What is Reflection ?
리플렉션(Reflection)은 :
-
객체를 통해 클래스의 정보를 분석해내는 프로그램 기법이다.
-
클래스 파일의 위치나 이름만 있으면 해당 클래스의 정보를 얻어내고, 객체를 생성하는 것 또한 가능하게 해주는 유연한 프로그래밍을 위한 기법이다. 동적으로 객체를 생성하는 것 또한 가능하다.
-
Class 클래스
- Java 에서 사용되는 클래스들에 대한 구조에 관한 정보를 가지고 있는 클래스.
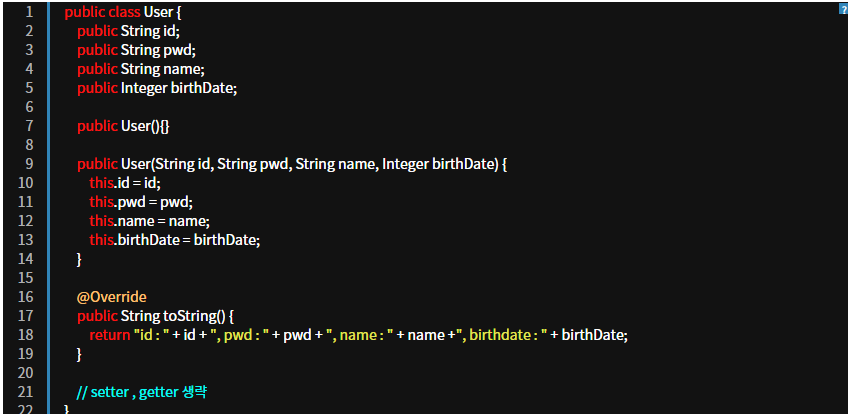
- User 클래스는 4개의 필드, 2개의 생성자, 9개의 메소드(getter/setter 포함)라는 속성을 가지고 있는 클래스로 정의 된다.
- 클래스라는 것 자체도 필드, 생성자, 메소드 등과 같은 속성을 가지고 있다고 생각 할 수 있다.
- 즉, Class 클래스는 이러한 클래스의 구조 자체를 하나의 클래스로 표현해놓은 클래스 이다.
Example
Class Reflection
package kr.klokov.Reflection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class ClassReflection {
private static void getClassHelper(Object o) {
System.out.println(o.getClass());
}
private static void dotClassHelper(Class c) {
System.out.println(c);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// getClass()
getClassHelper("string"); // class java.lang.String
getClassHelper(new HashSet()); // class java.util.HashSet
getClassHelper(new byte[1024]); // class [B
getClassHelper(new ArrayList<String>()); // class java.util.ArrayList
// .class
dotClassHelper(boolean.class); // boolean
dotClassHelper(java.io.File.class); // class java.io.File
}
}
Field Reflection
package kr.klokov.Reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
public class FieldReflection {
public static final int a = 10;
private double b;
protected static final String s = "hello!";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Class c = Class.forName("kr.klokov.Reflection.FieldReflection");
Field[] fields = c.getDeclaredFields();
for(int i = 0; i < fields.length ; i++) {
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Field field = fields[i];
System.out.println("name : " + field.getName());
System.out.println("declare Class : " + field.getDeclaringClass());
System.out.println("type : " + field.getType());
System.out.println("modifier : " + Modifier.toString(field.getModifiers()));
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Method Reflection
package kr.klokov.Reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class MethodReflection {
public int sum(int a, int b) throws NoSuchFieldException {
return a+b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Class c = Class.forName("kr.klokov.Reflection.MethodReflection");
Method[] m = c.getDeclaredMethods();
for (int i = 0 ; i < m.length ; i++) {
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
Method method = m[i];
System.out.println("name : " + method.getName());
System.out.println("declare Class : " + method.getDeclaringClass());
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int j = 0; j < parameterTypes.length ; j++) {
System.out.println("Param : " + parameterTypes[j]);
}
Class[] exceptionTypes = method.getExceptionTypes();
for (int j = 0; j < exceptionTypes.length ; j++) {
System.out.println("Exception : " + exceptionTypes[j]);
}
System.out.println("Return Type : " + method.getReturnType());
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Constructor Reflection
package kr.klokov.Reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
public class ConstructorReflection {
public ConstructorReflection() {}
protected ConstructorReflection(String s, int b) {}
private ConstructorReflection(String s, int b, int c) {}
ConstructorReflection(String a, int b, char c) {}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Class c = Class.forName("kr.klokov.Reflection.ConstructorReflection");
Constructor[] constructors = c.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (int i = 0 ; i < constructors.length ; i++) {
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
Constructor constructor = constructors[i];
System.out.println("name : " + constructor.getName());
System.out.println("declare Class : " + constructor.getDeclaringClass());
System.out.println("modifier : " + Modifier.toString(constructor.getModifiers()));
Class[] parameterTypes = constructor.getParameterTypes();
for (int j = 0 ; j < parameterTypes.length ; j++) {
System.out.println("Params : " + parameterTypes[j]);
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}More (Other post available in HERE)
1. The Reflection API | Java Doc
2. 자바 Reflection 이란?
3. Java Reflection 개념 및 사용법
4. Reflection, Class 클래스
5. String in Java | JournalDev
