AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)
관점 지향 프로그래밍
스프링 어플리케이션은 대부분 특별한 경우를 제외하고는 MVC 웹 어플리케이션에서는 Web Layer, Business Layer(로직), Data Lagyer 로 정의
- Web Layer : REST API를 제공하며, Client 중심의 로직 적용
- Business Layer : 내부 정책에 따른 logic을 개발하며, 주로 해당 부분을 개발
- Data Layer : 데이터 베이스 및 외부와의 연동을 처리
스프링 DI 가 의존성(new) 에 대한 주입이라면 스프링 AOP 는 로직(code) 주입이라고 볼 수 있다.
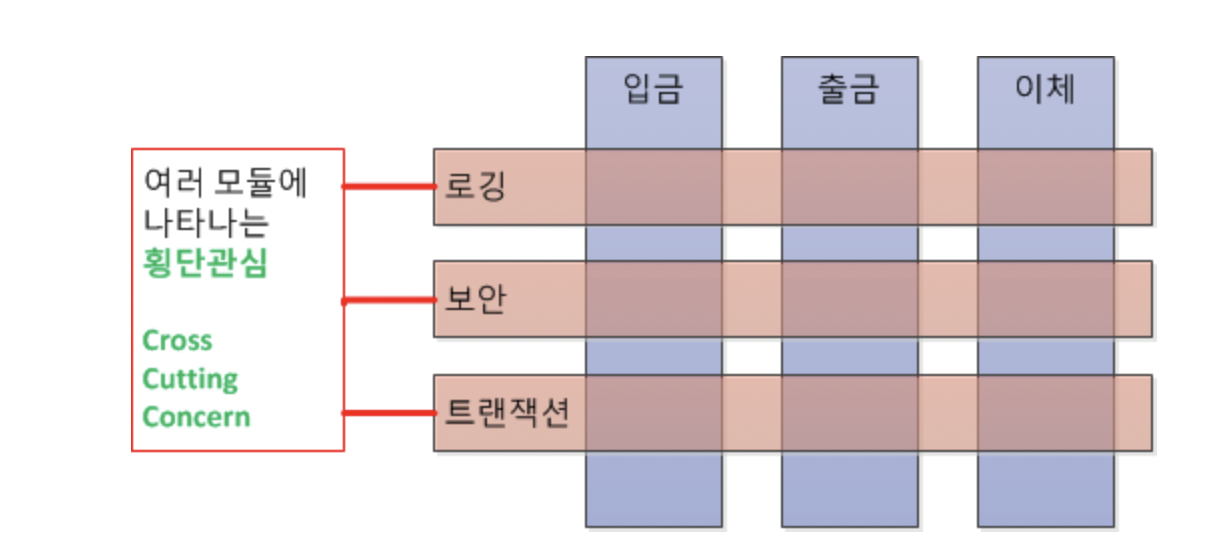
로깅, 보안, 트랜잭션 등등 다수의 모듈에서 반복적으로 나타나는 부분이 존재하는데 이것이 횡단관심

빨간색 부분 : 횡단 관심 사항
파란색 부분 : 핵심 관심 사항
이해를 위한 예시
출처 : https://expert0226.tistory.com/200


package aop001;
public class Boy {
public void housework() {
System.out.println("열쇠로 문을 열고 집에 들어간다.");
try {
System.out.println("컴퓨터로 게임을 한다.");
} catch (Exception ex) {
if(ex.getMessage().equals("집에 불남")) {
System.out.println("119 에 신고한다.");
}
} finally {
System.out.println("소등하고 잔다.");
}
System.out.println("자물쇠를 잠그고 집을 나선다.");
}
}package aop001;
public class Girl {
public void housework() {
System.out.println("열쇠로 문을 열고 집에 들어간다.");
try {
System.out.println("요리를 한다.");
} catch (Exception ex) {
if(ex.getMessage().equals("집에 불남")) {
System.out.println("119 에 신고한다.");
}
} finally {
System.out.println("소등하고 잔다.");
}
System.out.println("자물쇠를 잠그고 집을 나선다.");
}
}package aop001;
public class Start {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boy romeo = new Boy();
Girl juliet = new Girl();
romeo.housework();
juliet.housework();
}
}여기서 로직을 주입 할려면 어디에 해야할까? -> 객체 지향에서 코드는 메서드 안
메서드에서 코드를 주입할 수 있는 곳은 몇군데 일까?
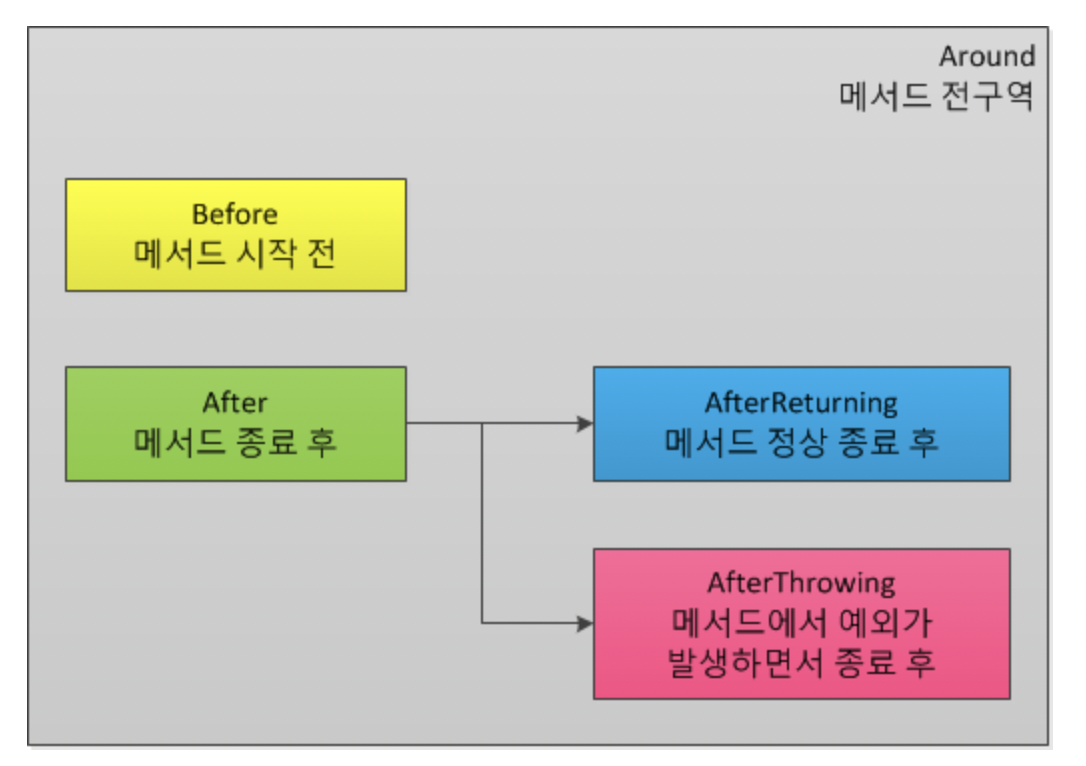
5군데 입니다. Around, Before, After, AfterReturning, AfterThrowing
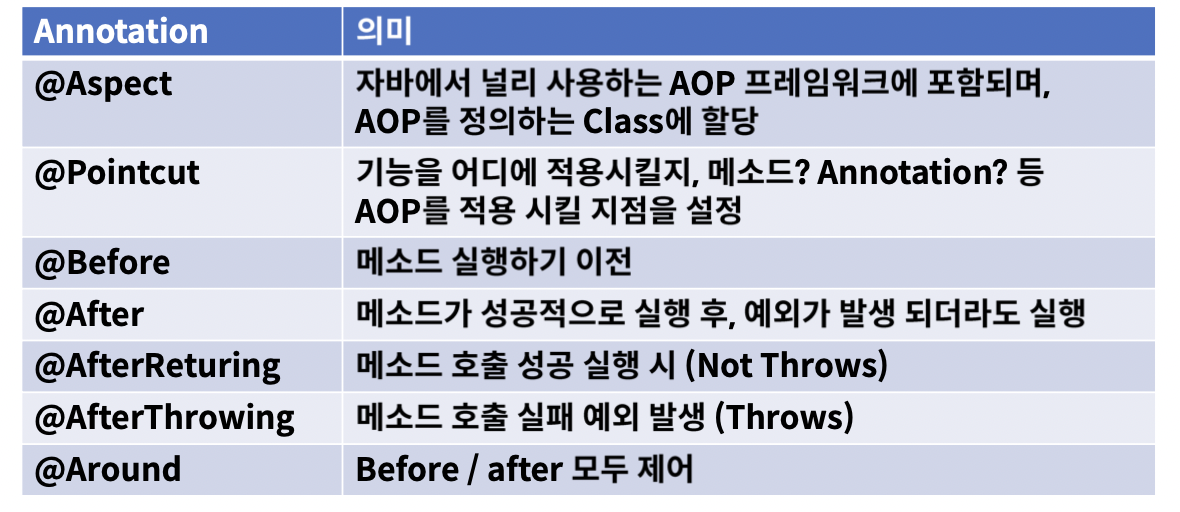
주요 어노테이션
코드 예시
시작전 우선 build.gradle의 Dependency에 aop 추가
ex) org.springframework.boot::spring-boot-starter-aop
user dto
package com.example.aop.dto;
public class User {
private String id;
private String password;
private String email;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
ParameterAOP : @Aspect 및 Before, AfterReturning 사용
package com.example.aop.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Aspect
@Component
public class ParameterAop {
// 여러 수식이 있기에 모르는건 잘 찾아보자
// controller 패키지 하위에 있는 모든 메서드를 aop로 보겠다
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut(){}
// 메서드가 실행 되기 전 넘어가는 매개변수
@Before("cut()") // 위에 메서드 넣어주고 Pointcut이 실행되기 이전에 이 메서드를 실행하겠다
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
System.out.println(method.getName());
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); // 메서드의 매개변수 배열 받음
for(Object obj : args){
System.out.println("type : " + obj.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("value : " + obj);
}
}
// 메서드 성공적 실행 후 리턴될 때 , 받고 싶은 객체의 이름을 넣었음
@AfterReturning(value = "cut()", returning = "returnObj")
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object returnObj){
System.out.println("return obj");
System.out.println(returnObj);
}
}
package com.example.aop.controller;
import com.example.aop.dto.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class RestAPIController {
//http://localhost:9090/api/get/100?name=steve
// 밑에 각 메서드 마다 System.out.println으로 로그 찍는 것을 한곳에 모을 다 있다
// @GetMapping("/get/{id}")
// public void get(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestParam String name){
// System.out.println("get method");
// System.out.println("get method" + id);
// System.out.println("get method" + name);
// }
//
// @PostMapping("/post")
// public void post(@RequestBody User user){
// System.out.println("post method: "+ user);
// }
// 두 메서드다 반환 타입 바꿈
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
public String get(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestParam String name){
// System.out.println("get method: ");
// System.out.println("get method: " + id);
// System.out.println("get method: " + name);
return id + " "+ name;
}
@PostMapping("/post")
public User post(@RequestBody User user){
// System.out.println("post method: "+ user);
return user;
}
}
get
type : Long
value : 100
type : String
value : steve
return obj
100 steve
post
type : User
value : User{id='steve1', password='123123213', email='123123@gmail.com'}
return obj
User{id='steve1', password='123123213', email='123123@gmail.com'}메서드실행시간으로 서버의 상태및 부하를 로깅으로 나타내는 코드 추가
Timer Annotation 생성
package com.example.aop.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 런타임 중 적용 되게끔
public @interface Timer {
}TimerAOP
package com.example.aop.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
@Aspect
@Component // @Bean 같은 경우엔 클래스에 붙일순 없다
public class TimerAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut(){}
// Timer가 설정된 메서드만 로깅을 할거야!
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.aop.annotation.Timer)")
private void enableTimer(){}
// 아까처럼 Before,After로는 Time을 공유 불가
// 업무 로직 실행전과 실행 후 모두 실행(Around)
@Around("cut() && enableTimer()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// delete 메서드에 그대로 코드를 작성하였다면 이부분만 Thread.sleep(1000*2)
// post,get에도 다 넣어야됨 -> 비즈니스 로직 뿐 아니라 불필요 한거까지 넣는 것
Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); // 메서드가 여기서 실행됨
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println("total time" + stopWatch.getTotalTimeSeconds());
}
}
@Timer
@DeleteMapping("/delete")
public void delete() throws InterruptedException {
// db logic 처리하는데 2초 정도 걸린다 가정
// 필요한 서비스 로직만 여기에 작성한다고 생각하자
Thread.sleep(2000);
}외부에서 암호화된 값이 들어오는 경우
-> 코드로 복호화X, AOP단에서 복호화 된 채로 들어오게 할 수 있다, 내보낼때도 특정 회원사한테 보낸다고 하면 AOP단에서 변경하여 보내게끔 할 수 있다
package com.example.aop.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Decode {
}package com.example.aop.aop;
import com.example.aop.dto.User;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Base64;
@Aspect
@Component
public class DecodeAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut(){}
// Timer가 설정된 메서드만 로깅을 할거야!
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.aop.annotation.Decode)")
private void enableDecode(){}
@Before("cut() && enableDecode()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
// 1. 메서드 파라미터 중에 내가 아는 User라는 클래스가 매칭이되면
// 2. User라는 클래스로 형변환을 시키고 기존에 BASE64로 인코딩 되어있는 이메일 꺼냄
// 3. 다시 decoding을 시켜서 세팅을 해줌
// 컨트롤러 코더에서는 디코딩 코드 만들필요 X
for(Object arg : args){
if(arg instanceof User){
User user = User.class.cast(arg);
String base64Email = user.getEmail();
String email = new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode(base64Email), "UTF-8");
user.setEmail(email);
}
}
}
@AfterReturning(value = "cut() && enableDecode()", returning = "returnObj")
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object returnObj){
if(returnObj instanceof User){
User user = User.class.cast(returnObj);
String email = user.getEmail();
String base64Email = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(email.getBytes());
user.setEmail(base64Email);
}
}
}
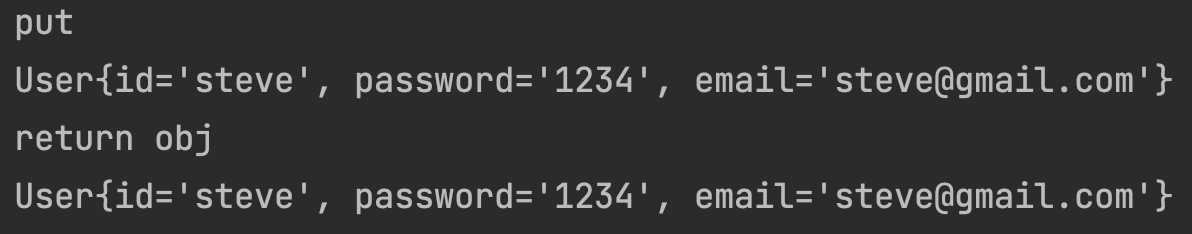
@Decode
@PutMapping("/put")
public User put(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println("put");
System.out.println(user);
return user;
}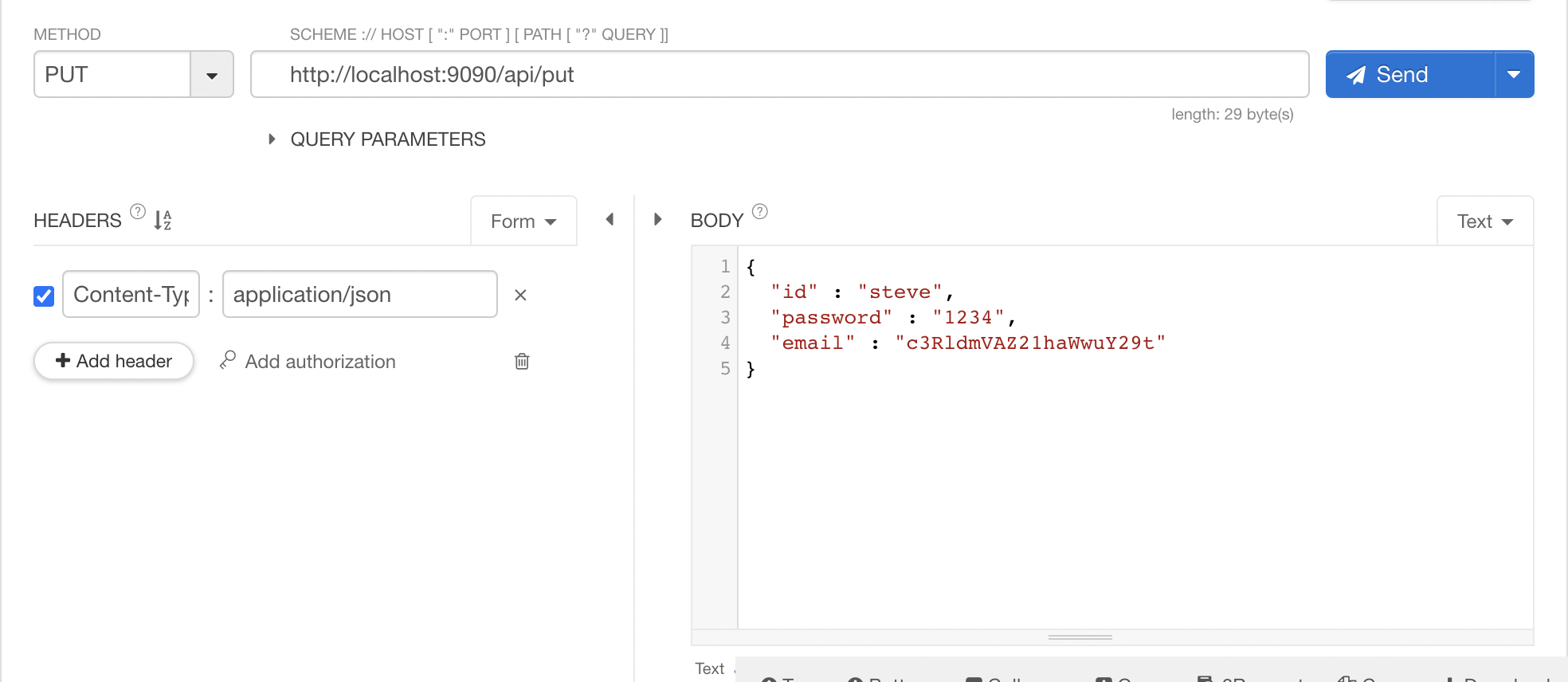
디코드 되어 잘 들어오는 것을 볼 수 있음!!