속성이름을 빠르게 보기위한 정리
Flex Container
display
flex, inline-flex
메인축(justify)
아이템 나열 축 <-> 교차축(align)
flex-flow
direction과 wrap을 한번에 지정
(예) row wrap
-
flex-direction : 메인축 방향
row(기본) /column /row-reverse /column-reverse -
flex-wrap : 줄넘김
nowrap(기본) /wrap /wrap-reverse
정렬
-
justify-content : 메인축 정렬
flex-start(기본) /flex-end /center /space-between /space-around /space-evenly(IE, Edge안됨) -
align-items : 교차축 정렬
stretch(기본), flex-start, flex-end, center, baseline -
align-content: 아이템이 2줄이상일 경우 수직축 정렬
stretch(기본), flex-start, flex-end, center, space-between, space-around, space-evenly(IE, Edge안됨)
Flex Item
flex
flex-grow flex-shrink flex-basis;
(예) flex: 0 1 auto; (기본)
-
flex-grow
늘어나는 비율(소수점도 가능).
flex-basis를 제외한 여백부분을 비율로 나눠가짐 -
flex-shrink
축소되는 비율 -
flex-basis
direction에 따라 최소 너비 혹은 높이.
auto는 해당 아이템의 width.
flex-basis는 작으면 맞춰주고, 넘으면 유지. width는 강제로 맞춤
align-self
해당 아이템의 수직축 정렬
auto(기본, align-items상속) /stretch /flex-start /flex-end /center /baseline
궁금
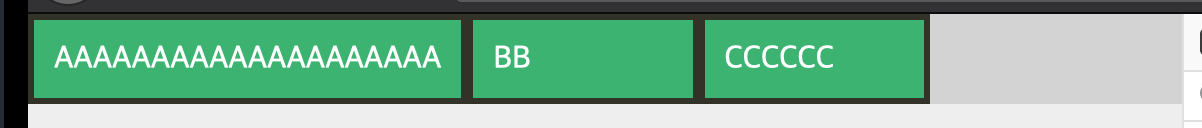
1. basis를 정했는데, 일부 아이템만 basis보다 큰 경우, flex-grow의 늘어나는 비율이 실제 최종 width기준인지, 설정된 basis기준인지?
정답: basis 기준
.flex-item {
flex-basis: 20%;
flex-grow: 0;
}flex-grow가 0인 상태에서 보면
basis는 20%이지만 첫번째 아이템의 실제 width는 훨씬 길다
.flex-item {
flex-basis: 20%;
flex-grow: 1;
}flex-grow에 1을 주어서 얼마나 늘어났는지 보면
첫번째 아이템은 늘어나지 못했다
즉, basis를 기준으로 늘어나는 셈
(basis를 기준으로 늘어난게, 내용물에 의한 width 보다 짧아서 width가 유지되었음)

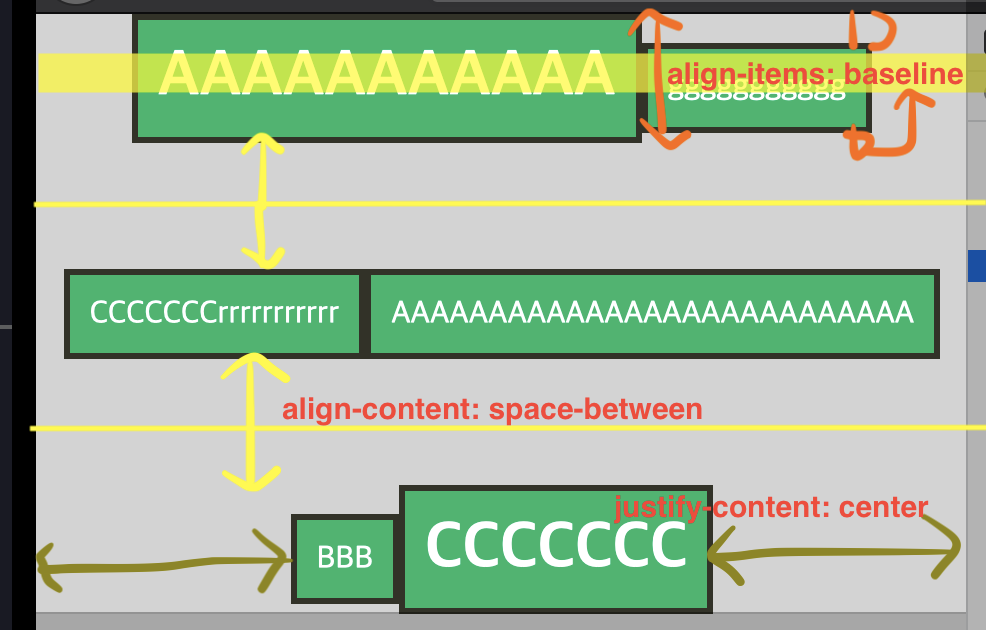
2. wrap으로 아이템이 줄바꿈 되었을때 정렬의 복합 사용
.flex-container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-items: baseline; //한 줄의 높낮이 배치
align-content: space-between; //여러줄의 높낮이 배치
justify-content: center; //row축 배치
height: 300px;
}