
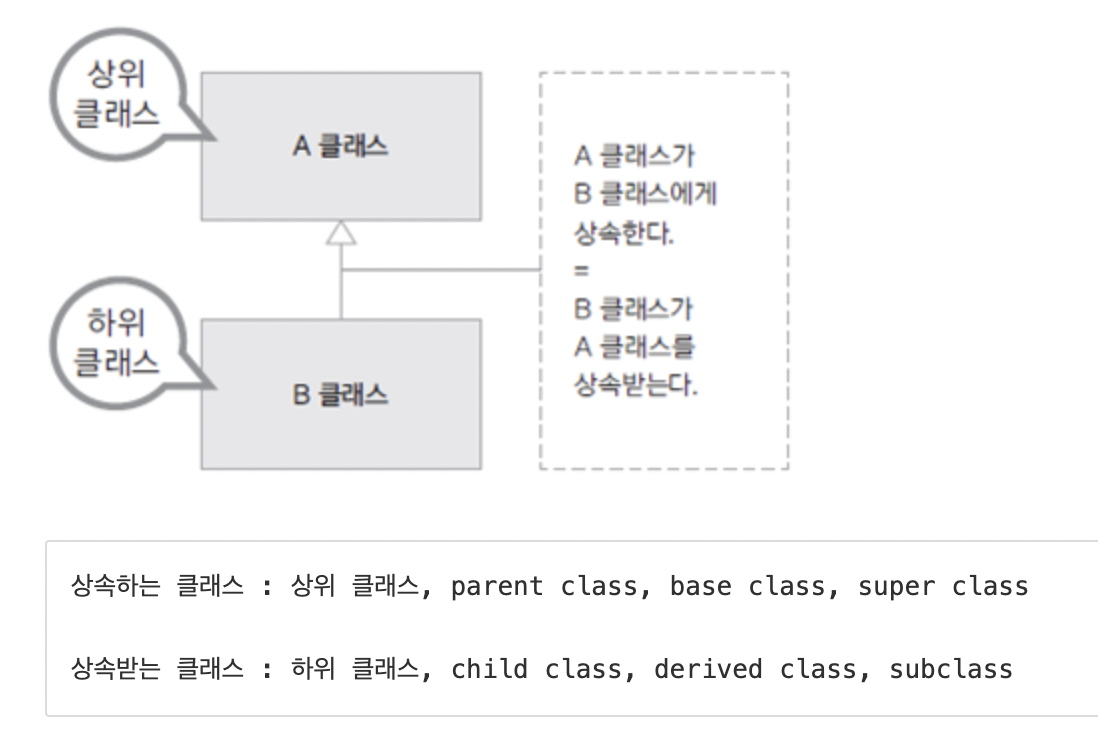
클래스 상속
새로운 클래스 정의 시 이미 구현된 클래스를 상속받아 속성이나 기능을 확장하여 클래스 구현
class B extends A{
{
// 자바는 단일 상속만을 지원- 상위 클래스는 하위 클래스 보다 더 일반적인 개념과 기능을 가짐
- 하위 클래스는 상위 클래스 보다 더 구체적인 개념과 기능을 가짐
- 하위 클래스가 상위 클래스의 속성과 기능을 확장 (extends)한다는 의미
상속을 이용한 멤버십 클래스 구현

일반 고객의 클래스 구현
고객의 속성 : 고객 아이디, 등급, 보너스 포인트, 포인트 적립 비율
package ch04;
public class Customer {
// protected -> 외부 클래스에서 접근 x, 하위 클래스 접근 가능
protected int customerID;
protected String customerName;
protected String customerGrade;
int bonusPoint;
double bonusRatio;
/* public Customer()
{
customerGrade = "SILVER";
bonusRatio = 0.01;
System.out.println("Customer() 호출");
}
*/
public Customer(int customerID, String customerName) {
this.customerID = customerID;
this.customerName = customerName;
}
public int calcPrice(int price) {
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
return price;
}
public int getCustomerID() {
return customerID;
}
public void setCustomerID(int customerID) {
this.customerID = customerID;
}
public String getCustomerName() {
return customerName;
}
public void setCustomerName(String customerName) {
this.customerName = customerName;
}
public String getCustomerGrade() {
return customerGrade;
}
public void setCustomerGrade(String customerGrade) {
this.customerGrade = customerGrade;
}
public String showCustomerInfo() {
return customerName + "님의 등급은 " + customerGrade + "이며, 보너스 포인트는 " + bonusPoint + "입니다 ";
}
}
우수 고객 구현
-
제품을 살때 10%를 할인해 줌
-
보너스 포인트는 제품 가격의 5%를 적립해 줌
-
담당 전문 상담원이 배정됨
package ch04;
public class VIPCustomer extends Customer{
private int agentID;
double salesRatio;
/* public VIPCustomer() {
// super(); 디폴트 값으로 자동으로 들어감
super(0,"no-name");
customerGrade = "VIP ";
bonusRatio = 0.05;
salesRatio = 0.1;
System.out.println("VIPCustomer() 호출");
}
*/
public VIPCustomer(int customerID, String customerName) {
super(customerID, customerName);
customerGrade = "VIP";
bonusRatio = 0.05;
salesRatio = 0.1;
}
@Override
public int calcPrice(int price) {
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
price -= price * salesRatio;
return price;
}
public void setAgentID(int agentID) {
this.agentID = agentID;
}
public int getAgentID() {
return agentID;
}
}
고객 테스트 클래스 구현
package ch04;
public class CustomerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer customerLee = new Customer(10010, "이순신");
customerLee.bonusPoint = 1000;
int price = customerLee.calcPrice(1000);
System.out.println(customerLee.showCustomerInfo() + price);
VIPCustomer customerKim = new VIPCustomer(10020, "김유신");
customerKim.bonusPoint = 10000;
price = customerKim.calcPrice(1000);
System.out.println(customerKim.showCustomerInfo() + price);
// Customer vc = new VIPCustomer(12345, "noname");
// vc는 일반 고객의 멤버 변수만을 사용가능함
Customer vc = new VIPCustomer(12345, "noname");
vc.calcPrice(1000);
System.out.println(vc.calcPrice(1000));
}
}
멤버십 클래스 이해를 위한 개념
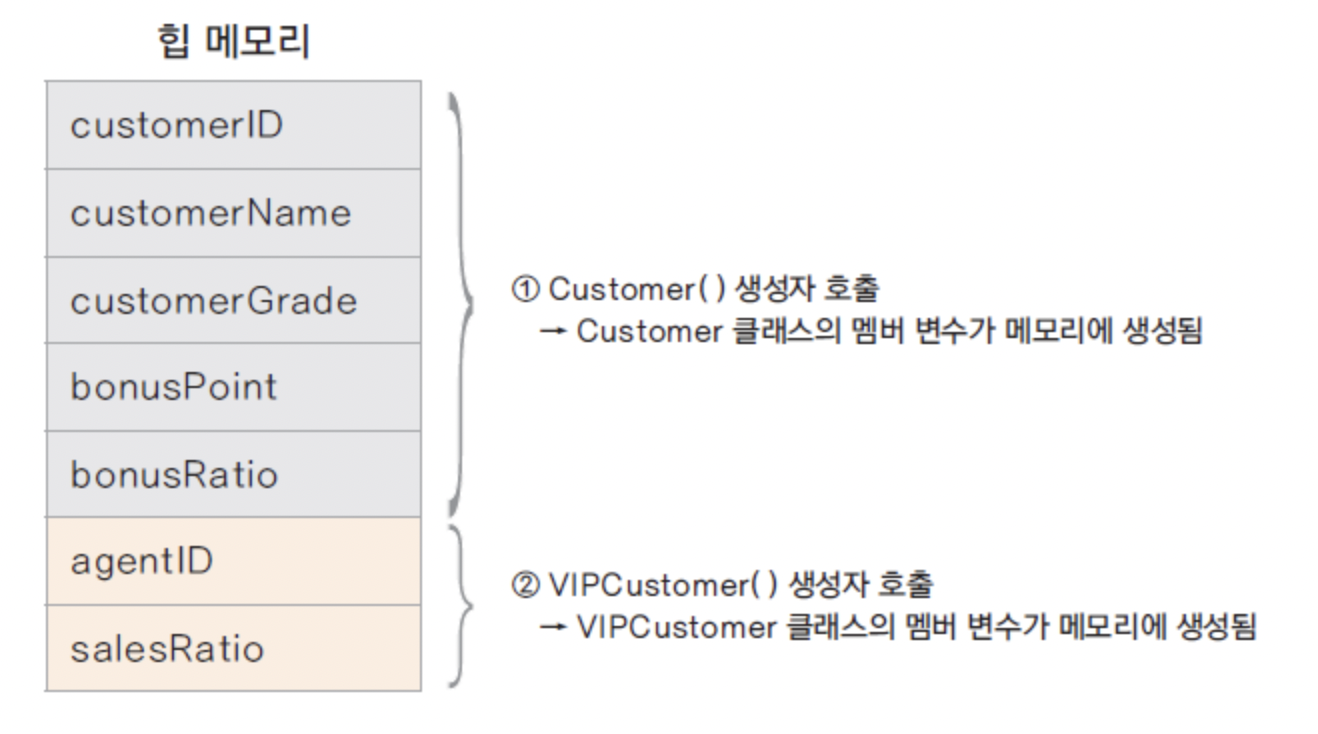
하위클래스 생성 되는 과정
- 하위 클래스를 생성하면 상위 클래스가 먼저 생성 됨
- new VIPCustomer()를 호출하면 Customer(), 즉
상위 클래스 생성자가 먼저 호출 됨
- 클래스가 상속 받은 경우 하위 클래스의 생성자에서는 반드시 상위 클래스의 생성자를 호출 함
super
- 하위 클래스에서 가지는 상위 클래스에 대한 참조 값
- super()는 상위 클래스의 기본 생성자를 호출 함
- 하위 클래스에서 명시적으로 상위 클래스의 생성자를 호출하지 않으면 super()가 호출 됨
- 상위 클래스의 기본 생성자가 없는 경우 ( 다른 생성자가 있는 경우 ) 하위 클래스에서는 생성자에서는 super를 이용하여
명시적으로 상위 클래스의 생성자를 호출 함
- super는 생성된 상위 클래스 인스턴스의 참조 값을 가지므로 super를 이용하여 상위 클래스의 메서드나 멤버 변수에 접근할 수 있음
상속에서 인스턴스 메모리의 상태
항상 상위 클래스의 인스턴스가 먼저 생성되고, 하위 클래스의 인스턴스가 생성 됨
upcasting이란?
출처 : https://velog.io/@smallcherry/Java-UpCastingAndDownCasting
casting == 형변환
Parent
|
ChildParent형의 객체를 생성하고자 할 때, Child형의 정보를 좌변에 제공
Parent p = new Child();상위클래스인 좌변이 요구하는 정보는 그의 하위클래스인 우변은 당연히 전부 가지고있기 때문에 위 문장은 옳은 문장
업캐스팅이란 하위 클래스의 정보를 담을 수 있는 객체에 상위 클래스의 자료형을 부여해서, 상위클래스처럼 사용하게 하는 것
downcasting이란?
업캐스팅된 객체의 자료형을 하위클래스의 정보를 담는 기능을 하도록 자료형을 되돌려 놓는 것!
Parent p = new Child(); //업캐스팅 -p는 Parent형.
Child c = (Child) p; //다운캐스팅! -p는 Child형.형 변환과 메모리
Customer vc = new VIPCustomer(); 에서 vc가 가리키는 것은?
-
VIPCustomer() 생성자에 의해 VIPCustomer 클래스의
모든 멤버 변수에 대한 메모리는 생성됨 -
그러나 변수의 타입이 Customer 이므로
실제 접근 가능한 변수나 메서드는 Customer의 변수와 메서드임
하위 클래스에서 메서드 재정의(overriding)
상위 클래스에 정의된 메서드의 구현 내용이 하위 클래스에서 구현할 내용과 맞지 않는 경우 하위 클래스에서 동일한 이름의 메서드를 재정의
@Override
public int calcPrice(int price) {
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
return price - (int)(price * salesRatio);
}
@ == 어노테이션
컴파일러에게 특별한 정보를 제공할 때 사용
형 변환과 오버라이딩 메서드 호출
Customer vc = new VIPCustomer();
vc 변수의 타입은 Customer지만 인스턴스의 타입은 VIPCustomer 임
-
자바에서는 항상
인스턴스의 메서드가호출 됨 (가상메서드의 원리) -
자바의 모든 메서드는
가상 메서드(virtual method)
Java 메모리 구조
출처 : https://coding-factory.tistory.com/830
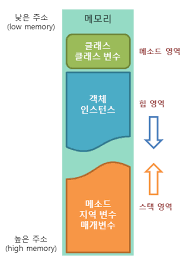
메서드 영역
static 영역이라고도 하며 전역 변수와 정적 멤버변수(static)가 저장되는 영역
스택(stack) 영역
-
지역변수,인자값,리턴값이 저장되는 영역 -
메서드 안에서 사용되는 기본형 변수들이 값과 함께 저장
-
Heap 영역에 생성되는
객체들을 참조하는 주소값이 할당
힙(Heap) 영역
- 자바의 모든
인스턴스 변수(멤버 변수)들이 저장되는 영역 =>new사용하여 객체 생성 시 힙 영역에 저장
스레드(thread)
프로세스의 자원을 이용해서 실제로 작업을 수행하는 주체
멀티 스레드에서의 메모리 사용
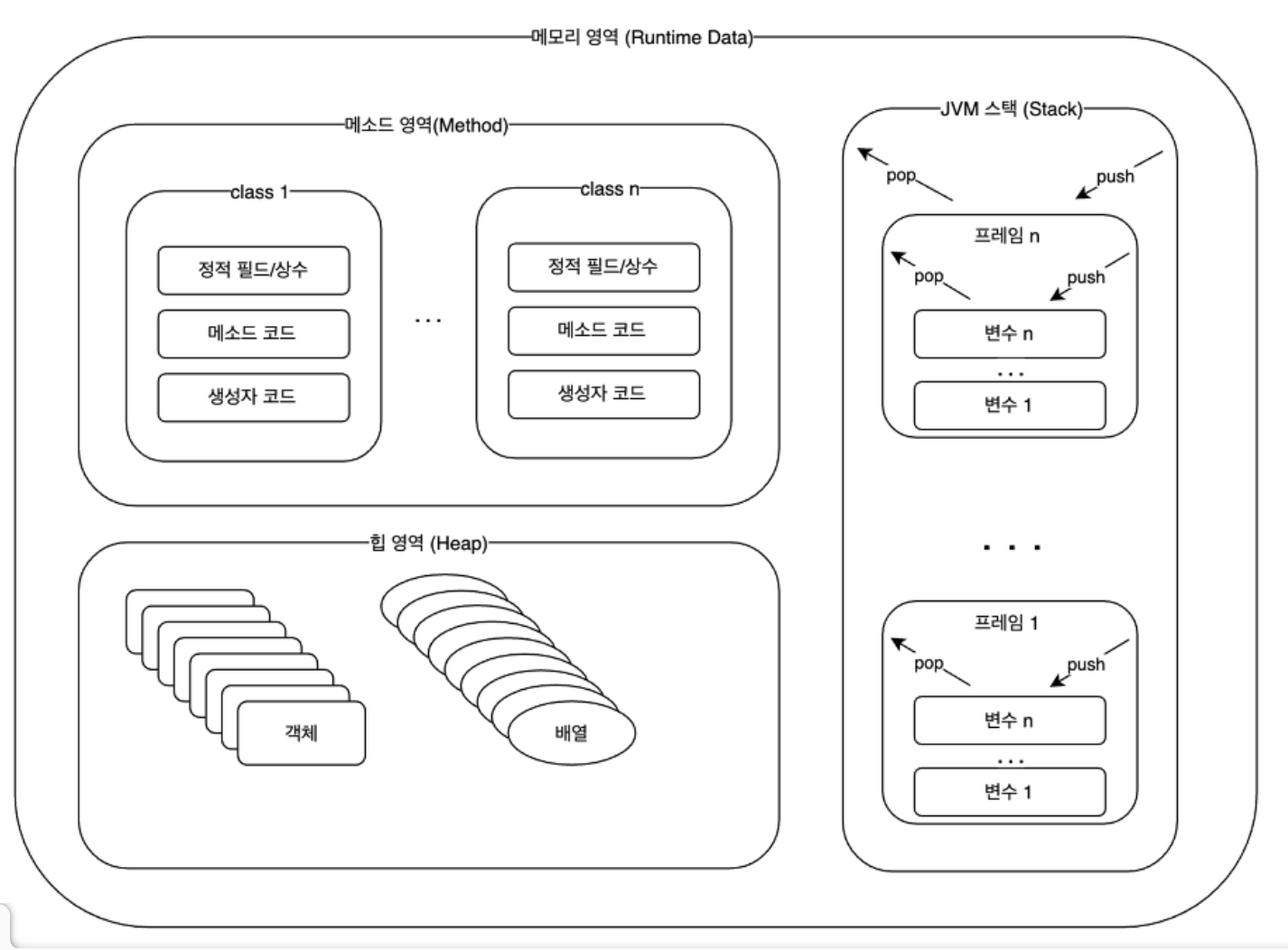
메모리 영역와 힙 영역은 모든 스레드가 공유
=> 전역변수는 어디서는 접근 가능, Heap 영역의 객체를 주기적으로 삭제해주어야 함
but 스택의 경우 스레드 마다 하나씩 생성
package ch00;
public class Employee {
String name;
Integer salary;
Integer sales;
Integer bonus;
public Employee(String name, Integer salary, Integer sales) {
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
this.sales = sales;
}
public class Test{
static int BONUS_PERCENTAGE = 10;
static int getBonusPercentage(int salary) {
int percentage = salary * BONUS_PERCENTAGE / 100;
return percentage;
}
static int findEmployeeBonus(int salary, int no0fSales) {
int bonusPercentage = getBonusPercentage(salary);
int bonus = bonusPercentage * no0fSales;
return bonus;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee john = new Employee("John", 5000, 5);
john.bonus = findEmployeeBonus(john.salary, john.sales);
System.out.println(john.bonus);
}
}
}
