Recursion : 회귀
이전의 결과를 활용하여 현재의 결과를 도출하는 알고리즘
A suitable method for circular definition
Recursion Structure
1. recursive call을 만드는 파트
ex) return n * factorial(n-1);
2. recursive call을 멈추는 파트
ex) if (n <= 1) return 1;
If there is no part that stops the recursive call, it is called continuously until a system error occurs
Recursion Principle
Devide-and-conquer
- Divide the problem into a set of sub-problems
- sub-problems의 수는 1 이상이어야 함
Recursion vs Iteration
대부분의 recursion은 iteration으로 표현(실행) 가능
Recursion
- pros : good choice for recursive problems (easy to implement)
- cons : overhead of function calls → usually slower execution time
Iteration
- pros : fast execution time
- cons : programming can be often very difficult for recursive problems
이러한 장단점들로 인하여 문제에 따라 무엇이 더 나은 방법인지 나뉨
ex 1) Factorial computation
- time complexity : recursion = iteration
- memory and call overhead : recursion > iteration
- total complexity : recursion > iteration
→ iteration is better choice
ex 2) Power computation
- time complexity : recursion < iteration
- memory and call overhead : recursion > iteration
- total complexity : recursion < iteration
→ recursion is better choice
ex 3) Fibonacci computation
- time complexity : recursion > iteration
- memory and call overhead : recursion > iteration
- total complexity : recursion > iteration
→ iteration is better choice
Examples of Recursion
1. Factorial
Iterative implementation

Recursive implementation

unsmart way
Time complexity of implementation(with n inputs)

Time complexity of recursion

2. Power Computation
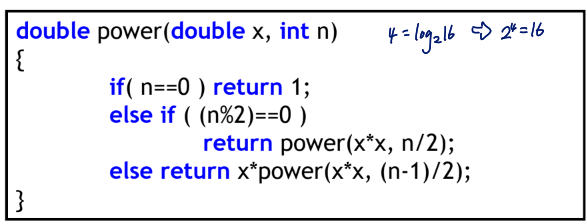
Iterative implementation
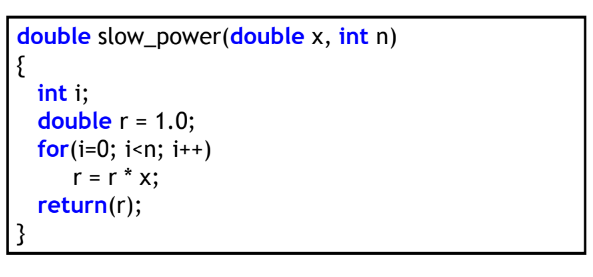
Recursive implementation
- pseudo code

- when n is even, power(x,n) = power(x², n/2)
- when n is odd, power(x,n) = power(x², (n-1)/2)
- C code
Time complexity 비교
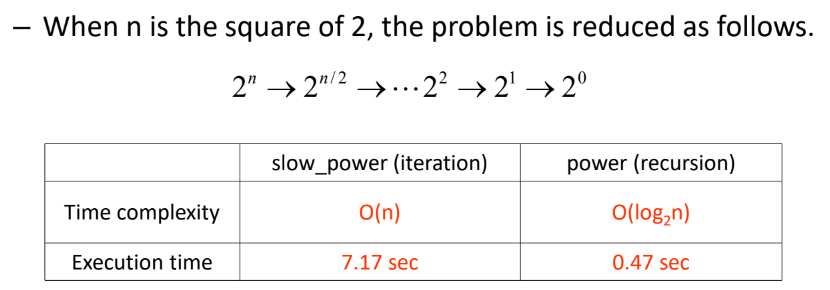
T(n) = xT(yn) + c
→ sub problem의 개수가 x배, size of subproblem이 y배가 됨
※ x == y인 경우, time complexity에는 변화가 없음
power computation에서는 recursive 사용하여 sub problem의 개수는 유지한 상태에서 size를 1/2로 줄임!
참고
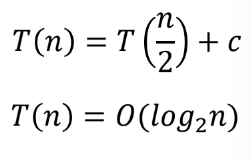
3. Fibonacci Series
Iterative implementation
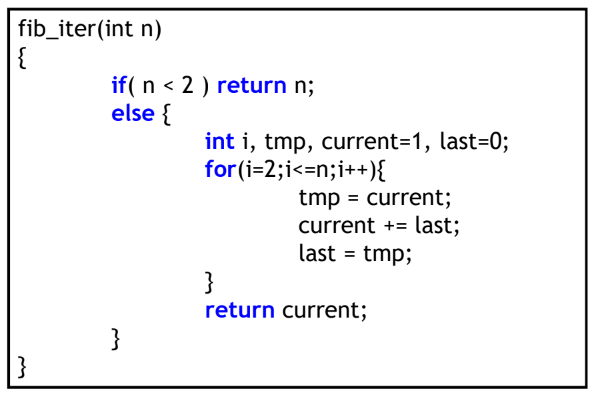
Time complexity of implementation(with n inputs)
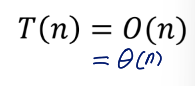
Recursive implementation

size 변화 없이 문제의 개수만 늘어서 비효율적임
Time complexity of recursion
대학원에서 더 자세히 알 수 있다고 함
Why is the recursion is inefficient for Fibonacci Series?
cuase the same terms are computed in dupliate
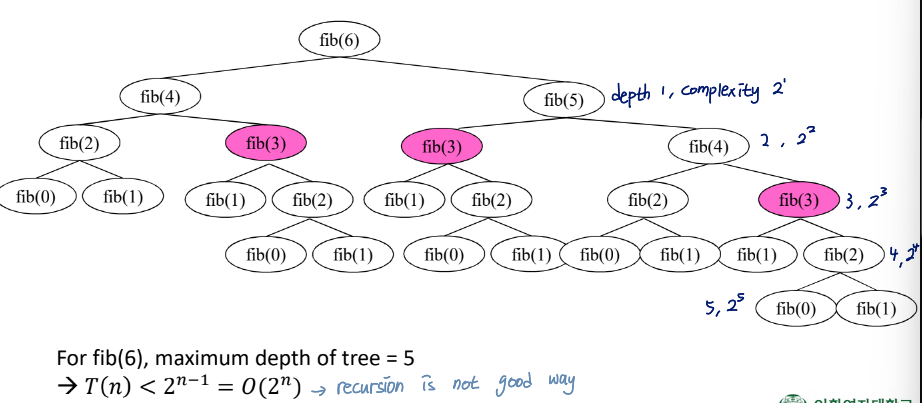
4. Hanoi Tower
Procedure
- move n-1 discs from A to B
- move n-th disc from A to C
- move n-1 discs from B to C
Pseudo code

Code
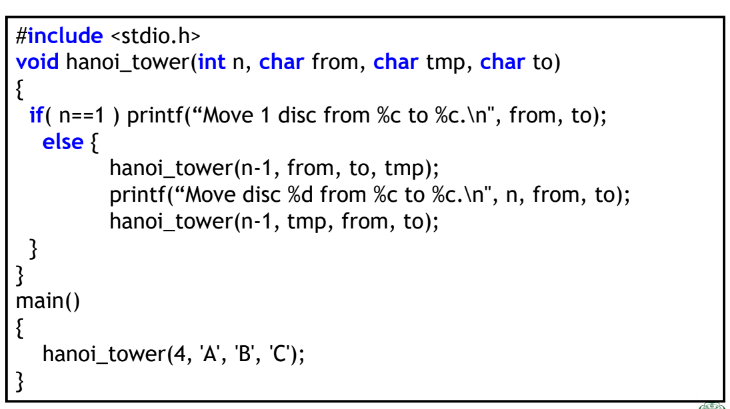
Time complextity
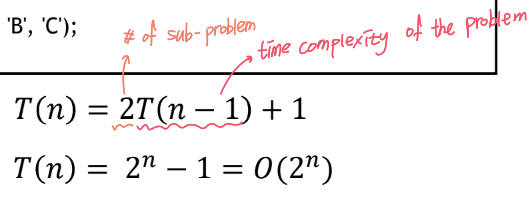
5. Binary Search
순서대로 나열된 숫자들의 집합 중 특정한 수의 인덱스를 찾고자 함
- input : a set of ordered numbers {a1,...,an}
- goal : query b
- output : an index k where ak = b_
Iterative implementation

Time complexity of implementation(with n inputs)
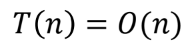
Recursive implementation

Time complexity of recursion
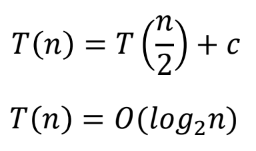
problem size는 절반으로 줄고 problem의 개수는 유지함
Recursion Types
1. Tail recursion
can be easily implemented using iteration
Ex) return n * factorial(n-1);
2. Head recursion
difficult to implement using iteration
Ex) return factorial(n-1) * n;
3. Multi-recursion
difficult to implement using iteration
Ex) 
if-else를 통해 각각에서 recursion을 사용하는 것은 multi-recursion이 아님!!!!