DFS,BFS
그래프의 탐색 중 많이 쓰이는 알고리즘이다.
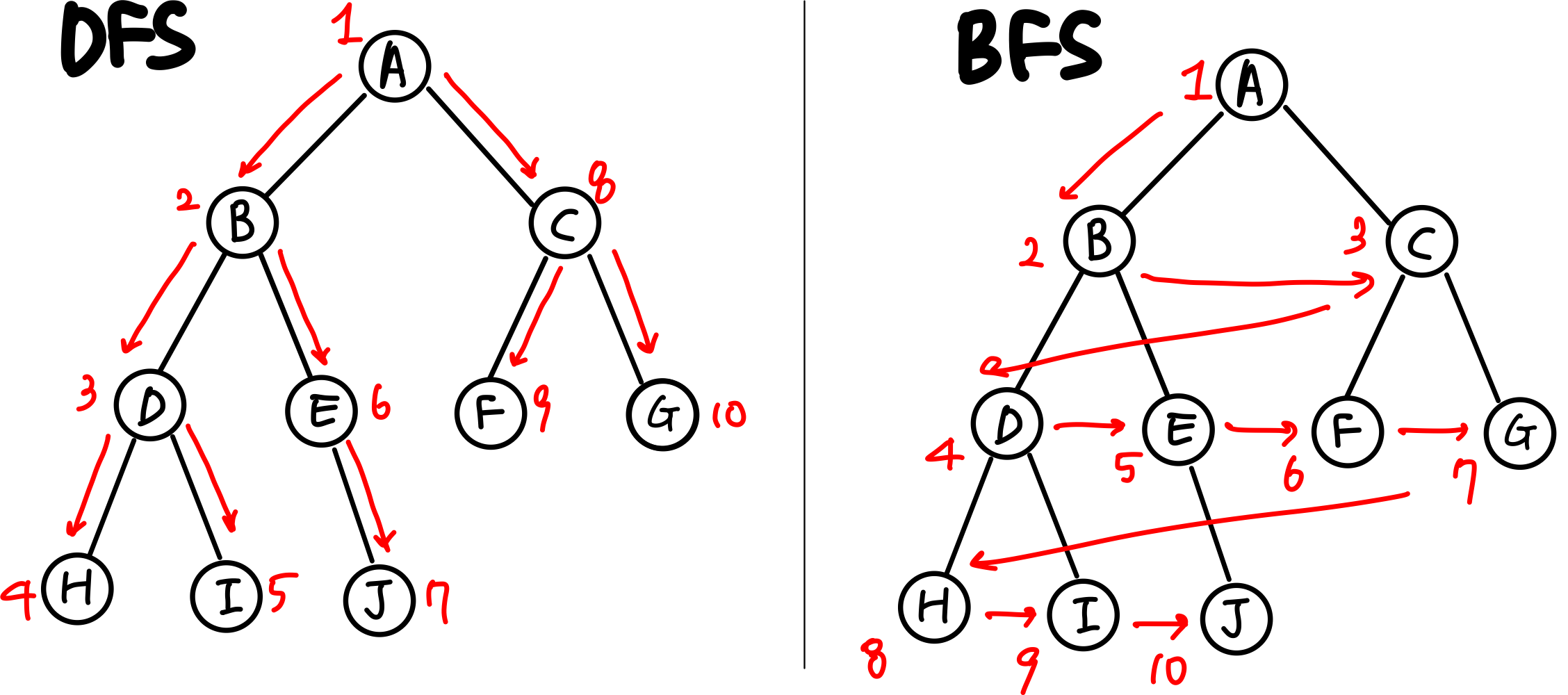
출처 : https://velog.io/@513sojin/C%EB%B0%B1%EC%A4%80-1260-DFS%EC%99%80BFS
DFS
해당 분귀를 완벽하게 탐색하고, 없으면 다음 분기로 넘어가는 형식이다.
- Stack 혹은 재귀함수로 구현된다.
- 깊게 살펴봐야하는 경우 쓴다.
BFS
해당 노드에서 인접한 노드를 먼저 탐색하는 방법이다.
- Queue를 사용해서 구현한다.
예제 문제
방향이 없는 간선들의 목록이 주어질때 연결된 정점의 컴포넌트가 몇개인지 반환하라.
입력
인자: ex) [[0,1],[1,2],[3,4]]
출력 : int타입. 연결된 정점의 컴포넌트 수
입출력 예시 :
int result = connectedVertices(new int[][]{
{0, 1},
{2, 3},
{4, 5},
});
System.out.println(result); // 3
int result = connectedVertices(new int[][]{
{0, 1},
{2, 3},
{3, 4},
{3, 5},
});
System.out.println(result); // 2풀이:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public static int connectedVertices(int[][] edges) {
//final로 해도 배열을 바꿀수 없지만, 배열 요소는 바꿀수 있다.
final int[] diretion = {0};
//가장 큰값 찾기
int max=0;
//하나하나 순회하기
for(int i=0; i<edges.length;i++){
for(int j =0; j<edges[i].length;j++){
if(max<edges[i][j])
max=edges[i][j];
}
}
int[][] direction = new int[max+1][max+1];
//방문 여부 배열 만들고
boolean[] visited = new boolean[edges.length+1];
//컴포넌트 갯수
int count=0;
//그 2차원 배열로 길을 구현
for(int i=0; i<edges.length; i++){
int from = edges[i][0];
int to= edges[i][1];
direction[from][to]=1;
direction[to][from]=1;
}
// 방문 여부를 체크한 배열을 모두 순회합니다.
for(int vertex=0; vertex<visited.length;vertex++){
if(!visited[vertex]){
count++;
// visited = bfs_array(direction,vertex,visited);
visited = dfs_array(direction,vertex,visited);
}
}
return count;
}
private static boolean[] dfs_array(int[][] direction, int vertex, boolean[] visited) {
//현재 버택스에 방문 표시
visited[vertex]=true;
//해당 버텍스 순회
for(int i=0; i<direction.length;i++){
//길이 있고 미방문이면
if(direction[vertex][i]==1&&!visited[i]){
//재귀를 이용해서 인덱스중 1인 값으로 다시 실행(이어진길)
dfs_array(direction,i,visited);
}
}
//다 끝나고 방문 배열 반환
return visited;
}
}
public boolean[] bfs_array(int[][] adjArray, int vertex ,boolean[] visited) {
//bfs의 경우 큐를 사용합니다.
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//시작지점을 큐에 넣어주고, 해당 버택스의 방문 여부를 변경합니다.
queue.add(vertex);
visited[vertex] = true;
//큐에 더이상 방문할 요소가 없을 경우까지 반복합니다.
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//현재 위치를 큐에서 꺼내온 후
int cur = queue.poll();
//전체 배열에서 현재 버택스의 행만 확인합니다.
for (int i = 0; i < adjArray[cur].length; i++) {
//길이 존재하고, 아직 방문하지 않았을 경우
if(adjArray[cur][i] == 1 && !visited[i]) {
//큐에 해당 버택스의 위치를 넣어준 이후
queue.add(i);
//방문여부를 체크합니다.
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
//이어진 모든 길을 순회한 후 방문여부가 체크된 배열을 반환합니다.
return visited;
}느낀점
이런 유형의 문제를 계속 풀어봐야겠다.
