다형성(Polymorphism)
하나의 클래스로 인터페이스를 정해두고
그 클래스의 파생을 통해 상속받은 클래스에서 하고자 하는 각각의 고유한 기능을 구현할 수 있다
핵심 부분 : virtual(가상함수)을 쓰는 것! virtual(가상함수)을 사용하지 않을 경우 재정의가 불가하다
ex : virtual int SetPolyPoints(int& points) = 0;
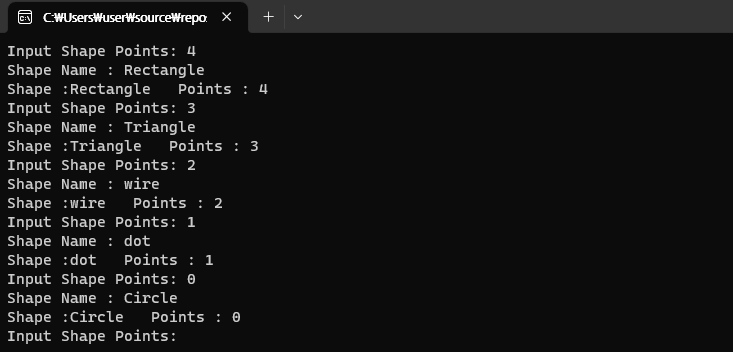
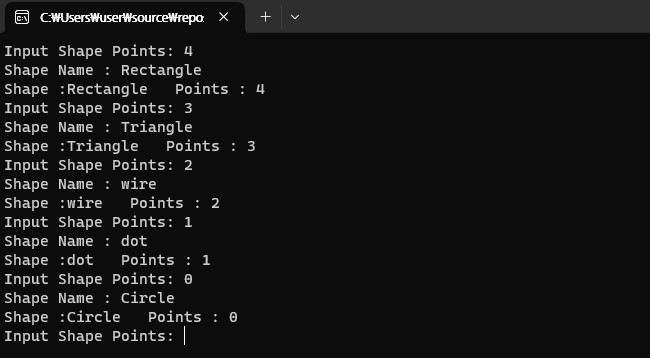
다형성을 이용해서 점의 개수 입력을 통해 도형 이름을 출력하자 (사각형까지만 진행)
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class IShape
{
public:
string name;
protected:
int _points;
public:
void Set(string nameOfShape)
{
name = nameOfShape; //Circle Triangle
}
virtual int SetPolyPoints(int& points) = 0;
void Display()
{
cout << "Shape Name : " << name << endl;
cout << "Shape :" << name << " Points : " << _points << endl;
}
private:
};
class Circle : public IShape
{
public:
int SetPolyPoints(int& points)
{
name = "Circle";
Set(name);
_points = points;
return 0;
}
};
class Triangle : public IShape
{
public:
int SetPolyPoints(int& points)
{
name = "Triangle";
Set(name);
_points = points;
return _points;
}
};
class Rectangle : public IShape
{
public:
int SetPolyPoints(int& points)
{
name = "Rectangle";
Set(name);
_points = points;
return _points;
}
};
class wire : public IShape
{
public:
int SetPolyPoints(int& points)
{
name = "wire";
Set(name);
_points = points;
return _points;
}
};
class dot : public IShape
{
public:
int SetPolyPoints(int& points)
{
name = "dot";
Set(name);
_points = points;
return _points;
}
};
void main()
{
int points;
IShape* pShape[10] = { new Circle(),new dot(),new wire(),new Triangle(),new Rectangle() };
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << "Input Shape Points"; cin >> points;
if (pShape[points] != nullptr)
{
pShape[points]->SetPolyPoints(points);
pShape[points]->Display();
}
}
}