▣ 조건문
■ if
-
조건을 부여하고 조건이 맞을 때 코드 실행
-
단일 if, if~else, 다중 if 의 3가지 형태
-
자바에서 존재하는 모든 값을 비교할 수 있다.
-
문자열은 같은지만 비교할 수 있다.
⇒ == 또는 변수명equals("비교문자열")
● 단일 if : 조건에 맞을 경우에만 코드 실행
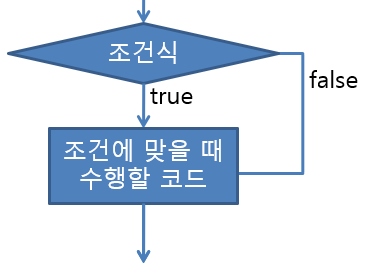
if (조건식) {
조건이 맞을 경우 실행되어야 할 코드
}
▶ 예제 if
/**
* 단일 if문 사용) <br>
* 조건에 맞을 때에만 코드를 실행해야할 때.<br>
* 문법)<br>
* if(조건식)<br>
* 조건에 맞을 때 수행할 문장들,,<br>
*/
public class Uself {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 매개변수로 입력된 수의 절대값
int num = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
System.out.print(num + "의 절대값은");
if (num < 0) { // 보다 작을때 절대값을 붙여줌
num = -num; // 상황에 따라 실행
} // end if
System.out.println(num + " 입니다."); // 반드시 실행
// char형의 변수를 만들고 임의의 문자를 넣는다
// 입력된 문자가 대문자,소문자인 경우에만 해당 문자를 출력하는 코드를 작성.
char c = 'z';
if ((65 >= c && c <= 90) || (c >= 90 && c <= 122)) {
}
System.out.println(c);
// int형의 변수를 만들고 임의의 숫자를 할당한다.
// 입력된 숫자가 0~100사이인 경우에만
// 과락 - 40점이하면
// 다른과목 참조 -60점 이하
// 합격을 출력한다.-60점 이상
int score = 59;
if (score >= 0 && score < 40) {
System.out.println("과락");
}
if (score >= 40 && score < 60) {
System.out.println("다른과목 참조");
}
if (score >= 60 && score <= 100) {
System.out.println("합격");
}
}
}
}
▶ 실행결과
13의 절대값은13 입니다.
z
다른과목 참조
● if ~ else : 둘 중 하나의 코드가 반드시 실행되어야 할 때
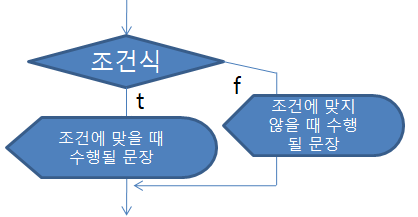
if (조건식) {
조건에 맞을 경우 실행될 코드
} else {
조건에 맞지 않을 경우 실행될 코드
}
▶ 예제 if~else
/**
* if-else<br>
* 둘 중 하나의 코드를 실행하기 위해
*
* @author user
*
*/
public class UseIfelse {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 입력값을 받아 홀수인지 짝수인지 판단하는 코드
int num = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
System.out.println(num + "은(는)");
if (num % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("짝수");
} else {
System.out.println("홀수");
} // end if
// arguments로 자바,C, PyThon이 입력 되었을 때에만 동작하는 코드 작성
// 입력값이 자바라면 1995를 그렇지않으면 1991을 변수에 넣고
// 변수값을 출력해라
if ((args[1].equals("자바")) || args[1].equals("C") || args[1].equals("PyThon")) {
int year = 0;
if (args[1].equals("자바")) {
year = 1995;
} else {
year = 1991;
} // end else
System.out.println(args[1] + "언어는 " + year + "년에 발표되었음.");
} // end if
}// main
}// class▶ 실행결과
12은(는)
짝수
자바언어는 1995년에 발표되었음.
● 다중 if (중첩 if) : 연관성 있는 여러 조건을 비교해야 할 때
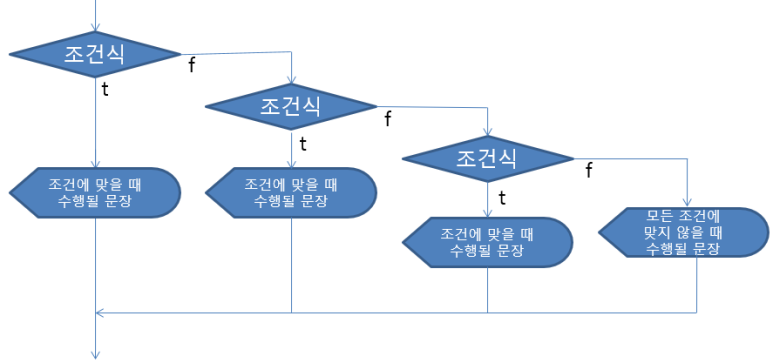
if (조건식) {
조건에 맞을 경우 실행될 코드} else if (조건식) {
첫 번째 조건에 맞지 않지만 두 번째 문장에 맞을 경우 실행될 코드…
} else {
나머지}
▶ 예제 다중 if
/**
* else~if (다중 if)<br>
* 연관된 여러 조건을 비교해야할 때 사용.
*
* @author user
*
*/
public class UseElseIf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 점수의 판정 : 0보다 작은지? 100보다 큰지, 범위안에 있는지?
int score = 101; // -1
System.out.print(score + " 점은");
if (score < 0) {
System.out.println(" 0보다 작을 수 없습니다.");
} else if (score > 100) {
System.out.println(" 100보다 클 수 없습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("입력성공 !!o^^o");
} // end else
// arguments로 자바,C, PyThon이 입력 되었을 때에만 동작하는 코드 작성
// 입력값이 자바라면 1995를 C라면 1972, 그렇지 않다면 1991을 변수에 넣고
// 변수값을 출력 => 다중if를 사용한다
if ((args[0].equals("자바")) || args[0].equals("C") || args[0].equals("PyThon")) {
int year = 0; // 발표 연도를 저장할 변수 초기화
if (args[0].equals("자바")) {
year = 1995;
} else if (args[0].equals("C")) {
year = 1972;
} else {
year = 1991;
}
System.out.println(args[0] + "언어는 " + year + "년에 발표되었음.");
} // end if
// 태어난 해를 입력받아 띠를 출력하는 코드 작성
// 0-원숭이 1-닭 2-개 3-돼지 4-쥐 5-소 6-호랑이 7-토끼 8-용 9-뱀 10-말 11-양
int birth = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); // 입력 인수로부터 생년을 받아 정수로 변환 //int birth=1996;
if (birth % 12 == 0) {
System.out.println(birth + "년생은 원숭이띠 입니다.");
} else if (birth % 12 == 1) {
System.out.println(birth + "년생은 닭띠 입니다.");
} else if (birth % 12 == 2) {
System.out.println(birth + "년생은 개띠 입니다.");
} else if (birth % 12 == 3) {
System.out.println(birth + "년생은 돼지띠 입니다.");
} else if (birth % 12 == 4) {
System.out.println(birth + "년생은 쥐띠 입니다.");
} else if (birth % 12 == 5) {
System.out.println(birth + "년생은 소띠 입니다.");
} else if (birth % 12 == 6) {
System.out.println(birth + "년생은 호랑이띠 입니다.");
} else if (birth % 12 == 7) {
System.out.println(birth + "년생은 토끼띠 입니다.");
} else if (birth % 12 == 8) {
System.out.println(birth + "년생은 용띠 입니다.");
} else if (birth % 12 == 9) {
System.out.println(birth + "년생은 뱀띠 입니다.");
} else if (birth % 12 == 10) {
System.out.println(birth + "년생은 말띠 입니다.");
} else if (birth % 12 == 11) {
System.out.println(birth + "년생은 양띠 입니다.");
}
} // main
} // class▶ 실행결과
101 점은 100보다 클 수 없습니다.
PyThon언어는 1991년에 발표되었음.
1996년생은 쥐띠 입니다.
■ swtich ~ case : 일치하는 정수를 비교할 때 사용
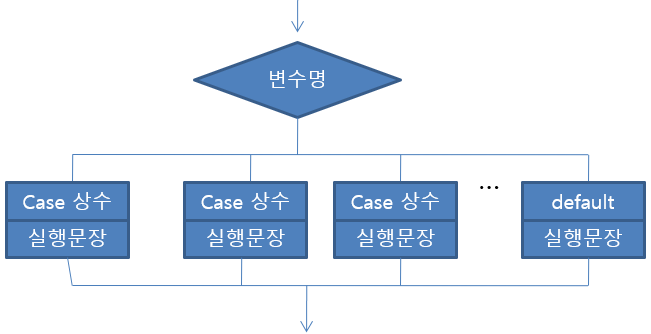
switch (변수명) {
case 상수 :
변수의 값이 상수와 같을 때 실행될 코드case 상수 :
변수의 값이 상수와 같을 때 실행될 코드case 상수 :
변수의 값이 상수와 같을 때 실행될 코드default :
해당하는 case가 없을 때 실행될 코드}
- break; - switch~case, for, while, do~while을 빠져나갈 때 사용(선택사항)
▶ 예제 switch~case
/**
* 일치하는 정수를 비교할 때 사용하는 switch~case
*
* @author user
*
*/
public class UseSwitchCase {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
// break; //switch~case, for, while문 안에서만 사용가능.
// 실행을 멈추고 빠져 나갈 때 사용.
switch (i) { // 일치하는 case를 찾고, 순차적인 흐름을 가진다.
case 0:
System.out.println("영");
case 1:
System.out.println("일");
case 2:
System.out.println("이");
break; // 필요에 따라 정의
case 3:
System.out.println("삼");
default:
System.out.println("해당 case 없음");
} // end switch
char key = 'A'; // byte,short,int,char
switch (key) { // byte,short,int,char를 받을 수 있다. (추후 String 가능)
// case의 상수는 입력되는 데이터형의 범위까지만 사용할 수 있다.
case 'A':
System.out.println("값0");
break;
case 1:
System.out.println("값1");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("값2");
break;
default:
System.out.println("해당 case 없음");
}
String s = "Java"; // Java Compiler가 JDK17이상 부터 가능
switch (s) {
case "Java":
System.out.println("WORA를 지원하는 완벽한 OOP언어");
break;
case "Oracle":
System.out.println("대용량 DBMS");
break;
}
}
}▶ 실행결과
일
이
값0
WORA를 지원하는 완벽한 OOP언어

