
ACL 을 이용한 도메인 객체 권한 관리
도메인 객체에 대한 접근 권한은 hasPermission() 메소드를 이용해 판별하면 편리
-> 그런데, 모든 도메인 객체에 대해 이런 접근 권한을 처음부터 설계하려면 많은 노하우가 필요
-> 스프링 시큐리티는 이를 위해 spring-security-acl 라이브러리를 제공
Spring Security 스펙에서 ACL을 설명하기 위해 만든 권한 체크의 3요소
- 누가 (Authentication)
- 어떤 메소드에서 (MethodInvocation)
- 어떤 객체에 접근할 수 있는지 (DomainObject) => ACL
이를 위해, spring-security-acl 모듈이 간단한 접근권한과 관련해 표준 DB 모델을 만들어서 제공
ACL 도메인 모델
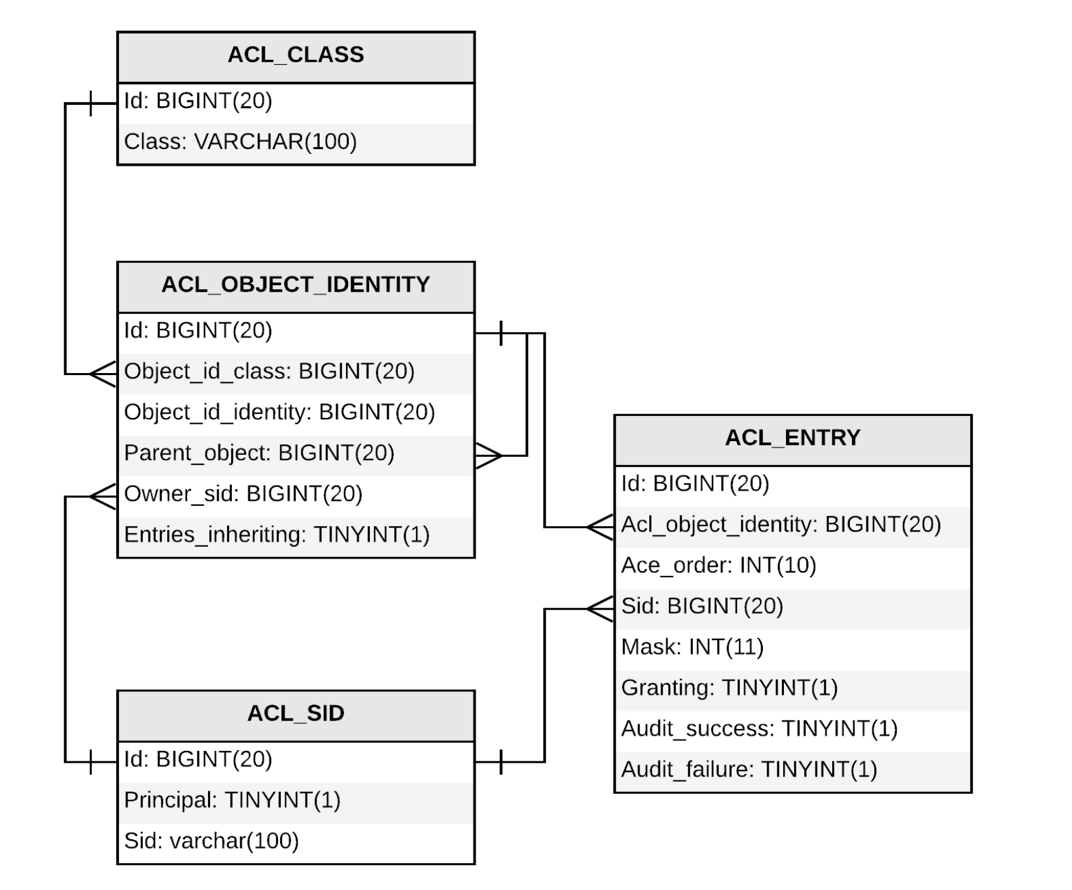
이는 spring-security-acl이 제공하는 것으로 접근 정보를 DB화
-
ACL_CLASS: 도메인 객체의 종류. 보통은 class 로 매핑되는 id 값을 조회 (ex : 앞서 사용한 Paper) -
ACL_SID: principal. 권한의 주체가 되는 사용자 정보와 Role 정보(ex: STUDENT, TUTOR) -
ACL_OBJECT_IDENTITY: 보안의 대상이 되는 정보 객체. 트리 구조로 되어 있음
Id : ACL_CLASS 의 id 값
어느 클래스의 어느 객체이고 생성자가 누구인지에 대한 정보를 갖는다.
ACL_ENTRY: 접근 권한 정보(어떤 접근 허용해줄지)
Ace_order:
Mask : 접근 권한 정보 ( READ,WRITE,ADMIN)
AOP의 Spring Evaluator는 기본적으로 Spring의 캐시를 사용해야 함
ex)
도메인 객체 : 3~4개
접근권한을 관리하려는 객체 : 4~5개
각 도메인 객체별로 실제 인스턴스화된 DB field가 10만개 있다고 하면 각 인스턴스에 대해 5개의 도메인이 있다면 50만개의 필드가 들어가야 함
각 사용자에 대해 ACCESS를 판별해줄려면 50만개의 배수가 테이블로 관리될 것
-> DB부하를 막기위해 Cache 기술 활용
ACL 기술의 장점
- Spring Security 가 바라보는 관점에서 도메인 객체에 대한 접근성 관리의 표준 모델을 샘플로 제공하고 있다.
(Custom ACL 테이블을 구현해서 관리할 수 있는 사례를 보여주고 있다.) - 도메인 객체의 상태나 관계를 접근성이라는 관심사로 부터 분리할 수 있다. (역으로 관리포인트가 늘어난다.)
- hasPermission 이라는 Expression 을 활용해 접근성 관리를 DB화 해서 사용할 수 있다
ACL 기술의 단점
- Domain 객체가 가지고 있는 접근성에 대한 정보를 활용하지 못하고, ACL 테이블을 별도로 관리해주어야 한다.
- 사용자와 도메인 객체가 많아지면, 접근 권한에 대한 경우의 수가 기하급수적으로 늘어난다.
- 기술의 난이도 높아 유지보수가 어렵다
코드 예시
@EnableCaching
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class AclGlobalMethodConfig extends GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration {
// hasPermission()을 통해 접근하는것 설계
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public DataSource dataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Override
protected MethodSecurityExpressionHandler createExpressionHandler() {
DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler expressionHandler = new DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler();
expressionHandler.setPermissionEvaluator(aclPermissionEvaluator());
return expressionHandler;
}
@Bean
public PermissionEvaluator aclPermissionEvaluator() {
AclPermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator = new AclPermissionEvaluator(
aclService()
);
return permissionEvaluator;
}
@Bean
public AclService aclService() {
JdbcMutableAclService aclService = new JdbcMutableAclService(
dataSource(),
lookupStrategy(),
aclCache()
);
return aclService;
}
@Bean
public EhCacheBasedAclCache aclCache() {
return new EhCacheBasedAclCache(
aclEhCacheFactoryBean().getObject(),
permissionGrantingStrategy(),
aclAuthorizationStrategy()
);
}
@Bean
public EhCacheManagerFactoryBean ehcacheFactoryBean() {
EhCacheManagerFactoryBean factoryBean = new EhCacheManagerFactoryBean();
return factoryBean;
}
@Bean
public EhCacheFactoryBean aclEhCacheFactoryBean() {
EhCacheFactoryBean ehCacheFactoryBean = new EhCacheFactoryBean();
ehCacheFactoryBean.setCacheManager(ehcacheFactoryBean().getObject());
ehCacheFactoryBean.setCacheName("aclCache");
return ehCacheFactoryBean;
}
@Bean
PermissionGrantingStrategy permissionGrantingStrategy(){
return new DefaultPermissionGrantingStrategy(consoleAuditLogger());
}
@Bean
AuditLogger consoleAuditLogger() {
return new ConsoleAuditLogger();
}
@Bean
LookupStrategy lookupStrategy() {
return new BasicLookupStrategy(
dataSource(),
aclCache(),
aclAuthorizationStrategy(),
consoleAuditLogger()
);
}
private AclAuthorizationStrategy aclAuthorizationStrategy() {
return new AclAuthorizationStrategyImpl(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN"));
}
}@EnableWebSecurity
public class AclSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser(
User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder()
.username("student1")
.password("1111")
.roles("STUDENT")
)
.withUser(
User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder()
.username("tutor1")
.password("1111")
.roles("TUTOR")
);
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests(request -> request.anyRequest().authenticated())
.httpBasic()
;
}
}@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig {
// Eh cache manager 등록
// @Bean
// public EhCacheCacheManager cacheManager(){
// EhCacheCacheManager cacheManager = new EhCacheCacheManager(); // 단순히 래퍼 클래스
// cacheManager.setCacheManager(ehcacheFactoryBean().getObject());
// return cacheManager;
// }
//
// private EhCacheManagerFactoryBean ehcacheFactoryBean() {
// EhCacheManagerFactoryBean factoryBean = new EhCacheManagerFactoryBean();
// return factoryBean;
// }
// ehcache.xml에서 설정
}@Configuration
@EntityScan(basePackageClasses = {
com.sp.fc.web.paper.Paper.class
})
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackageClasses = {
com.sp.fc.web.paper.PaperRepository.class
})
public class JpaConfig {
}@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
@Entity
public class Paper {
@Id
private Long id;
private String title;
private String tutorId;
// private List<String> studentIds;
private State state;
public static enum State {
PREPARE, // 출제 중
READY, // 시험 시작
END // 시험 종료
}
}@RequestMapping(value="/paper")
@RestController
public class PaperController {
private final PaperService paperService;
public PaperController(PaperService paperService) {
this.paperService = paperService;
}
@PostAuthorize("hasPermission(returnObject, 'READ')") // READ권한이 있는 사용자만 접근 가능
@GetMapping("/{paperId}")
public Paper getPaper(
@AuthenticationPrincipal User user,
@PathVariable Long paperId
){
return paperService.getPaper(paperId).get();
}
}public interface PaperRepository extends JpaRepository<Paper, Long> {
@Cacheable(value = "papers") // 캐시 등록, 기본적으로 스프링의 캐시는 AOP를 사용, 사용하는 것이 서버든, 서비스건, 컨트롤러건
// findById로 페이퍼를 가져오면 아이디가 key가 되는 HashMap이 만들어지며 이 이름을 papers로 지정
Optional<Paper> findById(Long id);
}@Service
public class PaperService {
private final PaperRepository paperRepository;
public PaperService(PaperRepository paperRepository) {
this.paperRepository = paperRepository;
}
public void setPaper(Paper paper){
paperRepository.save(paper);
}
public Optional<Paper> getPaper(Long paperId) {
return paperRepository.findById(paperId);
}
}테스트 코드
@SpringBootTest(classes = AuthorityACLApplication.class)
public class CachTest {
@Autowired
private PaperRepository paperRepository;
// 이 경우에는 cacheManager를 통해 cache를 가져오더라도 cache엔 Paper가 없음
@Autowired
private CacheManager cacheManager;
Optional<Paper> getPaper(Long id){
return Optional.ofNullable(cacheManager.getCache("papers").get(id, Paper.class));
}
@Test
void test1(){
// 1. 페이퍼를 Db에 등록하고 조회한 Paper는 캐시에 등록된다는 것을 확인
Paper paper1 = Paper.builder().id(1L).title("paper1").build();
paperRepository.save(paper1);
assertEquals(Optional.empty(), getPaper(1L)); // 이 경우엔 당연히 페이퍼 없음
paperRepository.findById(1L);
assertTrue(getPaper(1L).isPresent());
}
}@SpringBootTest(classes = AuthorityACLApplication.class, webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class PaperTest {
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
@Autowired
PaperRepository paperRepository;
public String url(Long paperId){
return "http://localhost:" + port + "/paper/" + paperId;
}
// Paper를 도메인 객체에 등록해주어야 함(sql에서)
// 사용자도 ex) id = 1, principal = 1, sid = student1
// 이후 identity, entry 도 등록
@BeforeEach
void before(){
paperRepository.deleteAll();
Paper paper1 = new Paper(1L, "paper1",
"tutor1", Paper.State.PREPARE);
paperRepository.save(paper1);
}
@Test
void test1(){
// Student1이 1L 시험지를 가져온다.
TestRestTemplate client = new TestRestTemplate("student1", "1111");
ResponseEntity<Paper> response = client.getForEntity(url(1L), Paper.class);
System.out.println(response.getBody());
}
}