
Browser는 get을 통해 통신
우리는 개발 시 이외에 메서드들을 테스트 해야함(POST,PUT 등)
-> Talend API Tester(크롬 웹스토어) 사용
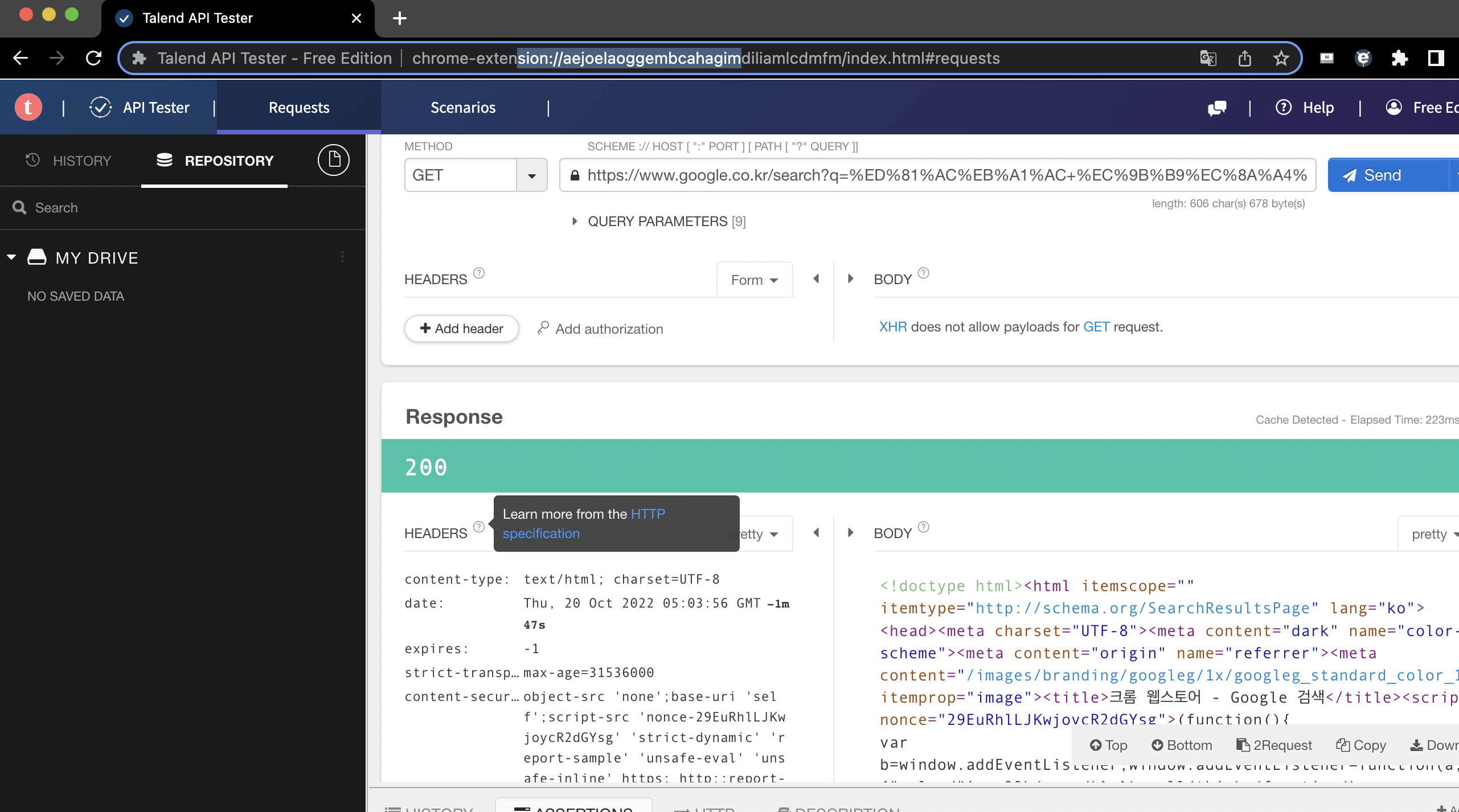
각종 정보들 볼 수 있음
Hello World API
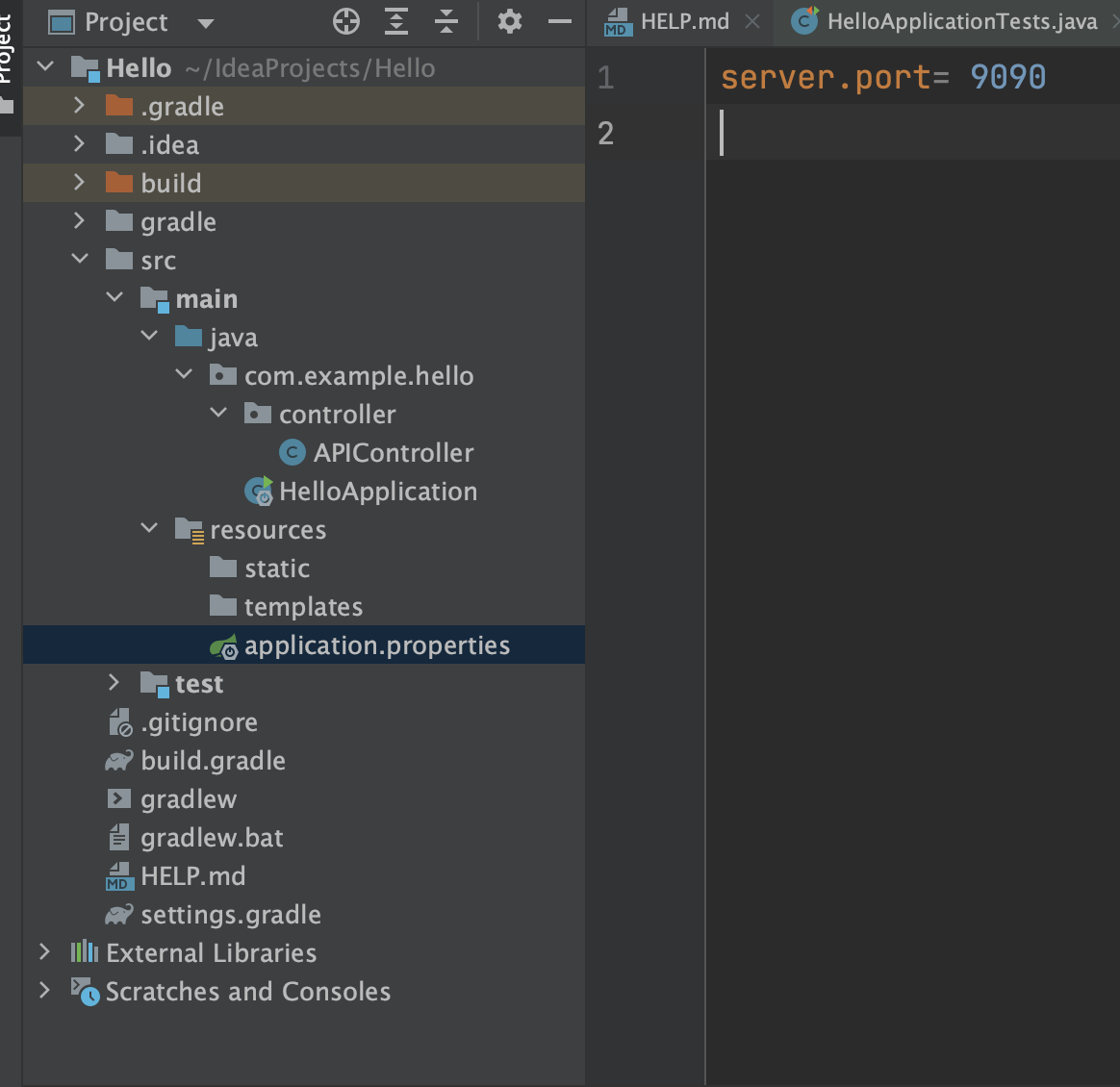
사용하고자 하는 포트 번호를 바꾸고자 한다면 : main -> Resources -> application.properties 이용
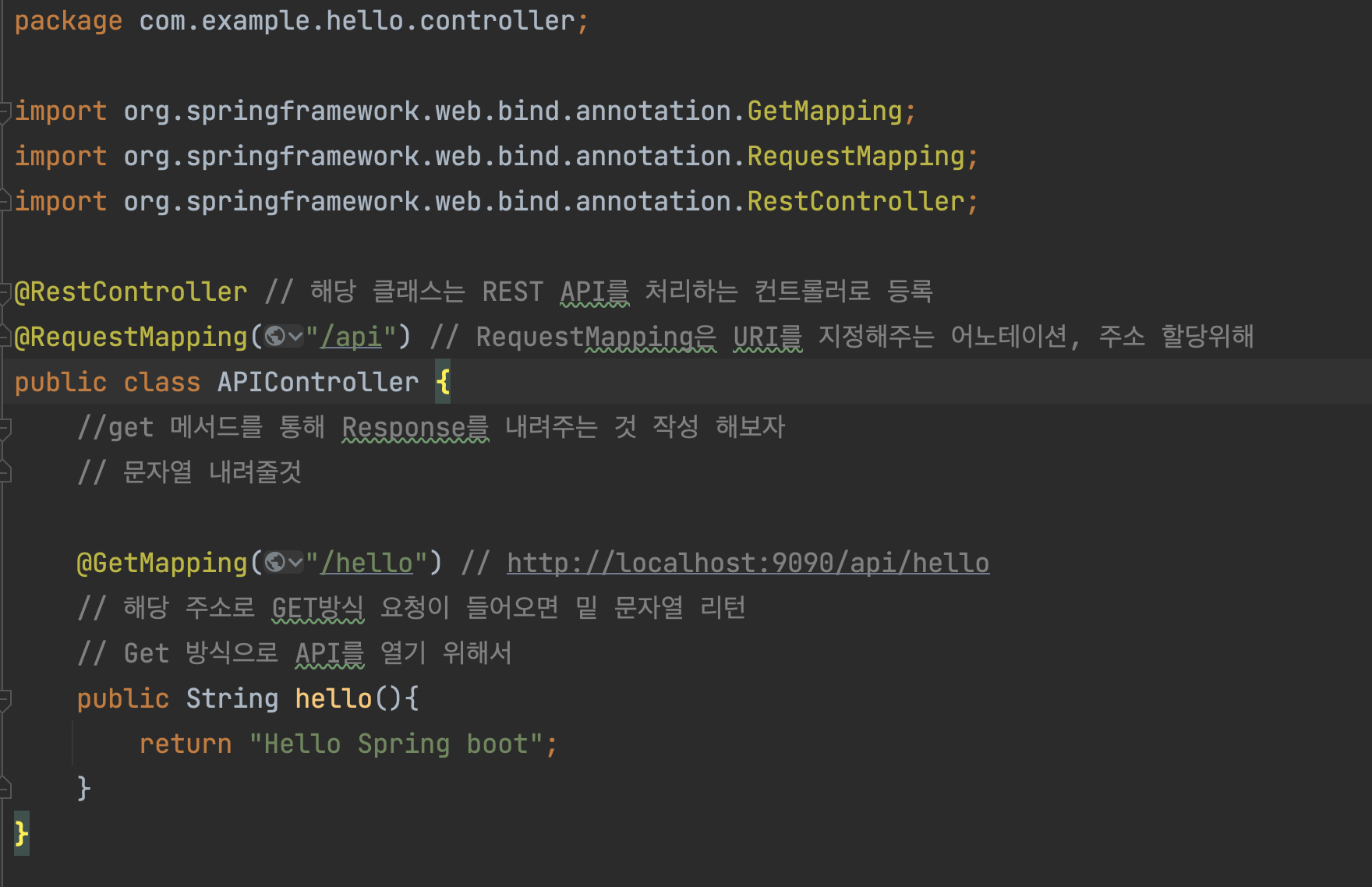
get에 대한 요청을 받는 부분 -> Controller 생성 해주어야함
controller 밑에 APIController 생성 하였음
테스트 결과

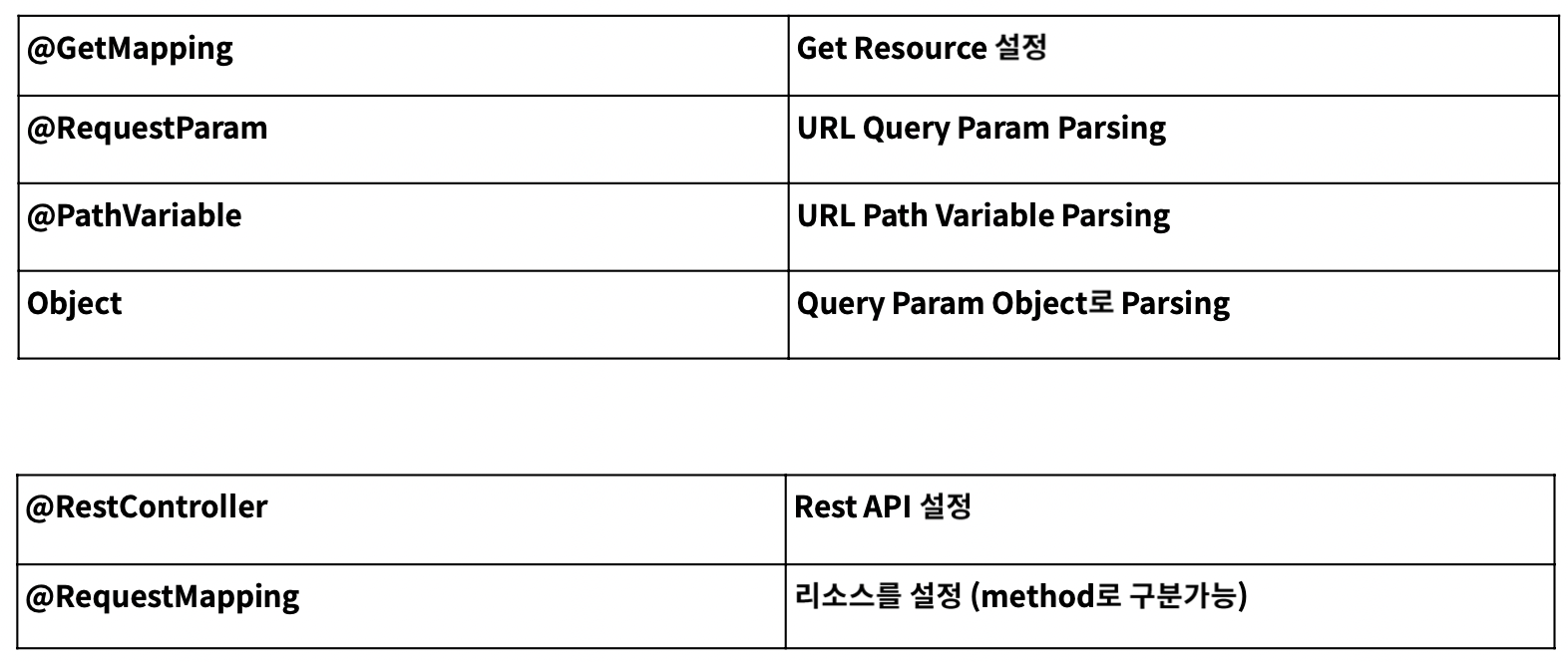
Get API
Get -> 리소스 취득 -> CRUD 중 R
package com.example.hello.controller;
import com.example.hello.dto.UserRequest;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/get")
public class GetApiController {
// 앞선 것 처럼 "/hello" 즉 value를 넣으면 path로 동작
// 밑 처럼(path = ) 도 가능, 밑에 hi보다는 윗방식을 요새 많이 사용
@GetMapping(path = "/hello") // http://localhost:9090/api/get/hello
public String getHello() {
return "get Hello";
}
// get/post/put/delete 등 모든 메서드가 동작(뒤 method 옵션을 지정 안해주면)
// http://localhost:9090/api/get/hi
@RequestMapping(path = "/hi", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String hi() {
return "hi";
}
//http://localhost:9090/api/get/path-variable/{name}
// 계속 변화하는 요소 {name}
// getMapping에 적어놓은 name과 밑에 name이 같아야함
// 다르게 하고자 한다면 pathVariable(name = "속성 이름") 형태로 사용
@GetMapping("/path-variable/{name}")
public String pathVariable(@PathVariable(name = "name") String pathName) {
System.out.println("PathVaraible : " + pathName);
return pathName;
}
//QueryParameter란 주소중에 ?시작 , 검색을 할때 사용하는 여러 인자들이 표시되어있음
// & 연산자를 기준, key-value 형태로 되어있으며(=), 그다음 key-value가 오기 위해 & 연산자
// ?key = value1 & key2 = value2;
// search?q = intellj
// &rlz = 1C5CHFA_enKR1017KR1017
// &oq = intellj
// &aqs = chrome..69i57j0i10i131i433i512j0i10i512j0i10i131i433i512j69i60l2j69i61j69i60.1956j0j7
// &sourceid = chrome&ie=UTF-8
//http://localhost:9090/api/get/query-param?user=steve&email=steve@gmail.com&age=30
//@GetMapping(path = "query-param")
//map으로 받는 경우에는 key가 뭔지 확실히 알 수 없다 user, email,age 지정할 수 X
public String queryParam(@RequestParam Map<String, String> queryParam) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
queryParam.entrySet().forEach(entry -> {
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
System.out.println("\n");
sb.append(entry.getKey() + " = " + entry.getValue() + "\n");
});
return sb.toString();
}
@GetMapping("query-param2")
public String queryParam2(
@RequestParam String name,
@RequestParam String email,
@RequestParam int age
){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(email);
System.out.println(age);
return name+ " " + email + " "+age;
}
// 여러 파라미터 있을 때 사용 방법 : 현업에서 가장 많이 사용, RequestParam 붙이지 않음
// 미리 정의해 놨으면 RequestParam 붙이지 않음(dto 패키지 밑에 UserRequest Class)
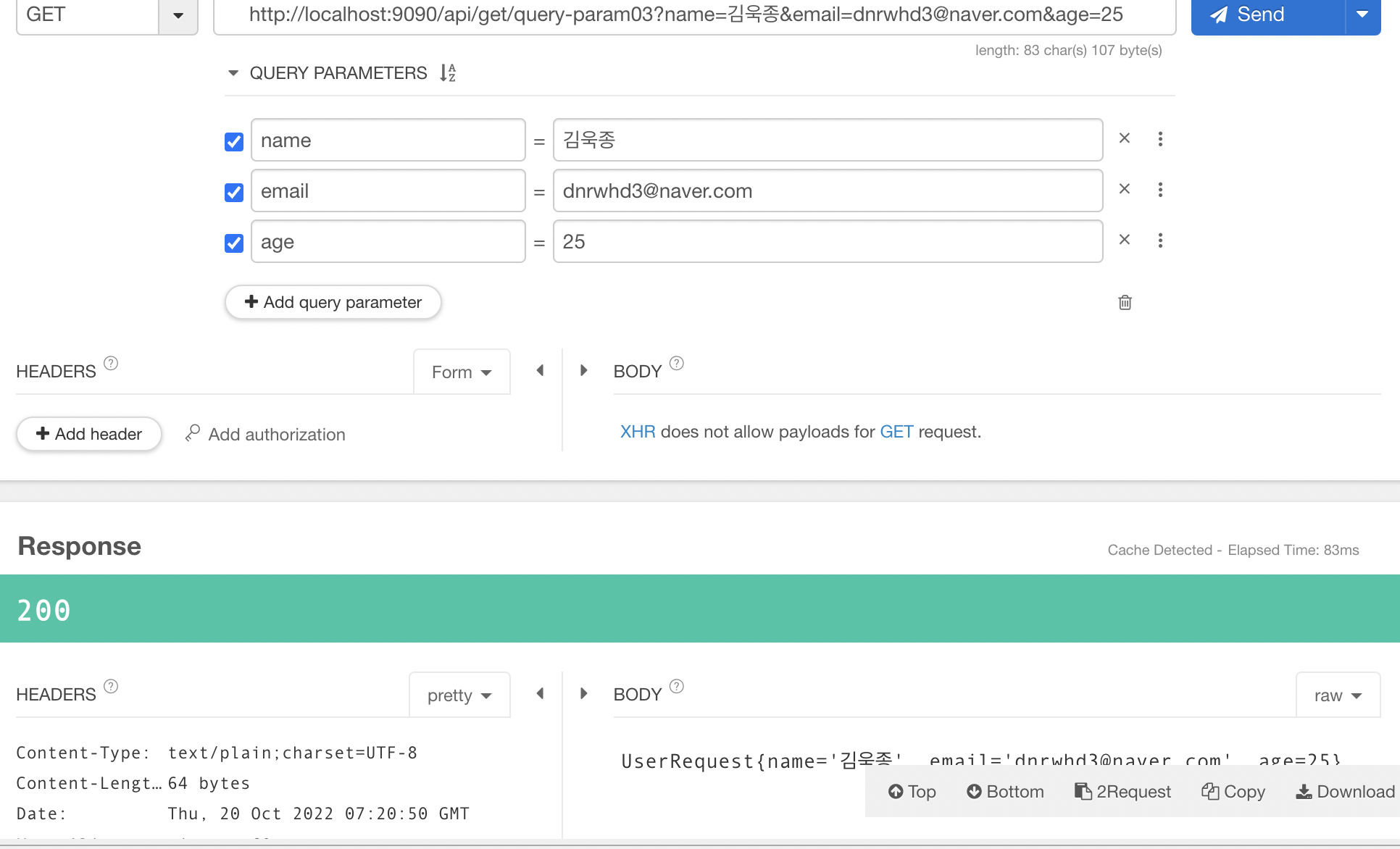
@GetMapping("query-param03")
public String queryParam03(UserRequest userRequest){
System.out.println(userRequest.getName());
System.out.println(userRequest.getEmail());
System.out.println(userRequest.getAge());
return userRequest.toString();
}
}package com.example.hello.dto;
public class UserRequest {
private String name;
private String email;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserRequest{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
POST API
POST -> 생성 or 추가 -> CRUD의 C
Query Parameter 왠만하면 사용 X
웹에서는 주로 json 데이터를 주고 받음
// 괄호로 시작하며 key value 값으로 이어짐
JSON
// String :value
// number :value
// boolean : value
// object : value { } -> 괄호 형태로 묶임
// array : value [ ]
json에서는 snake 표기법 -> 즉 언더바 자주사용
camel case는 -> 그다음 단어부터 대문자
{
"phone_number" : "010-1111-2222"
"phoneNumber" : "value"
"age" : 10,
"isAgree" : false,
"account" : {
"email" : "steve@gamil.com",
"password" : "1234"
}
}
//user 객체를 서버에서 조회하는 경우
{
//같은 key, value 속성 값을 가진 여러 객체들이 나열되어 있는 것을 볼 수 있다
"user_list" : [
{ "account" : "abcd",
"password" : "1234"
},
{ "account" : "aaaa"
"password" : "1111"
}
]
}
{
"account" : "abcd",
"password" : "1234"
}활용
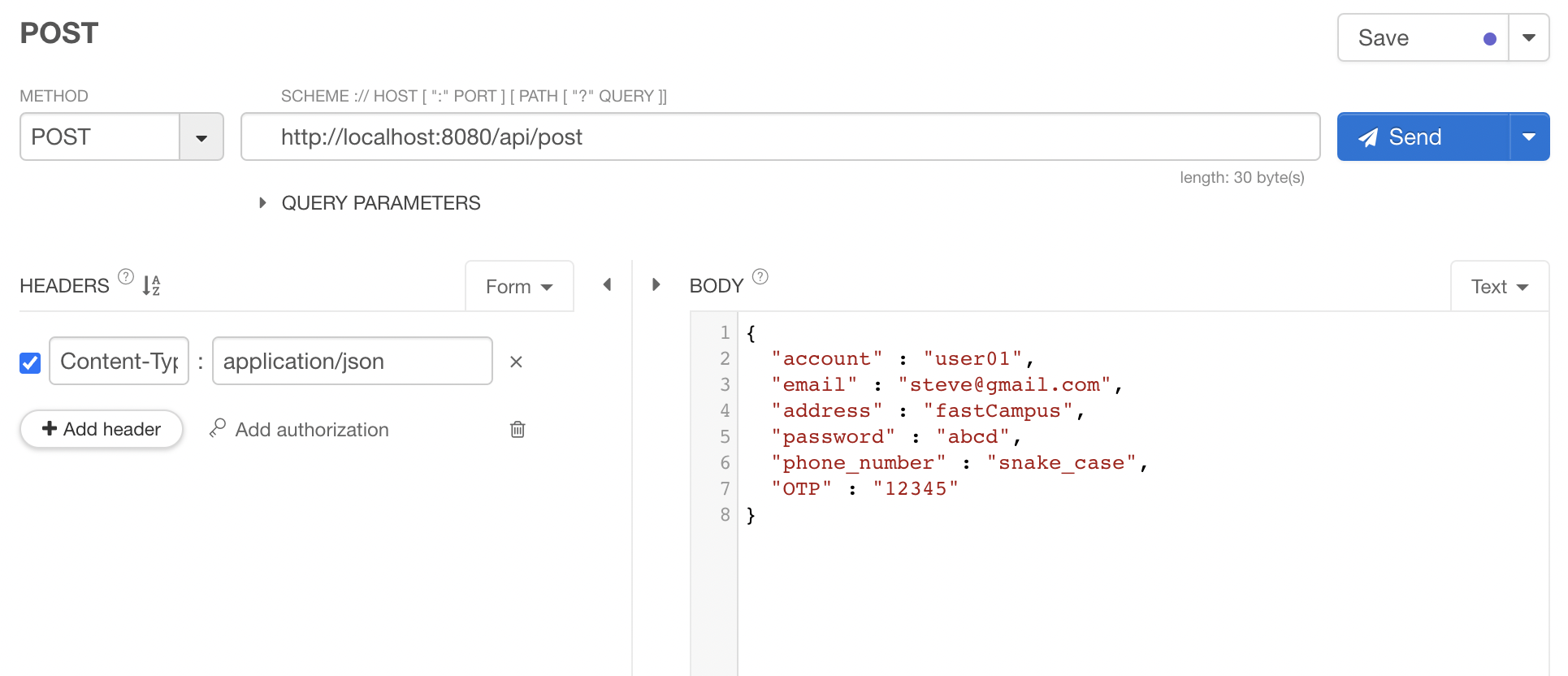
//json, 사용자 계정 생성 했다 가정, 서버에서 어떻게 받을지 주목!
{
//HTTP POST를 통해 보낼 JSON
"account" : "user01",
"email" : "steve@gmail.com",
"address" : "fastCampus",
"password" : "abcd",
"phone_number" : "snake_case",
"OTP" : "12345"
}
컨트롤러
package com.example.post.controller;
import com.example.post.dto.PostRequestDto;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PostApiController {
//@PostMapping("/post")
// 키는 String, 벨류는 여러가지 일수 있으니 Object
// POST때는 Body에 데이터 심음
// public void post(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> requestData){
// requestData.forEach((key, value) -> {
// System.out.println("key:" + key);
// System.out.println("value:" + value);
// });
// }
@PostMapping("/post")
// RequestBody 사용
public void post(@RequestBody PostRequestDto postRequestDto){
System.out.print(postRequestDto);
}
}
dto
package com.example.post.dto;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
public class PostRequestDto {
// 키에 해당하는 값들에 선언
private String account;
private String email;
private String address;
private String password;
@JsonProperty("phone_number") // 이 부분 작성 시 phone_number로 키 값이 오더라도 값 받음
private String phoneNumber; // snake -> phone_number // 변수 형식이 다르면 값을 넣더라도 null값 받음
@JsonProperty("OTP") // camel,snake 둘다 아닌 경우, 즉 변수에 특정 이름 매칭시키기 위해 사용
private String OTP;
public String getOTP() {
return OTP;
}
public void setOTP(String OTP) {
this.OTP = OTP;
}
public String getPhoneNumber() {
return phoneNumber;
}
public void setPhoneNumber(String phoneNumber) {
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
}
public String getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(String account) {
this.account = account;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PostRequestDto{" +
"account='" + account + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", phoneNumber='" + phoneNumber + '\'' +
", OTP='" + OTP + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
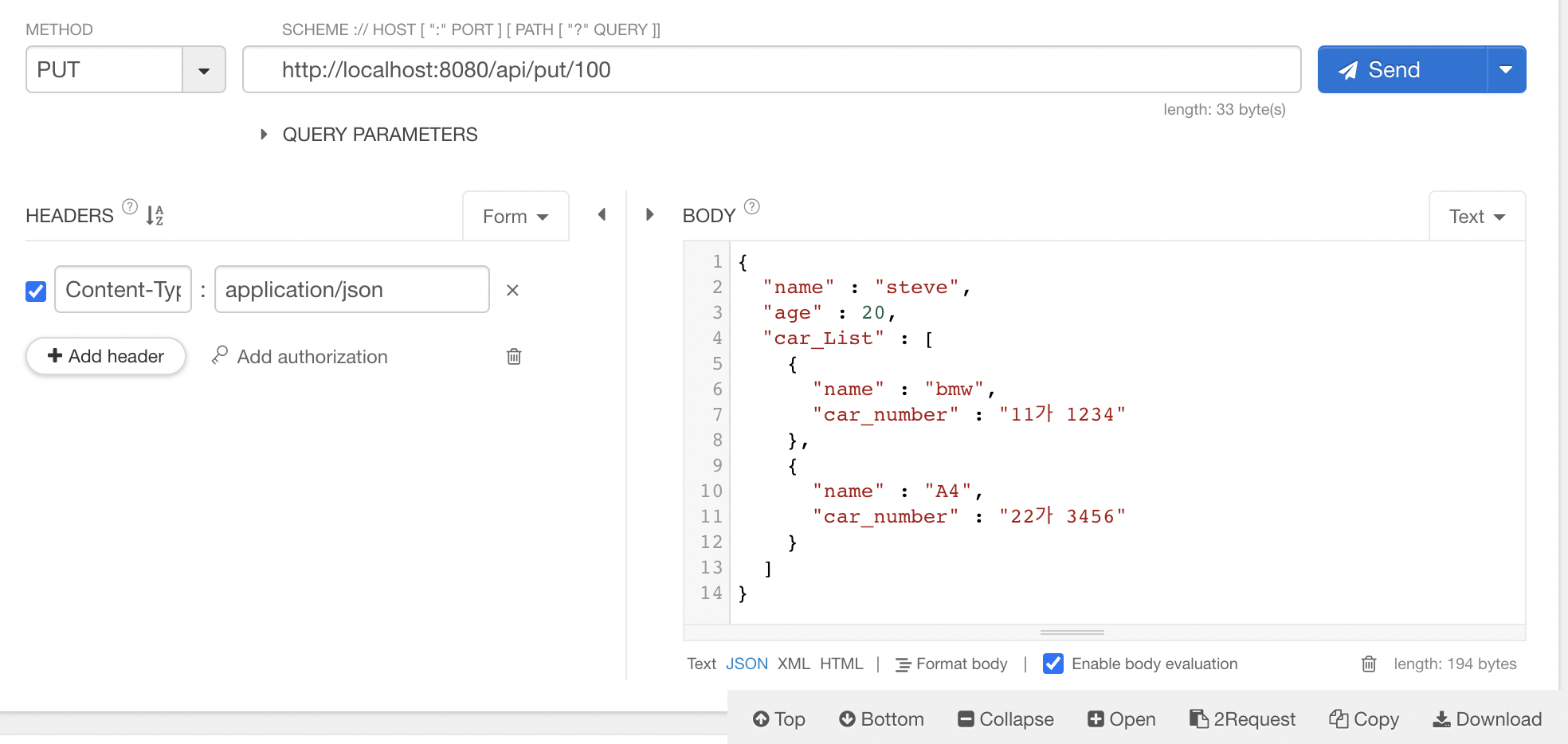
PUT API
//JSON
{
"name" : "steve",
"age" : 20,
"carList" : [
{
"name" : "bmw",
"carNumber" : "11가 1234"
},
{
"name" : "A4",
"carNumber" : "22가 3456"
}
]
}
// car dto
package com.example.put.dto;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
public class CarDto {
private String name;
@JsonProperty("car_number")
private String carNumber;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCarNumber() {
return carNumber;
}
public void setCarNumber(String carNumber) {
this.carNumber = carNumber;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CarDto{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", carNumber='" + carNumber + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
// User DTO
package com.example.put.dto;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
import java.util.List;
public class PostRequestDto {
private String name;
private int age;
@JsonProperty("car_List")
private List<CarDto> carList;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public List<CarDto> getCarList() {
return carList;
}
public void setCarList(List<CarDto> carList) {
this.carList = carList;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PostRequestDto{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", carList=" + carList +
'}';
}
}
package com.example.put;
import com.example.put.dto.CarDto;
import com.example.put.dto.PostRequestDto;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PutApiController {
@PutMapping("/put/{userId}")
public PostRequestDto put(@RequestBody PostRequestDto requestDto, @PathVariable(name="userId")Long id){
System.out.print(id);
// 보낸 데이터 그래도 리턴 될것! (Response) return request.getName() 이럴 필요 없음
// JSON 형태로 자동으로 Response가 내려감!
return requestDto;
}
}
DELETE API
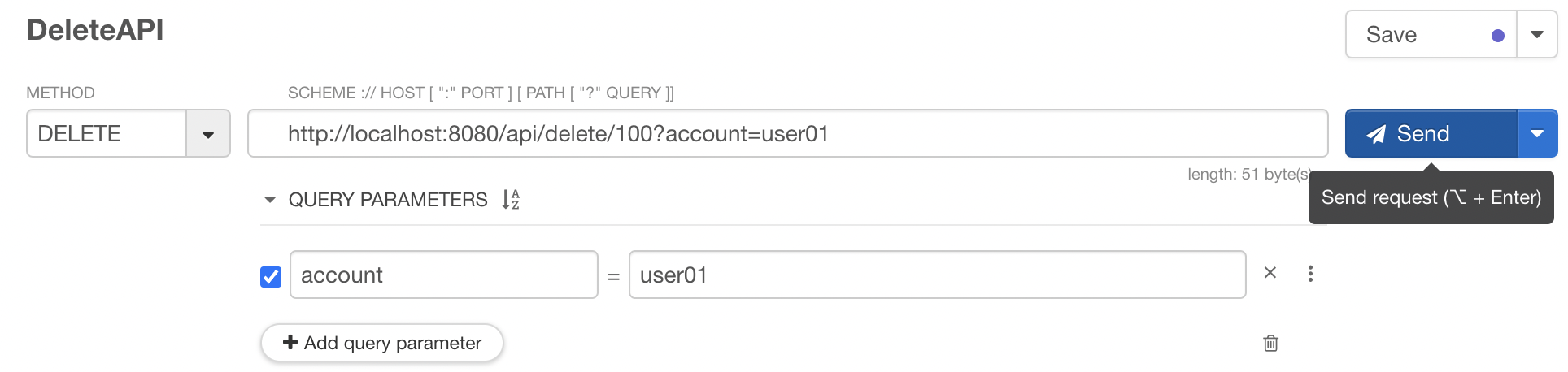
package com.example.deleteapi.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class DeleteApiController {
@DeleteMapping("/delete/{userId}")
public void delete(@PathVariable String userId, @RequestParam String account){
System.out.println(userId);
System.out.println(account);
}
}