
Thread
process
실행 중인 프로그램, 프로그램이 실행되면 OS로 부터 메모리를 할당받아 프로세스 상태가 됨
thread
하나의 프로세스는 하나 이상의 thread를 가지게 되고, 실제 작업을 수행하는 단위는 thread임
multi-threading
- 여러 thread가 동시에 수행되는 프로그래밍,
여러 작업이 동시에 실행되는 효과
- thread는 각각
자신만의 작업 공간을 가짐 ( context )
- 각 thread 사이에서 공유하는 자원이 있을 수 있음 (자바에서는 static instance)
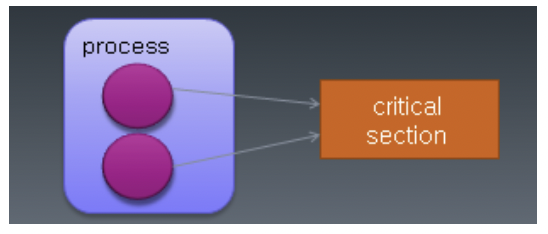
- 여러 thread가 자원을 공유하여 작업이 수행되는 경우 서로 자원을 차지하려는
race condition이 발생할 수 있음
- 이렇게 여러 thread가 공유하는 자원중 경쟁이 발생하는 부분을
critical section이라고 함
critical section에 대한 동기화( 일종의 순차적 수행)를 구현하지 않으면 오류가 발생할 수 있음
Thread 만들기
- Thread 클래스 상속하여 만들기
class MyThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
int i;
for(i=0; i< 200; i++){
System.out.print(i + "\t");
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(thread.currentThread());
MyThread th1 = new MyThread();
th1.start();
MyThread th2 = new MyThread();
th2.start();
}
}- Runnable 인터페이스 구현하여 만들기
자바는 다중 상속이 허용되지 않으므로 이미 다른 클래스를 상속한 경우 thread를 만들기 위해 Runnable interface를 구현하도록 한다.
// Main end가 가장 먼저 출력 -> 멀티쓰레딩 방식이기 때문에!!
class MyThread2 implements Runnable{
public void run(){
int i;
for(i=0; i<200; i++){
System.out.print(i + "\t");
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main start");
MyThread2 mth = new MyThread2();
Thread th1 = new Thread(mth);
th1.start();
Thread th2 = new Thread(new MyThread2());
th2.start();
System.out.println("main end");
}
}Thread Status

조인은 자기 자신을 not runnable 상태로 빠지게 함
Thread 클래스의 여러 메서드들
우선순위
- Thread.MIN_PRIORITY(=1) ~ Thread.MAX_PRIORITY(=10)
- 디폴트 우선순위 : Thread.NORMAL_PRIORITY(=5)
- 우선 순위가 높은 Thread가 CPU의 배분을 받을 확률이 높다
- setPriority()/getPriority()
Thread 우선순위 예제
class PriorityThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
int sum = 0;
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println( t + "start");
for(int i =0; i<=1000000; i++){
sum += i;
}
System.out.println( t.getPriority() + "end");
}
}
public class PriorityTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i;
for(i=Thread.MIN_PRIORITY; i<= Thread.MAX_PRIORITY; i++){
PriorityThread pt = new PriorityThread();
pt.setPriority(i);
pt.start();
}
}
}
join()
- 동시에 두 개 이상의 Thread가 실행 될 때
다른 Thread의 결과를 참조 하여 실행해야 하는 경우join() 함수를 사용
- join() 함수를 호출한 Thread가
not-runnable상태가 감
- 다른 Thread의 수행이 끝나면
runnable 상태로 돌아옴
// join을 하지 않으면 lastTotal에 1~50까지의 합 밖에 안들어감
public class JoinTest extends Thread{
int start;
int end;
int total;
public JoinTest(int start, int end){
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
public void run(){
int i;
for(i = start; i <= end; i++){
total += i;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JoinTest jt1 = new JoinTest(1, 50);
JoinTest jt2 = new JoinTest(51, 100);
jt1.start();
jt2.start();
try{
// main쓰레드가 jt1,jt2 쓰레드가 종료될때 까지 기다림
jt1.join();
jt2.join();
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
int lastTotal = jt1.total + jt2.total;
System.out.println("jt1.total = " + jt1.total);
System.out.println("jt2.total = " + jt2.total);
System.out.println("lastTotal = " + lastTotal);
}
}
interrupt()
다른 Thread에 예외를 발생시키는 interrupt를 보낸다.
Thread가 join(), sleep(), wait() 함수에의해 not-runnable 상태일 때 interrupt() 메서드를 호출하면 다시 runnable 상태가 될 수 있음
Thread 종료하기
Thread를 종료할 때 사용함
무한 반복의 경우 while(flag)의 flag 변수값을 false로 바꾸어 종료를 시킴
Thread 종료하기 예제
세 개의 thread를 만든다.
각각 무한 루프를 수행하게 한다.
작업 내용 this.sleep(100);
‘A’ 를 입력 받으면 첫 번째 thread를
‘B’ 를 입력 받으면 두 번째 thread를
‘C’ 를 입력 받으면 세 번째 thread를
‘M’을 입력 받으면 모든 thread와 main() 함수를 종료한다.
import java.io.IOException;
public class TerminateThread extends Thread {
private boolean flag = false;
int i;
public TerminateThread(String name) {
super(name);
}
public void run() {
while(!flag) {
try {
sleep(100);
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(getName() + "end");
}
public void setFlag(boolean flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
TerminateThread threadA = new TerminateThread("A");
TerminateThread threadB = new TerminateThread("B");
TerminateThread threadC = new TerminateThread("C");
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
threadC.start();
int in;
while(true) {
in = System.in.read();
if(in == 'A') {threadA.setFlag(true);}
else if(in == 'B') { threadB.setFlag(true);}
else if(in == 'C') { threadC.setFlag(true);}
else if(in == 'M') {
threadA.setFlag(true);
threadB.setFlag(true);
threadC.setFlag(true);
break;
} else {
System.out.println("type again");
}
}
System.out.println("main end");
}
}M
main end
Aend
Cend
Bend
멀티 Thread 프로그래밍에서의 동기화
동기화
두 개의 thread 가 같은 객체에 접근 할 경우, 동시에 접근 함으로써 오류가 발생
동기화는 임계영역에 접근한 경우 공유자원을 lock 하여 다른 thread의 접근을 제어
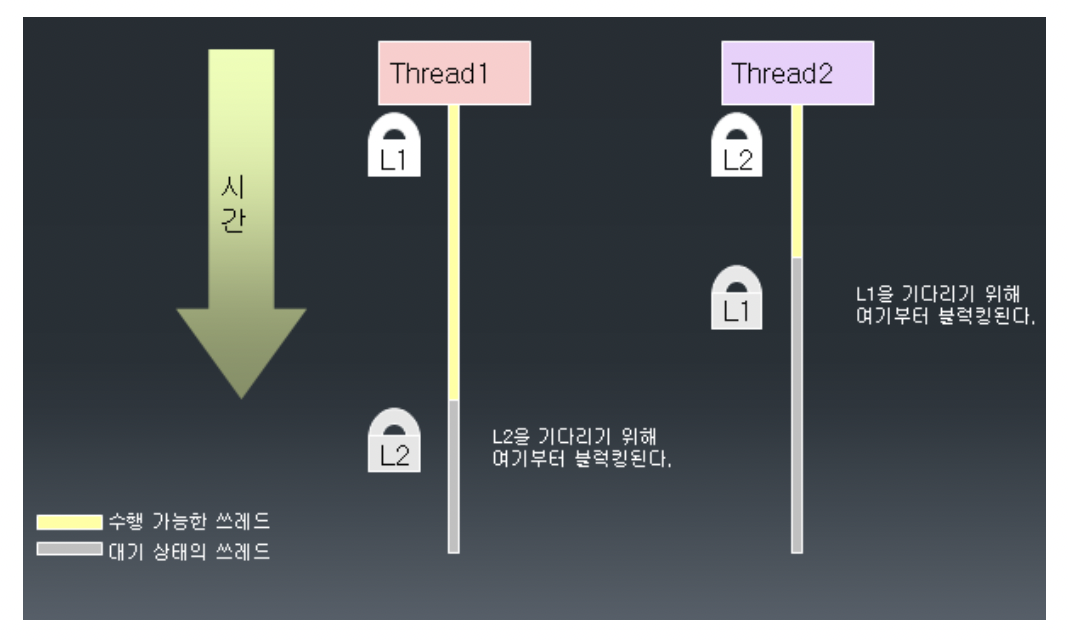
동기화를 잘못 구현하면 deadlock에 빠질 수 있다.
critical section 과 semaphore
critical section은 두 개 이상의 thread가 동시에 접근 하는 경우 문제가 생길 수 있기 때문에 동시에 접근할 수 없는 영역
semaphore는 특별한 형태의 시스템 객체이며get/release두 개의 기능이 있다.
- 한 순간 오직 하나의 thread 만이 semaphore를 얻을 수 있고, 나머지 thread들은 대기(blocking) 상태가 된다.
- semaphore를 얻은 thread 만이 critical section에 들어갈 수 있다.

class Bank{
private int money = 10000;
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public synchronized void saveMoney(int save) {
// 어떠한 쓰레드가 syncrhonized 되어있는 메서드를 수행하는 동안
// 이 메서드가 포함 된 객체의 인스턴스에 Lock을 건다!!!!!!!!!
int m = this.getMoney();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
setMoney(m + save);
}
public synchronized void minusMoney(int minus) {
int m = this.getMoney();
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
setMoney(m-minus);
}
}
class Park extends Thread{
public void run() {
System.out.println("start save");
SyncMain.myBank.saveMoney(3000);
System.out.println("saveMoney(3000):"+SyncMain.myBank.getMoney());
}
}
class ParkWife extends Thread{
public void run() {
System.out.println("start minus");
SyncMain.myBank.minusMoney(1000);
System.out.println("minusMoney(1000):"+SyncMain.myBank.getMoney());
}
}
public class SyncMain {
//myBank가 SharedResource!
public static Bank myBank = new Bank();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Park p = new Park();
p.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
ParkWife pw = new ParkWife();
pw.start();
}
}자바에서는 synchronized 메서드나 synchronized 블럭을 사용
synchronized 블럭
-> 현재 객체 또는 다른 객체를 lock으로 만든다.
synchronized(참조형 수식) {
수행문;
}public void saveMoney(int money){
// 이 메서드 실행 시 접근을 제한하고자 하는 객체를 넣어줌!!
synchronized(this){
...
}
}class Park extends Thread{
public void run(){
synchronized(SyncMain.myBank){
System.out.println("start save")
...
}
}
}
결과가 에상대로 가장 잘나옴!synchronized 메서드
객체의 메소드에 synchronized 키워드 사용
현재 이 메서드가 속해있는 객체에 lock을 건다.
자바에서는 deadlock을 방지하는 기술이 제공되지 않으므로 되도록이면 synchronized 메서드에서 다른 synchronized 메서드는 호출하지 않도록 한다.
deadlock의 예
wait()/notify() 메서드를 활용한 동기화 프로그래밍
리소스가 어떤 조건에서 더 이상 유효하지 않은 경우 리소스를 기다리기 위해 Thread 가 wait() 상태가 된다.
-> wait() 상태가 된 Thread은 notify() 가 호출 될 때까지 기다린다.
유효한 자원이 생기면 notify()가 호출되고 wait() 하고 있는 Thread 중 무작위로 하나의 Thread를 재시작 하도록 한다.
notifyAll()이 호출되는 경우 wait() 하고 있는 모든 Thread가 재시작 된다.
이 경우 유효한 리소스만큼의 Thread만이 수행될 수 있고 자원을 갖지 못한 Thread의 경우는 다시 wait() 상태로 만든다.
자바에서는 notifyAll() 메서드의 사용을 권장한다.
도서관에서 책을 빌리는 예제
import java.util.ArrayList;
class FastLibrary{
public ArrayList<String> shelf = new ArrayList<String>();
public FastLibrary() {
shelf.add("태백산맥 1");
shelf.add("태백산맥 2");
shelf.add("태백산맥 3");
}
public synchronized String lenBook() throws InterruptedException{
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
if(shelf.size() == 0) {
System.out.println(t.getName() + "waiting start");
wait();
System.out.println(t.getName() + "waiting end");
}
String book = shelf.remove(0);
System.out.println(t.getName() + ":" + book + "lend");
return book;
}
public synchronized void returnBook(String book) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
shelf.add(book);
notify();
System.out.println(t.getName() + ":" + book + "return");
}
}
class Student extends Thread{
public void run() {
try {
String title = LibraryMain.library.lenBook();
if(title == null) return;
sleep(5000);
LibraryMain.library.returnBook(title);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
public class LibraryMain {
public static FastLibrary library = new FastLibrary();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student std1 = new Student();
Student std2 = new Student();
Student std3 = new Student();
Student std4 = new Student();
Student std5 = new Student();
Student std6 = new Student();
std1.start();
std2.start();
std3.start();
std4.start();
std5.start();
std6.start();
}
}notifyAll() 사용 경우
public synchronized String lendBook() throws InterruptedException{
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// 책을 못빌리더라도 계속 웨이팅 상태에 있게 하기 위해 if대신 while
while( shelf.size() == 0 ){
System.out.println(t.getName() + " waiting start");
wait();
System.out.println(t.getName() + " waiting end");
}
String book = shelf.remove(0);
System.out.println(t.getName() + ": " + book + " lend");
return book;
}
}
public synchronized void returnBook(String book){
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
shelf.add(book);
notifyAll();
System.out.println(t.getName() + ": " + book + " return");
}
