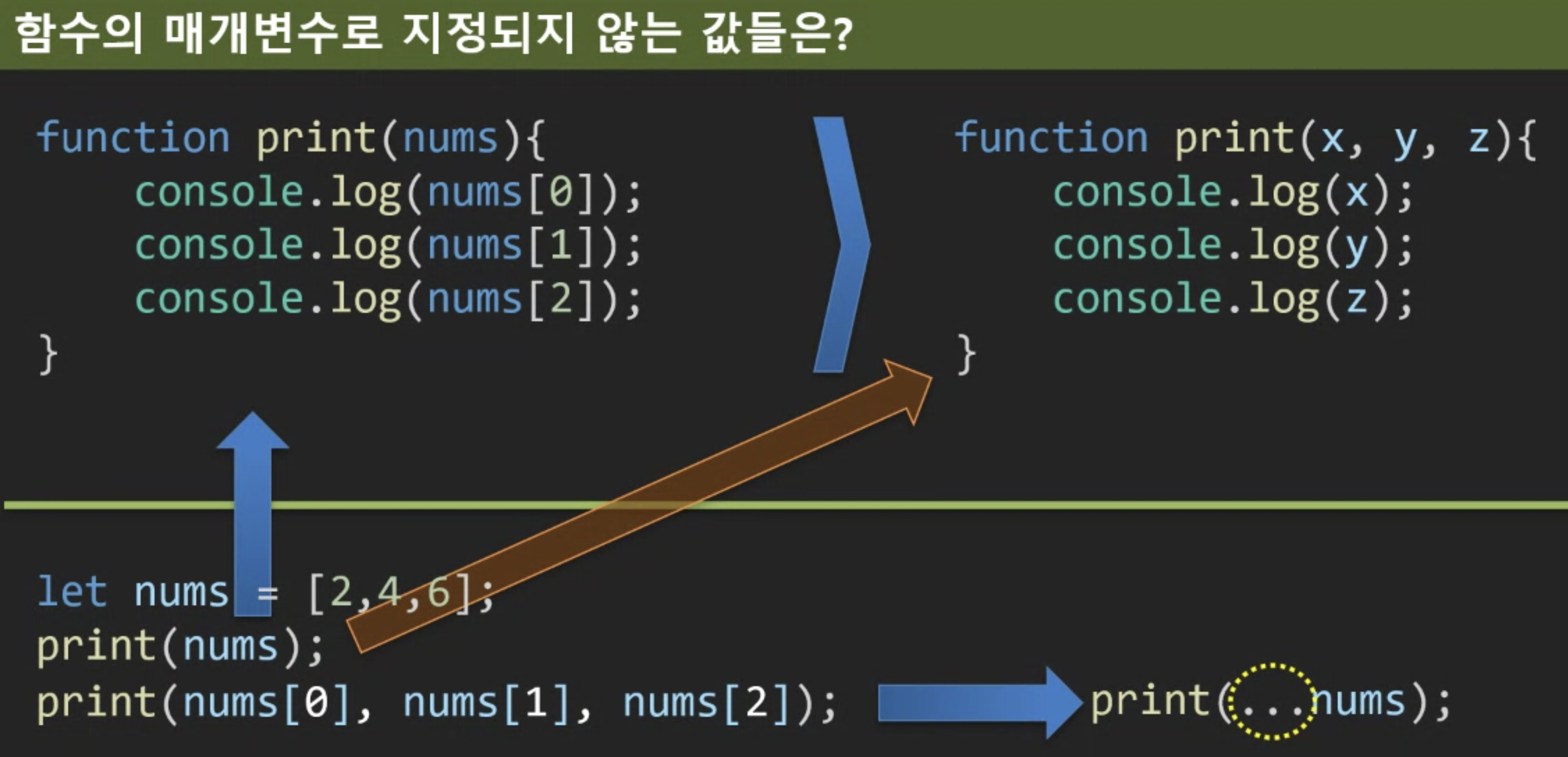
2. Function
javascript는 매게변수를 받는것이 아니라 arguments를 받는다!

매개변수 갯수가 달라도 오류가 나지 않는다
Rest Parameter >> ECMAScript6 이후 문법
function (x,y,…values){
}스프레드 연산자
클로져 closure
함수를 닫히게 하는 것
- 외부함수 스코프에서 내부함수 스코프로 접근 불가능하다.
- 내부함수에서는 외부함수 스코프에서 선언된 변수에 접근 기능하다.
- 따라서 내부 함수는 외부함수에 선언된 변수에 접근 가능하다.
let f3;
let x = 100;
let f1 = function () {
let x = 40;
f3 = function (x = 10) { // 클로저 역할
console.log(x);
};
};
f1();
f3(); // 10 출력 let f3;
let x = 100;
let f1 = function () {
let x = 40;
f3 = function (x = 10) { // 전역변수를 사용하기 때문에 클로저 역할을 하지 않는다
console.log(x);
};
};
f1();
f3(); // 10 출력Closures in a Loop
let funcs = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
funcs[i] = function () {
console.log(i);
};
}
funcs[0](); // 1
funcs[1](); // 2
funcs[2](); // 3let funcs = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
funcs[i] = function () {
console.log(i);
};
}
funcs[0](); // 3
funcs[1](); // 3
funcs[2](); // 3- var는 함수 스코프 let은 블록스코프
3. JSON
let x = "hello";
let y = "hello";
console.log(x === y); // true let x = "hello";
let y = new String("hello");
console.log(x === y); // falseJSON 파싱
- JSON.parse()
var json = '{"kor":100,"eng":90,"math":80}';
var obj = JSON.parse(json); //{"kor":100,"eng":90,"math":80} 객체로 변환
console.log(obj.kor, obj.eng, obj.math); // 100 90 80JSON 문자열 만들기
- JSON.stringify()
var exam = {kor:30, eng:40, math:50};
alert(exam.kor);
var jsonString = JSON.stringify(exam);
alert(jsonString);Arrow Function
array 정렬
정렬기준을 인자로 전달/ a-b : 오름차순, b-a : 내림차순
nums.sort(function (a, b) {
return a - b;
});
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b);
array 항목 필터링
필터링 기준연산을 인자로 전달한다.
객체 초기화의 변화
- 속성 초기화에서 키 이름과 값 변수의 이름이 같다면 생략할 수 있다.
- 객체 속성으로 함수를 초기화 할 때 function 키워드를 생략할 수 있다.
구조분해할당
- 객체가 중첩된경우
let {student : {name}} = exam;
const exam = {
kor: 10,
eng: 50,
math: 90,
student: {
name: "ds",
phone: "010-xxxx-xxxx",
},
};
let {student: { name, phone }} = exam;
console.log(phone);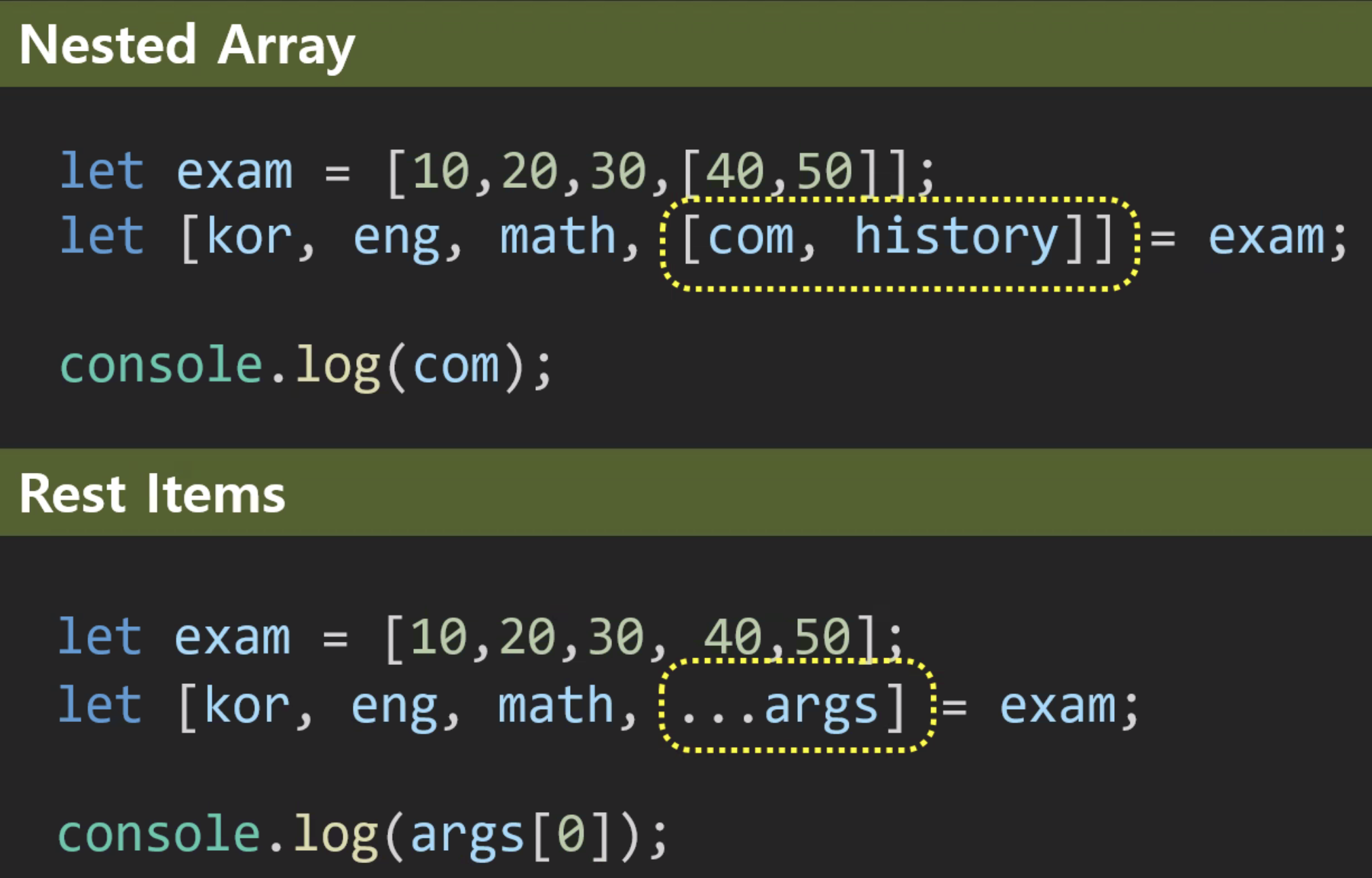
const notice = {
tile: "공지사항",
files: ["img1.png", "img2.png"],
};
let {
files: [first, second],
} = notice;
console.log(second); // img2.png 출력