- 이미지 출처 : 위키북스
💭 GET API 만들기
@RequestMapping으로 구현하기
- 📁 main>java>com>springboot>api>controller>GetController.java
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/get-api")
public class GetController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getHello() {
return "Hello World";
}
}
매개변수가 없는 GET 메서드 구현
- 📁 main>java>com>springboot>api>controller>GetController.java
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/get-api")
public class GetController {
//매개 변수가 없는 GET 메서드 구현
@GetMapping(value = "/name")
public String getName(){
return "Flature";
}
}
@PathVariable을 활용한 GET 메서드 구현
- 📁 main>java>com>springboot>api>controller>GetController.java
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/get-api")
public class GetController {
// @PathVariable을 활용한 GET 메서드 구현 -> {String 값}
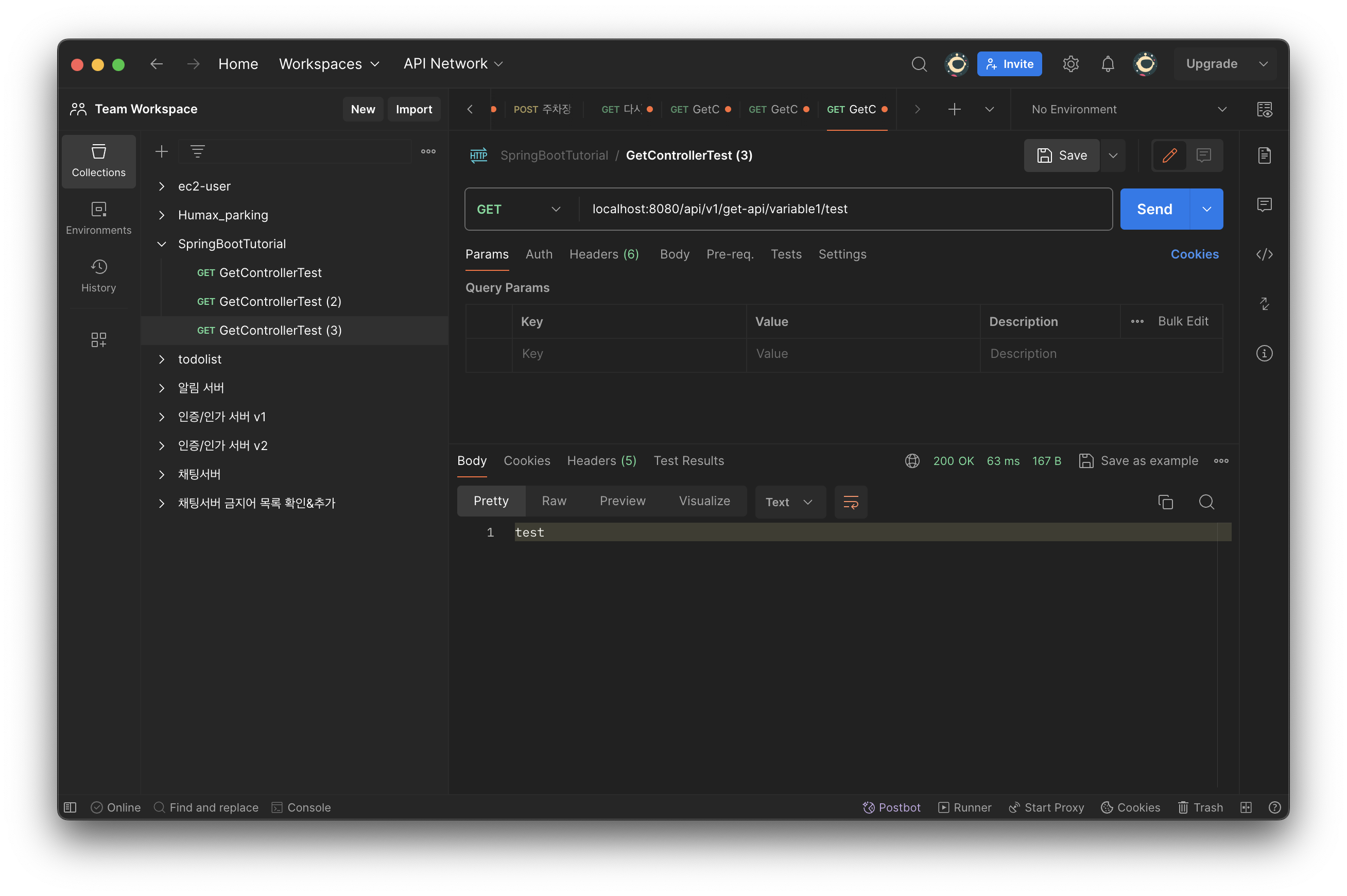
@GetMapping(value = "/variable1/{variable}")
public String getVariable1(@PathVariable String variable){
return variable;
}
}
- @GetMapping 어노테이션에 지정한 변수의 이름과 메서드 매개변수의 이름을 동일하게 맞추기 어렵다면?
- @PathVariable 뒤에 괄호를 열어 @GetMapping 어노테이션의 변수명을 지정
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/get-api")
public class GetController {
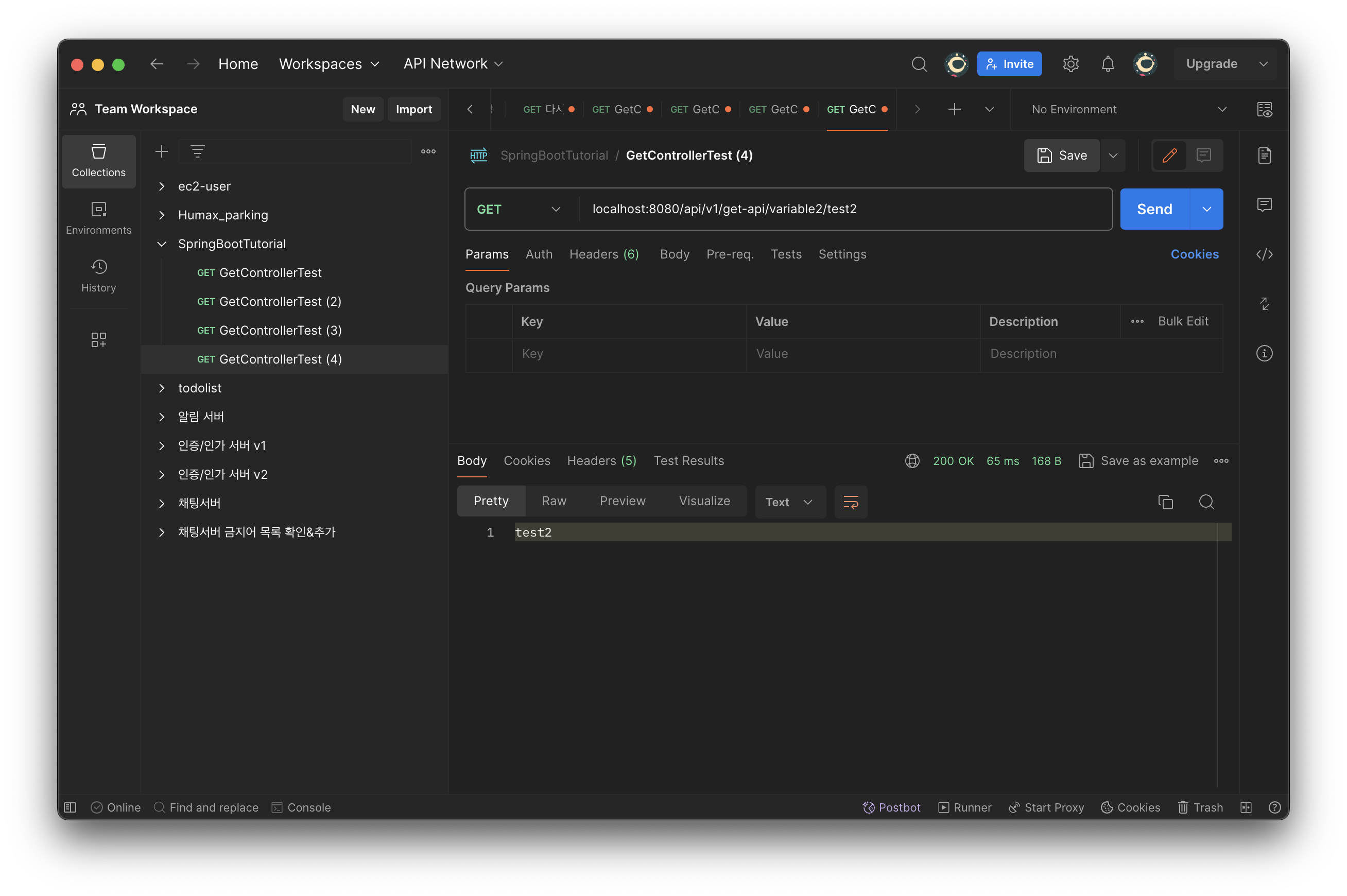
// @PathVariable에 변수명을 매핑하는 방법
@GetMapping(value = "/variable2/{variable}")
public String getVariable2(@PathVariable("variable") String var){
return var;
}
}
@RequestParam을 활용한 GET 메서드 구현
- 📁 main>java>com>springboot>api>controller>GetController.java
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.context.annotation.RequestScope;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/get-api")
public class GetController {
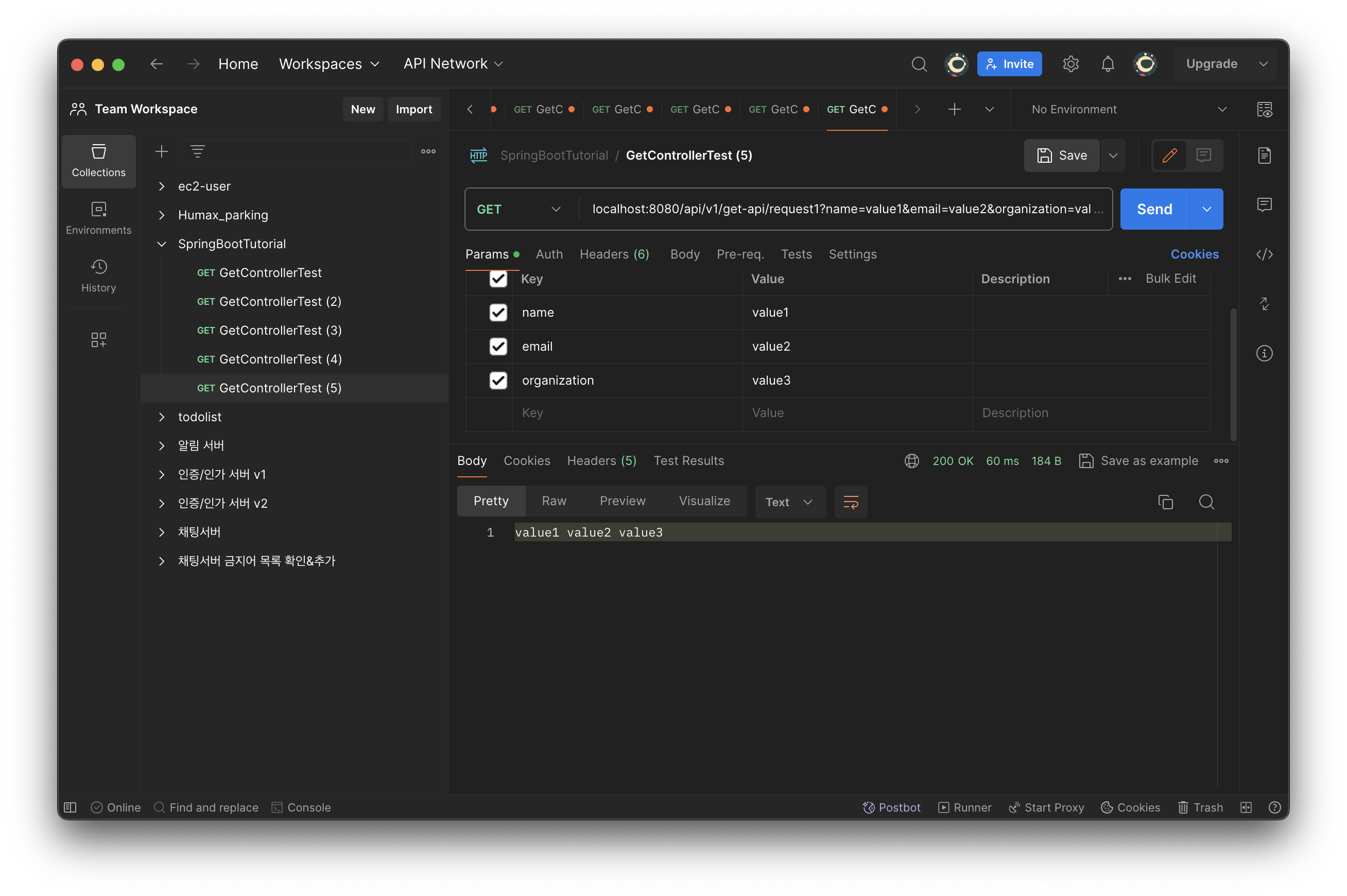
//@RequestParam을 활용한 GET 메서드 구현
@GetMapping(value = "/request1")
public String getRequestParam1(
@RequestParam String name,
@RequestParam String email,
@RequestParam String organization) {
return name + " " + email + " " + organization;
}
}
@RequestParam과 Map을 조합한 GET 메서드 구현
- 쿼리스트링에 어떤 값이 들어올지 모를 경우 Map 활용
- 📁 main>java>com>springboot>api>controller>GetController.java
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.context.annotation.RequestScope;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/get-api")
public class GetController {
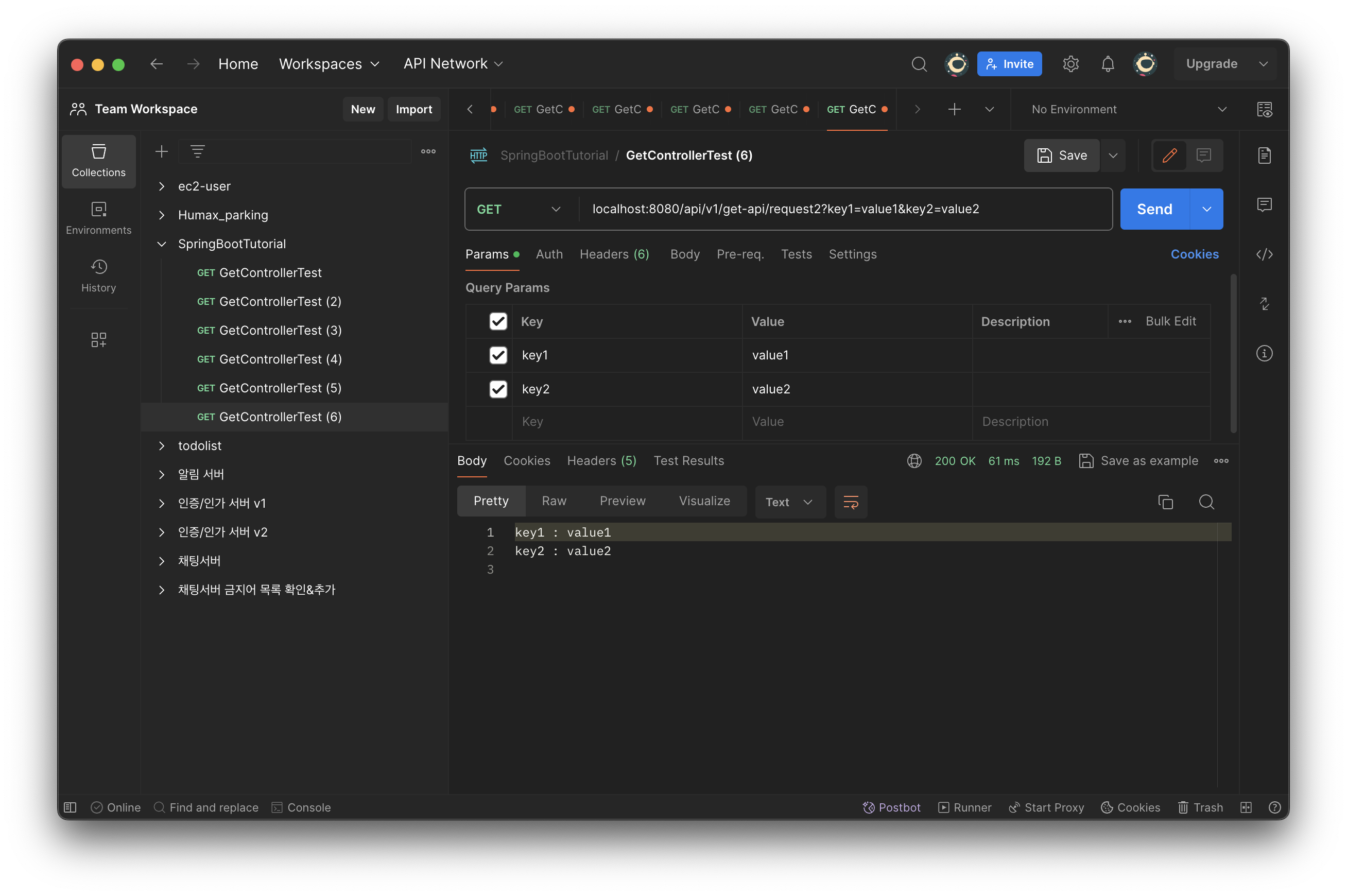
//@RequestParam과 Map을 조합한 GET 메서드 구현
@GetMapping(value = "request2")
public String getRequestParam2(@RequestParam Map<String, String> param) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
param.entrySet().forEach(map -> {
sb.append(map.getKey() + " : " + map.getValue() + "\n");
});
return sb.toString();
}
}
DTO 객체를 활용한 GET 메서드 구현
- 📁 main>java>com>springboot>api>controller>GetController.java
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.context.annotation.RequestScope;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/get-api")
public class GetController {
// DTO 객체를 활용한 GET 메서드 구현
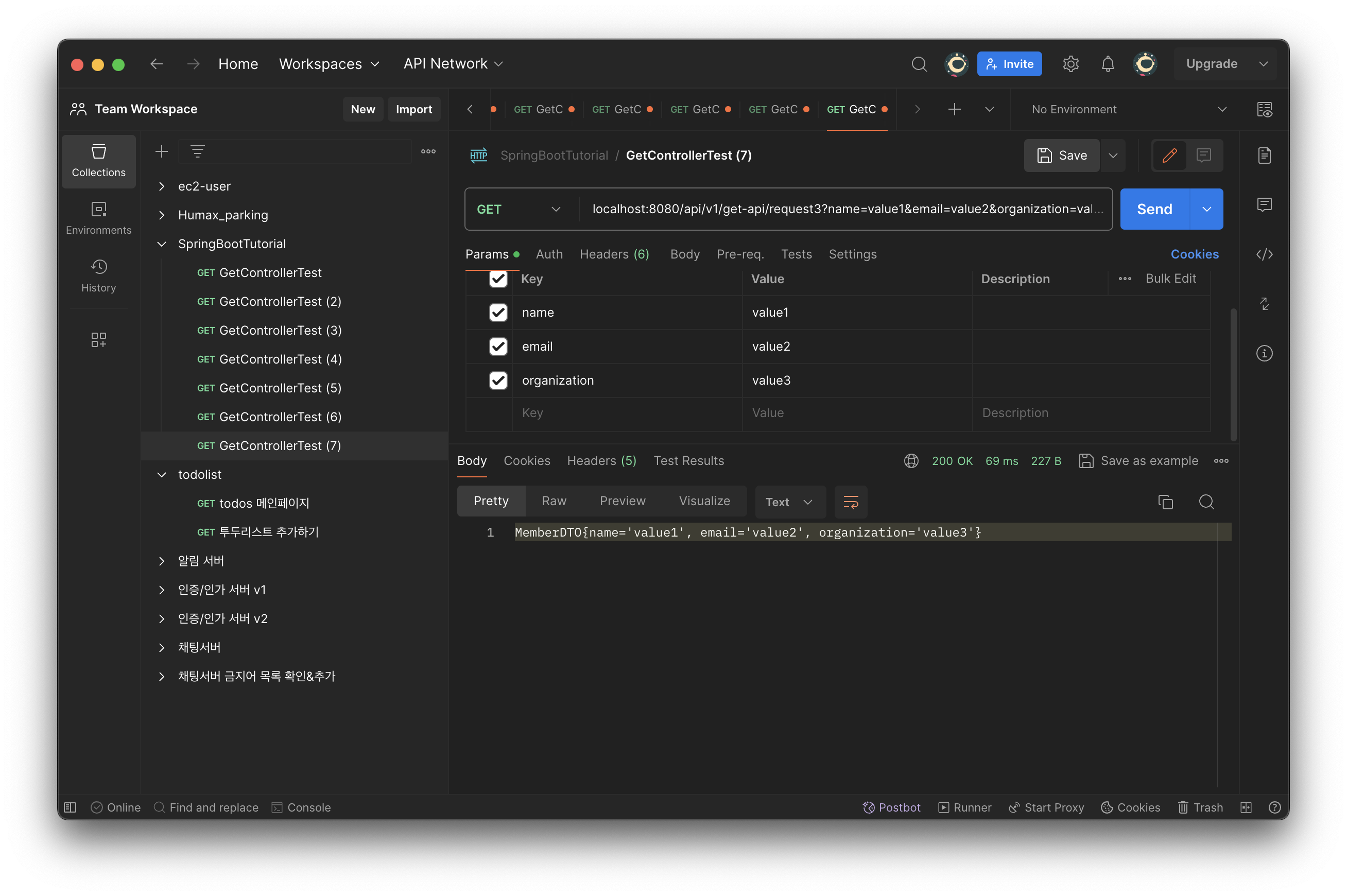
@GetMapping(value = "request3")
public String getRequestParam3(MemberDTO memberDTO) {
return memberDTO.toString();
}
}- 📁 main>java>com>springboot>api>dto>MemberDTO.java
package com.springboot.api.dto;
public class MemberDTO {
private String name;
private String email;
private String organization;
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail(){
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email){
this.email = email;
}
public String getOrganization(){
return organization;
}
public void setOrganization(String organization){
this.organization = organization;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "MemberDTO{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", organization='" + organization + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
💭 POST API 만들기
컨트롤러 클래스에서 공통 URL 설정
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/post-api")
//컨트롤러 클래스에서 공통 URL 설정
public class PostController {
}@RequestMapping으로 구현하기
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/post-api")
//컨트롤러 클래스에서 공통 URL 설정
public class PostController {
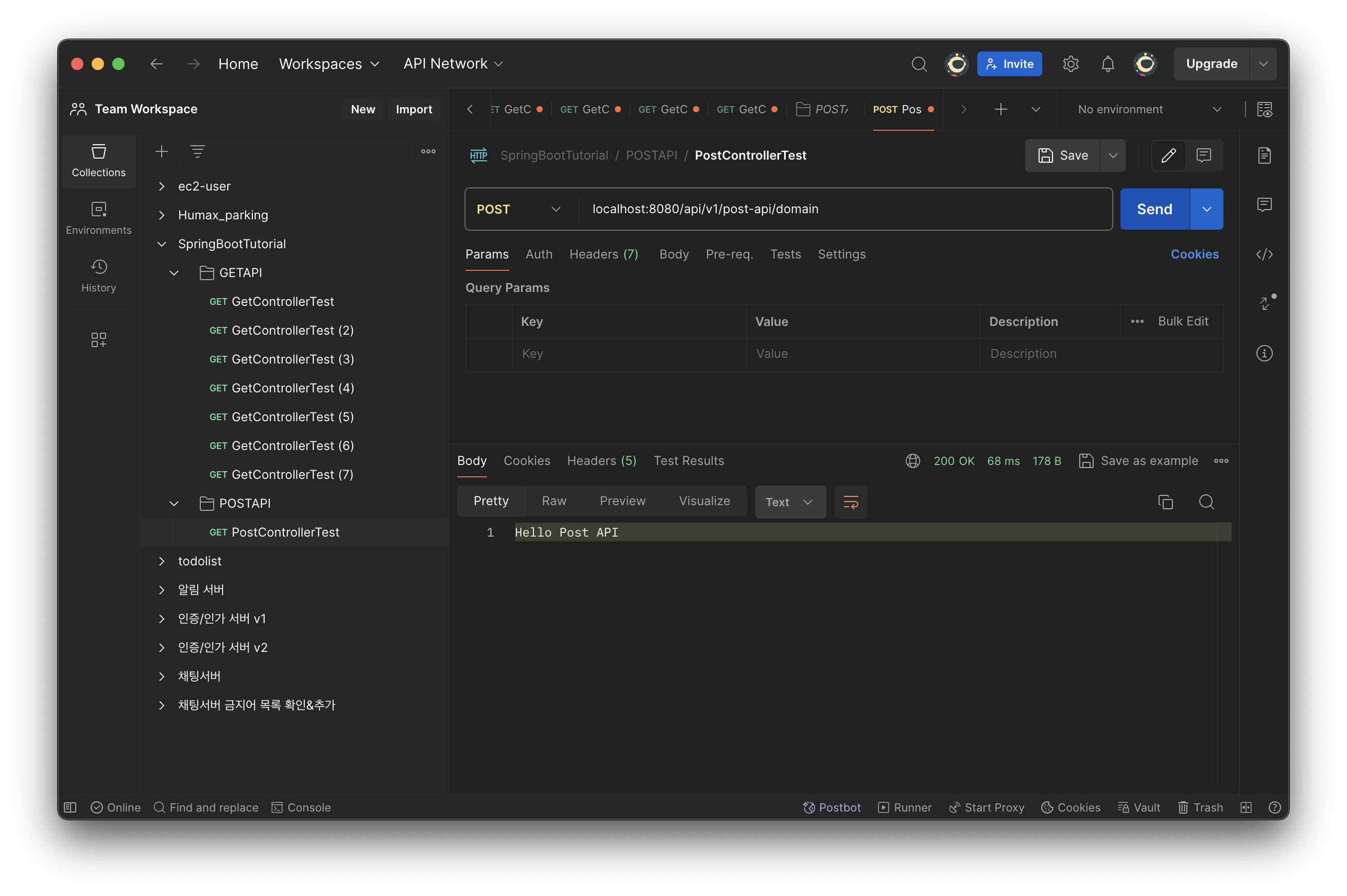
//@RequestMapping으로 구현하기
@RequestMapping(value = "/domain", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String postExample() {
return "Hello Post API";
}
}
@RequestBody를 활용한 POST 메서드 구현
- POST 형식의 요청은 클라이언트가 서버에 리소스를 저장하는데 사용
- 클라이언트의 요청 트래픽에 값이 포함되어 있음
- 즉, POST 요청에서는 리소스를 담기 위해 HTTP Body에 값을 넣어 전송
- 주로 JSON 형식
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/post-api")
public class PostController {
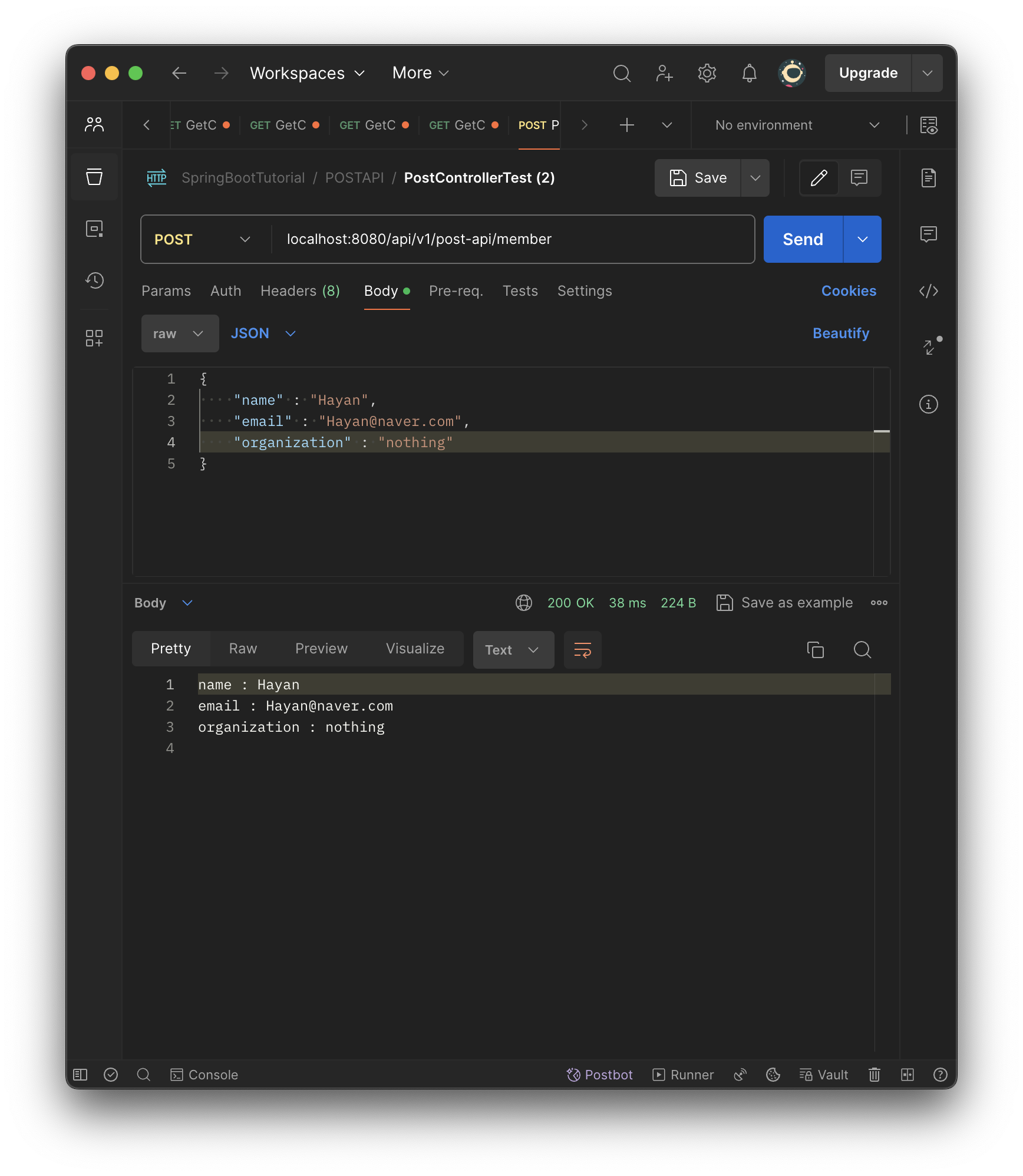
//@RequestBody를 활용한 POST 메서드 구현
@PostMapping("member")
public String postMember(
@RequestBody Map<String, String> postData
){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
postData.entrySet().forEach(
map -> {
sb.append(map.getKey() + " : " + map.getValue() + "\n");
}
);
return sb.toString();
}
}
💭 PUT API 만들기
@RequestBody와 Map을 활용한 PUT 메서드 구현
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/put-api")
public class PutController {
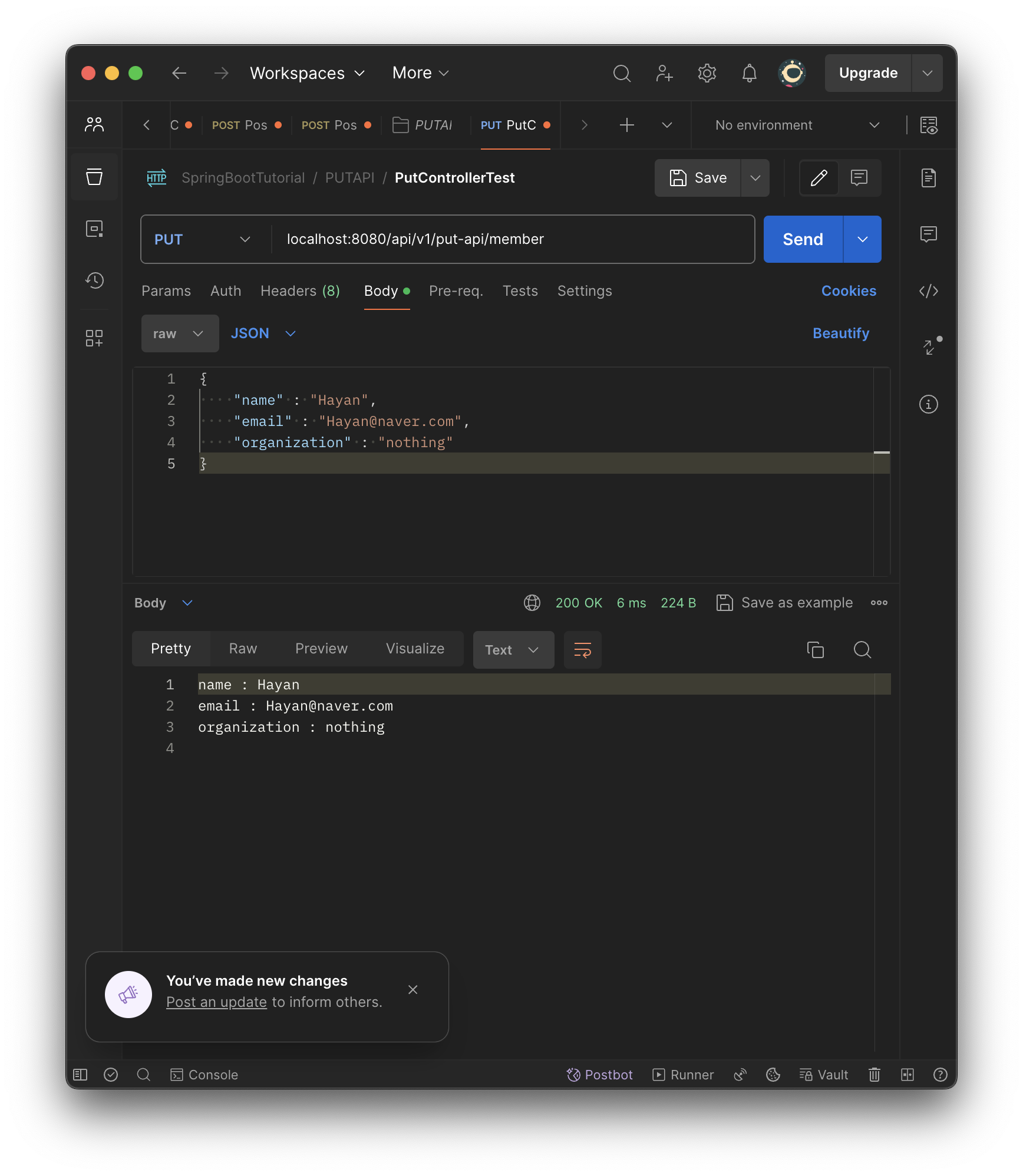
//@RequestBody와 Map을 활용한 PUT 메서드 구현
@PutMapping(value = "/member")
public String postMemver(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> putData) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
putData.entrySet().forEach(map -> {
sb.append(map.getKey() + " : " + map.getValue() + "\n");
});
return sb.toString();
}
}
DTO 객체를 활용한 PUT 메서드 구현
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import com.springboot.api.dto.MemberDTO;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/put-api")
public class PutController {
//DTO 객체를 활용한 PUT 메서드 구현 - String 리턴
@PutMapping(value = "/member1")
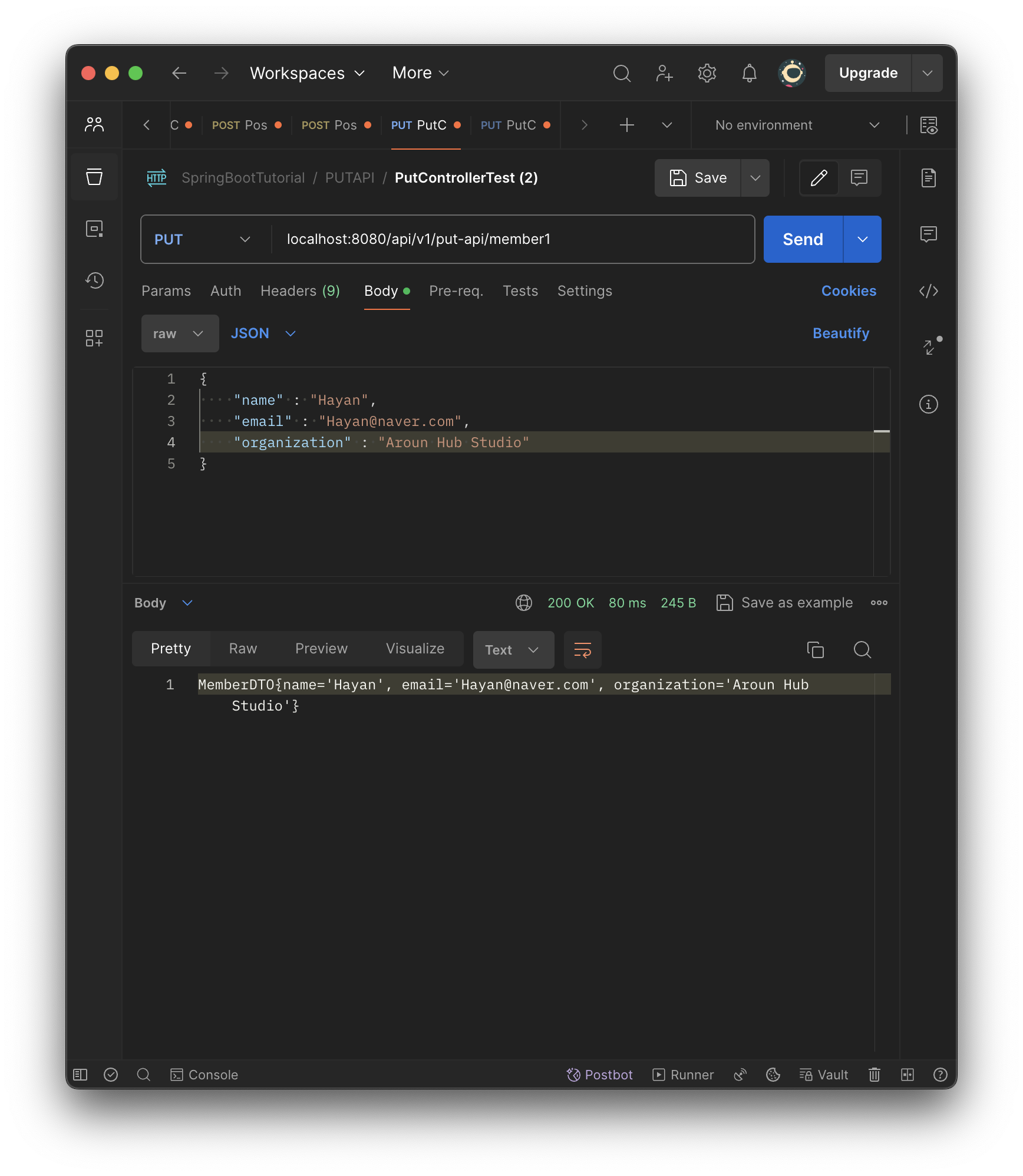
public String postMemberDTO1(@RequestBody MemberDTO memberDTO){
return memberDTO.toString();
}
//DTO 객체를 활용한 PUT 메서드 구현 - memberDTO 리턴
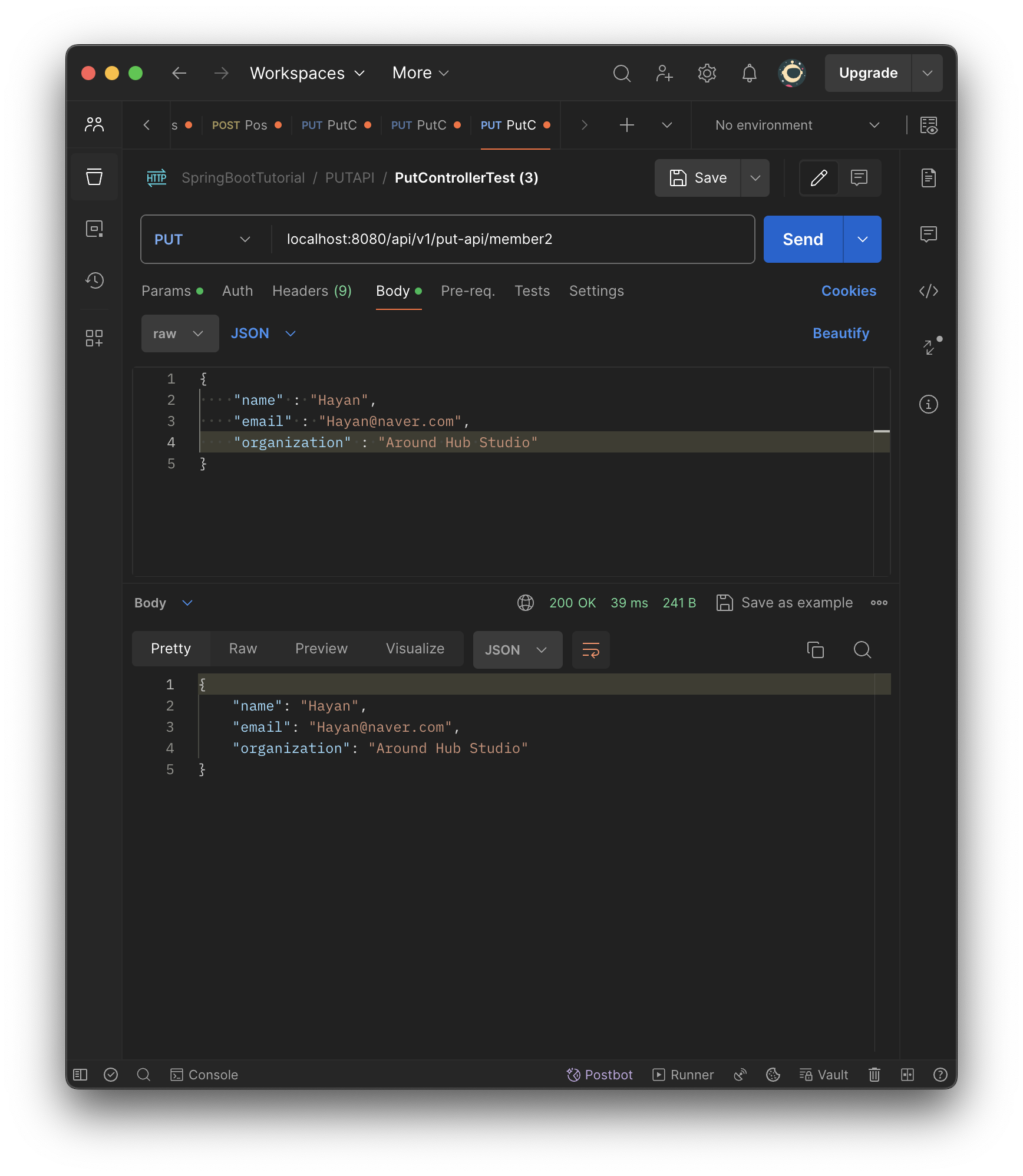
@PutMapping(value = "/member2")
public MemberDTO postMemberDTO2(@RequestBody MemberDTO memberDTO){
return memberDTO;
}
}- String 리턴
- memberDTO 리턴
ResponseEntity를 활용한 PUT 메서드 구현
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import com.springboot.api.dto.MemberDTO;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/put-api")
public class PutController {
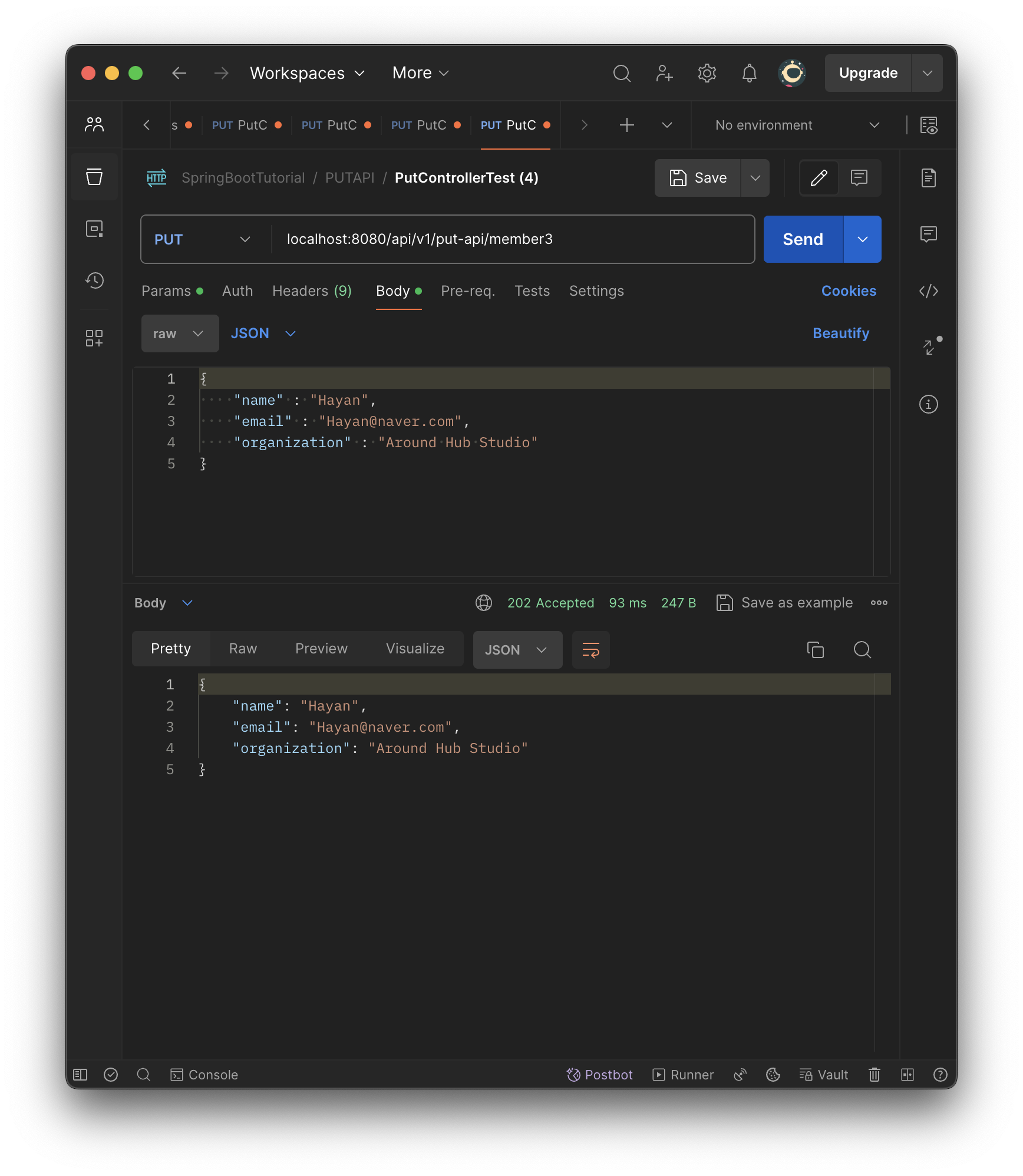
//ResponseEntity를 활용한 PUT 메서드 구현
@PutMapping(value = "/member3")
public ResponseEntity<MemberDTO> postMemberDTO3(@RequestBody MemberDTO memberDTO){
return ResponseEntity
.status(HttpStatus.ACCEPTED)
.body(memberDTO);
}
}
💭 DELETE API 만들기
@PathVariable과 @RequestParam을 활용한 DELETE 메서드 구현
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/delete-api")
public class DeleteController {
//@PathVariable과 @RequestParam을 활용한 DELETE 메서드 구현
@DeleteMapping(value = "/{variable}")
public String DeleteVariable(@PathVariable String variable){
return variable;
}
}@RequestParam을 활용한 DELETE 메서드 구현
package com.springboot.api.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/delete-api")
public class DeleteController {
//@RequestParam을 활용한 DELETE 메서드 구현
@DeleteMapping(value = "request1")
public String getRequestParam1(@RequestParam String email){
return "e-mail : " + email;
}
}
💭 [한걸음 더] REST API 명세를 문서화하는 방법 - Swagger
- build.gradle에 Swagger 의존성 추가
//SWAGGER
implementation 'io.springfox:springfox-boot-starter:3.0.0'
implementation 'io.springfox:springfox-swagger-ui:3.0.0'- config>SwaggerConfig.java 추가
package com.springboot.api.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket restAPI() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.groupName("groupName1")
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.
basePackage("com.springboot.api"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build()
.apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("Spring Boot Open API Test with Swagger")
.version("1.0.0")
.description("Back to Spring API 명세서입니다.")
.build();
}
}
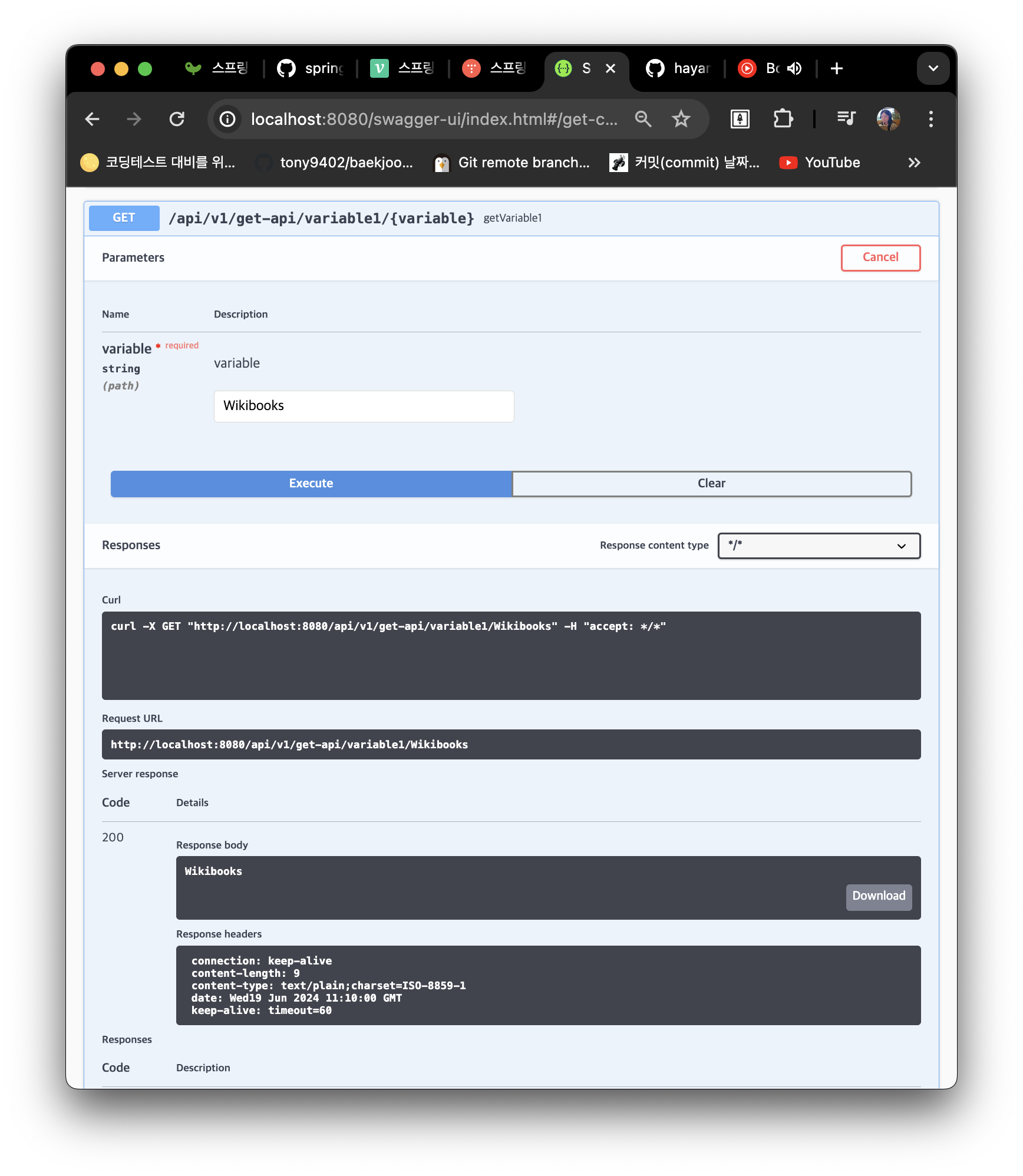
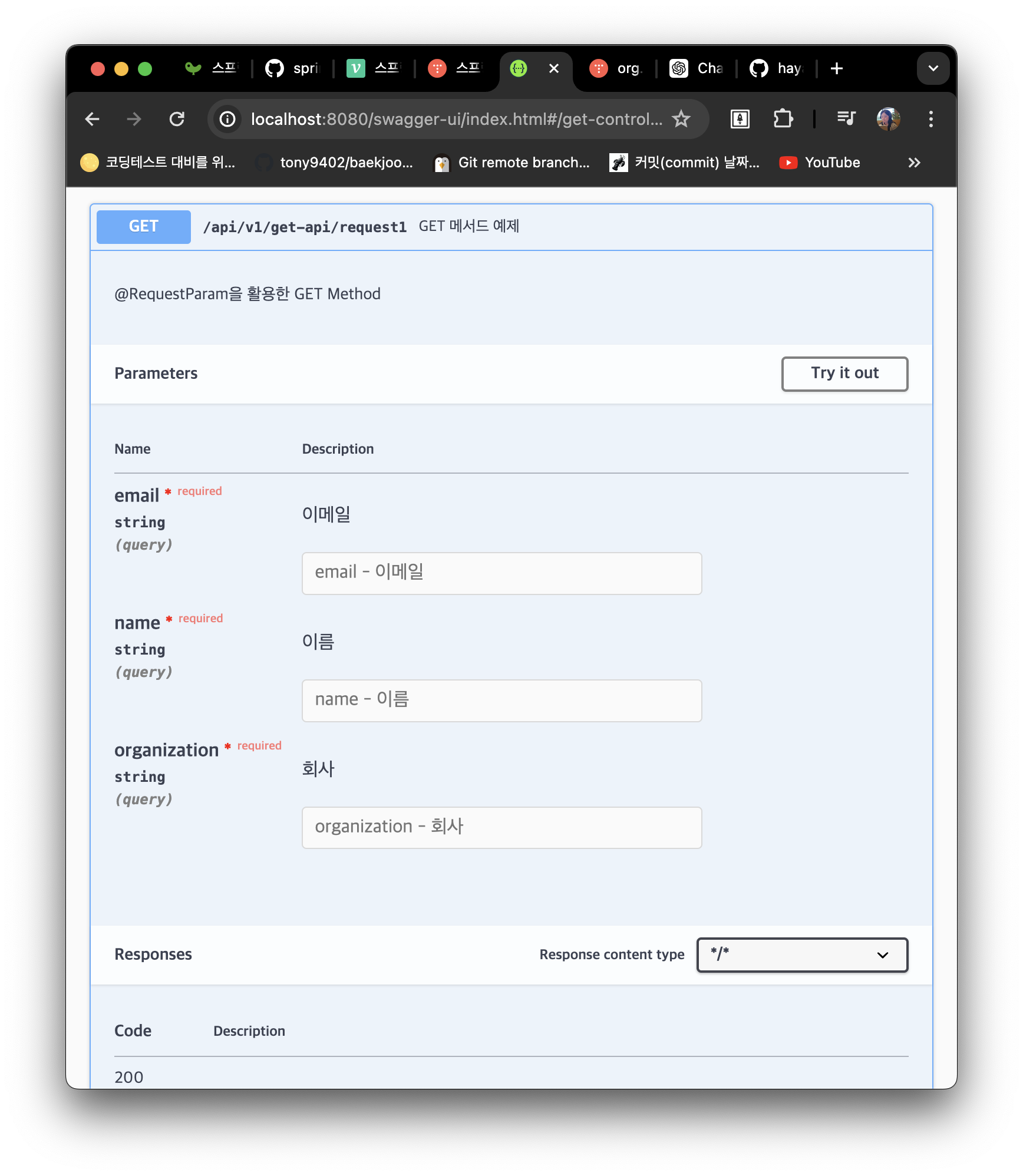
- 실제 API 작동 확인(예시)
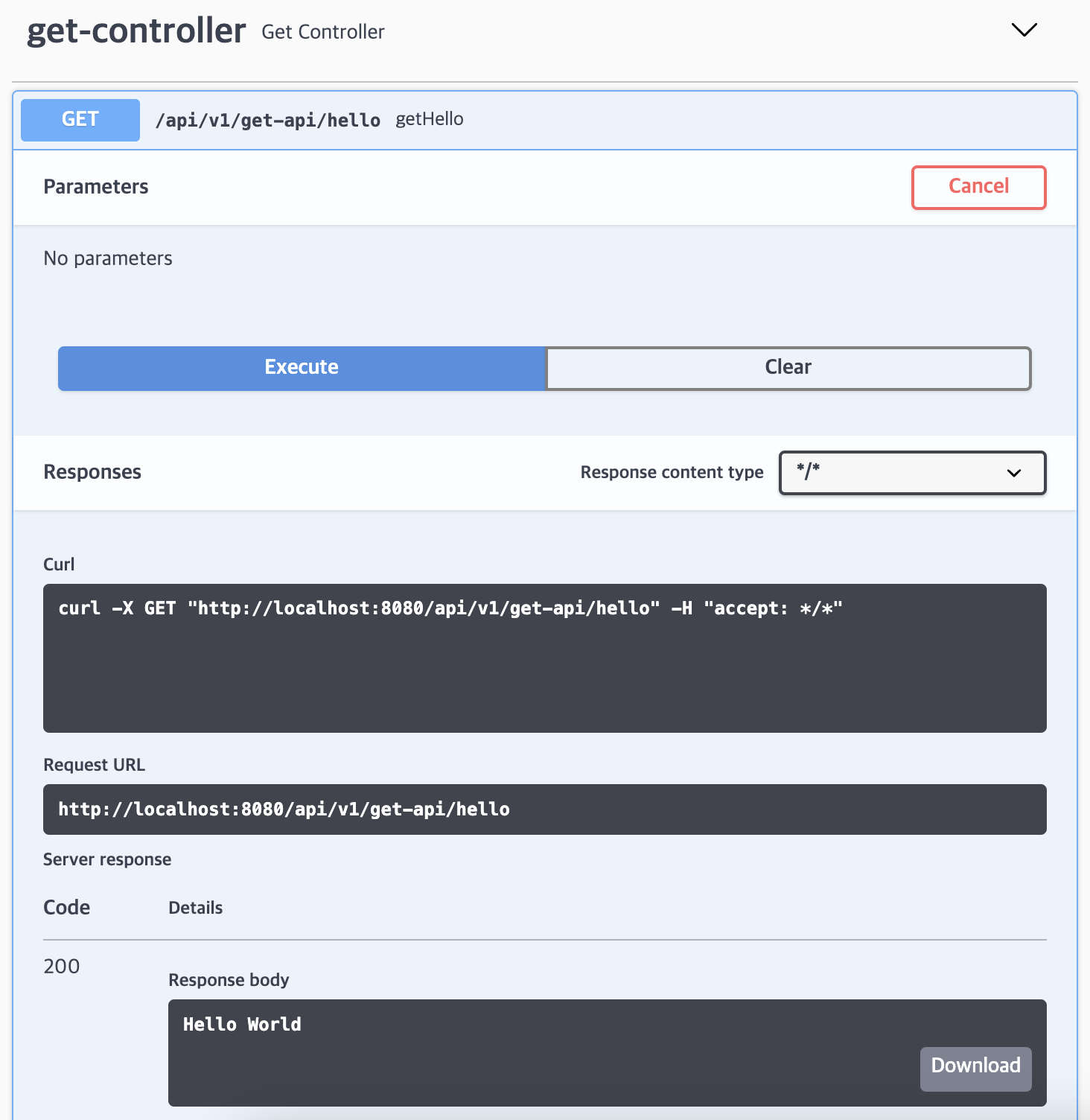
@RequestParam을 활용한 GET 메서드에 대한 명세의 세부 내용 설정
- 📁 main>java>com>springboot>api>controller>GetController.java
...
// @RequestParam을 활용한 GET 메서드 구현
@ApiOperation(value = "GET 메서드 예제", notes = "@RequestParam을 활용한 GET Method")
@GetMapping(value = "/request1")
public String getRequestParam1(
@ApiParam(value = "이름", required = true) @RequestParam String name,
@ApiParam(value = "이메일", required = true) @RequestParam String email,
@ApiParam(value = "회사", required = true)@RequestParam String organization) {
return name + " " + email + " " + organization;
}
...
💭 [한걸음 더] 로깅 라이브러리 - Logback
기본 개념
- 로깅(logging)
- 애플리케이션이 동작하는 동안 시스템의 상태나 동작 정보를 시간순으로 기록하는 것을 의미
- 디버깅하거나, 개발 이후 발생한 문제를 해결할 때 원인을 분석하는 데 꼭 필요한 요소
slf4j- 스프링부트의 spring-boot-starter-web 라이브러리 내부에 내장되어 있어 의존성 추가 안해도 사용 가능
- 5개의 로그 레벨 설정 가능
-
ERROR : 로직 수행 중 시스템에 심각한 문제가 발생해 애플리케이션의 작동이 불가능한 경우를 의미
-
WARN : 시스템 에러의 원인이 될 수 있는 경고 레벨을 의미
-
INFO : 애플리케이션의 상태 변경과 같은 정보 전달을 위해 사용
-
DEBUG : 애플리케이션의 디버깅을 위한 메시지를 표시하는 레벨을 의미
-
TRACE : DEBUG 레벨보다 더 상세한 메시지를 표현하기 위한 레벨을 의미
Logback 설정
-
resorce > logback-spring.xml 파일을 참조하도록 생성
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <configuration> <property name="LOG_PATH" value="./logs"/> <!-- Appenders --> <appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"> <filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.ThresholdFilter"> <level>INFO</level> </filter> <encoder> <pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%-5level] [%thread] %logger %msg%n</pattern> </encoder> </appender> <appender name="INFO_LOG" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender"> <filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.ThresholdFilter"> <level>INFO</level> </filter> <file>${LOG_PATH}/info.log</file> <append>true</append> <rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy"> <fileNamePattern>${LOG_PATH}/info_%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log.gz</fileNamePattern> <maxHistory>30</maxHistory> </rollingPolicy> <encoder> <pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%-5level] [%thread] %logger %msg%n</pattern> </encoder> </appender> <!-- TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR < OFF --> <!-- Root Logger --> <root level="INFO"> <appender-ref ref="console"/> <appender-ref ref="INFO_LOG"/> </root> </configuration>
-
Appender 영역
- 로그의 형태를 설정
- 어떤 방법으로 출력할지 설정하는 영역
- appender 자체는 하나의 인터페이스를 의미, 하위에 여러 구현체가 존재함.
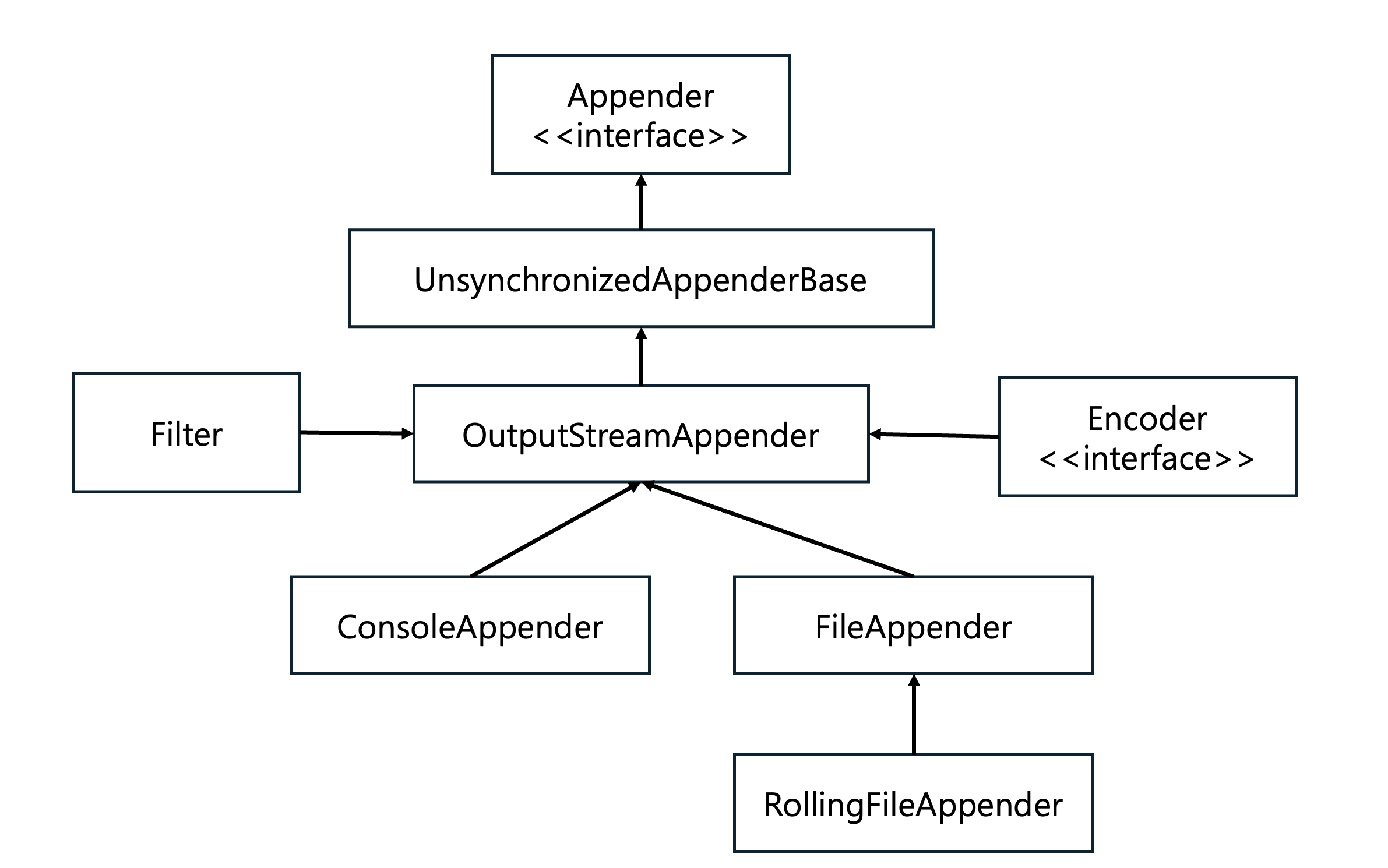
- Appender의 대표적 구현체
- ConsoleAppender : 콘솔에 로그 출력
- FileAppender : 파일에 로그 저장
- RollingFileAppender : 여러 개의 파일을 순회하면서 로그 저장
- SNTPAppender : 메일로 로그를 전송
- DBAppender : 데이터베이스에 로그 저장
대표적인 패턴(pattern)
- %Logger {length} : 로거의 이름
- %-5level : 로그 레벨(-5는 출력 고정폭의 값)
- %msg(%message) : 로그 메시지
- %d : 로그 기록 시간
- %p : 로깅 레벨
- %F : 로깅이 발생한 애플리케이션 파일명
- %M : 로깅이 발생한 호출지의 정보
- %thread : 현재 스레드명
- %t : 로깅이 발생한 스레드명
- %c : 로깅이 발생한 카테고리
- %C : 로깅이 발생한 클래스명
- %m : 로그 메시지
- %n : 줄바꿈
- %r : 애플리케이션 실행 후, 로깅이 발생한 시점까지의 시간
- %L : 로깅이 발생하는 호출 지점의 라인 수
//예시
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%-5level] [%thread] %logger %msg%n</pattern>Root 영역
- 설정 파일에 정의된 Appender를 활용하려면 Root 영역에서 Appender를 참조해 로깅 레벨을 설정
- 특정 패키지에 대해 다른 로깅 레벨을 설정하고 싶다면 root 대신 logger를 사용해 지정
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="console"/>
<appender-ref ref="INFO_LOG"/>
</root>
<!-- 또는 -->
<logger name="com.springboot.api.controller" level="DEBUG" additivity="false">
<appender-ref ref="console"/>
<appender-ref ref="INFO_LOG"/>
</logger>Logback 적용하기
- Logger 선언
...
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/get-api")
public class GetController {
//Logback 적용하기
private final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GetController.class);
...- 로그 출력 코드 삽입
...
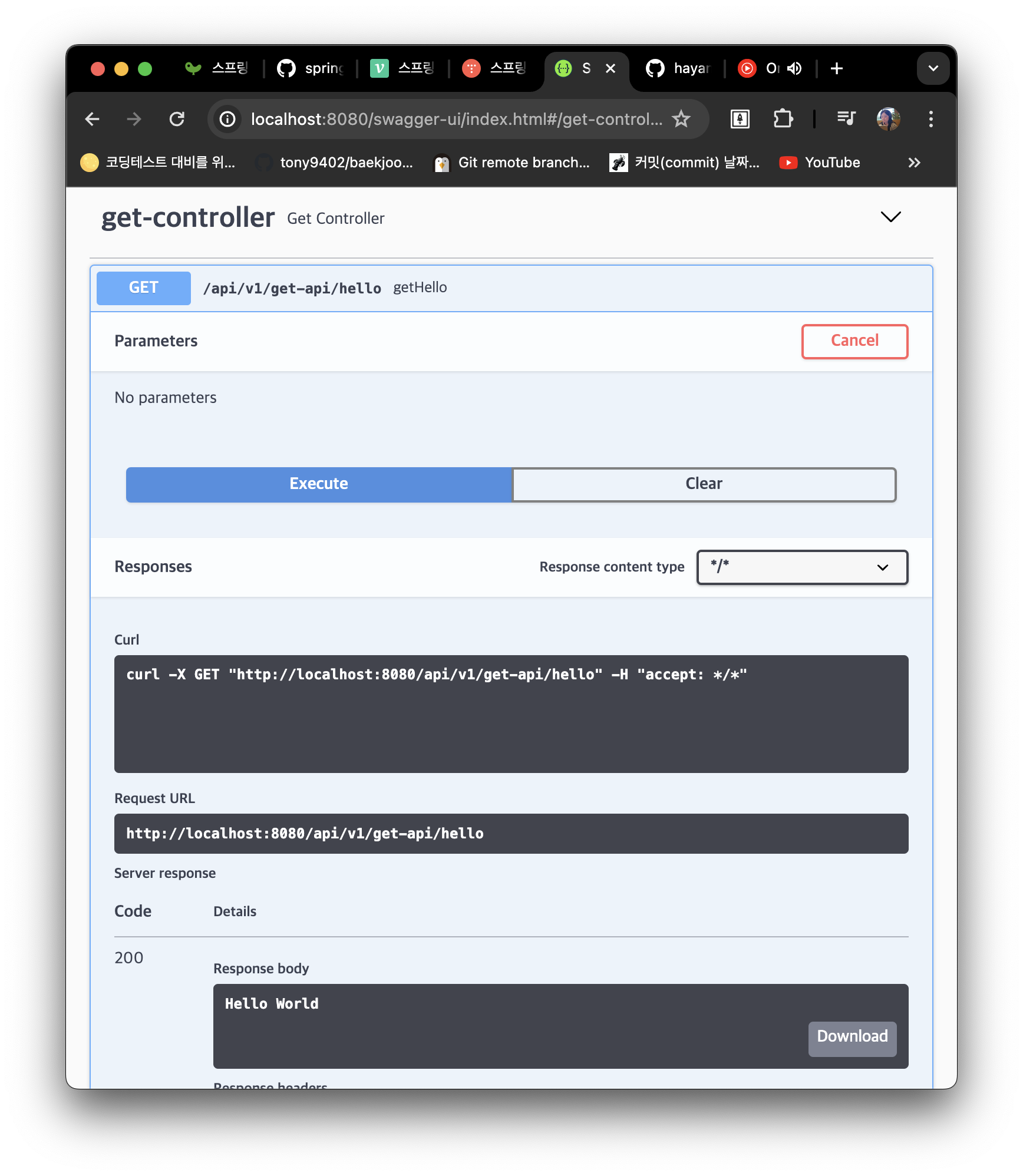
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getHello() {
LOGGER.info("getHello 메서드가 호출되었습니다.");
return "Hello World";
}
// 매개 변수가 없는 GET 메서드 구현
@GetMapping(value = "/name")
public String getName(){
LOGGER.info("getName 메서드가 호출되었습니다.");
return "Flature";
}
...
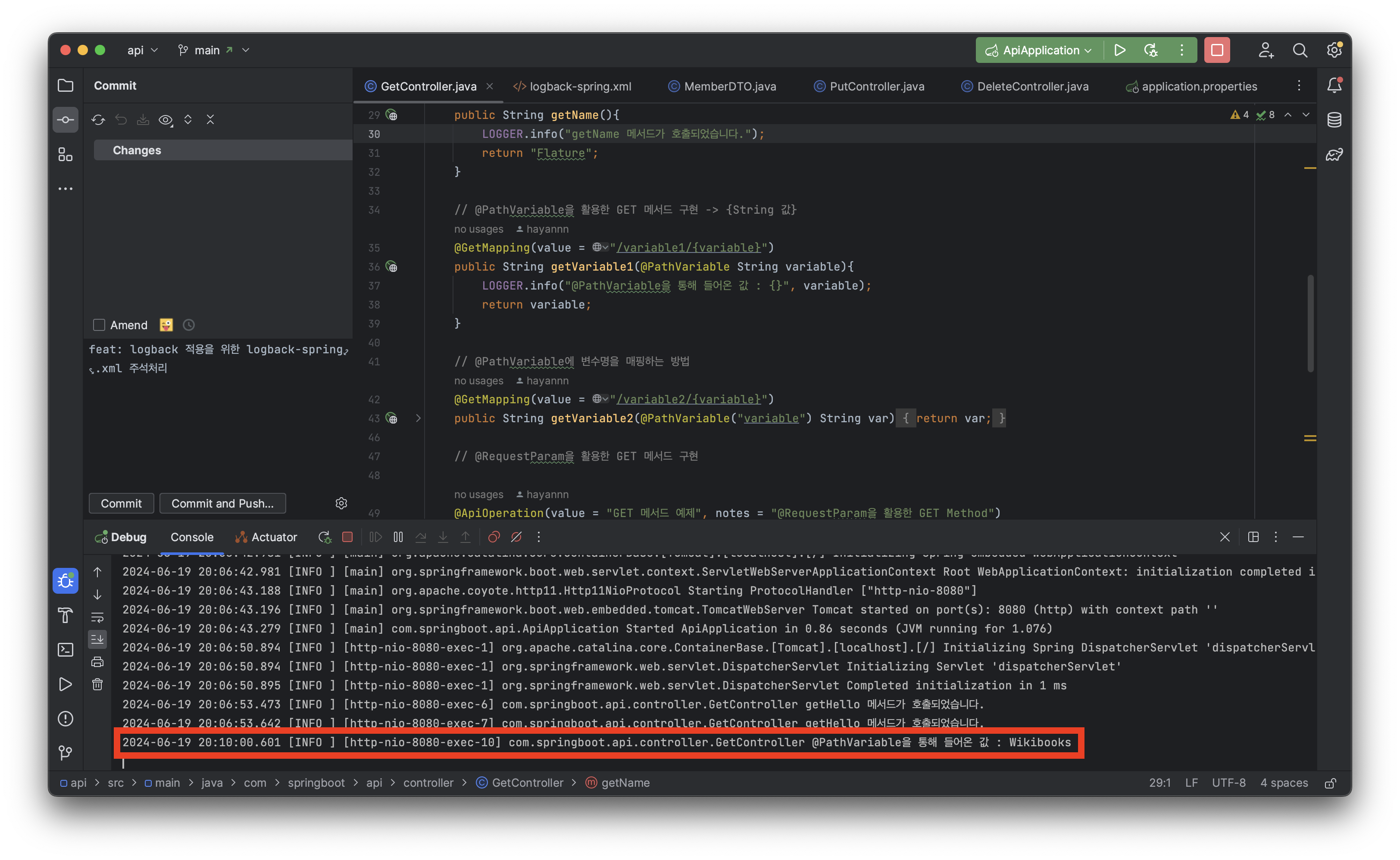
- 변수의 값을 로그로 출력
...
@GetMapping(value = "/variable1/{variable}")
public String getVariable1(@PathVariable String variable){
LOGGER.info("@PathVariable을 통해 들어온 값 : {}", variable);
return variable;
}
...