우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)
우선 순위가 높은 데이터가 먼저 나옴 (!= FIFO)
- 모든 데이터에 우선순위가 있음
- Dequeue 시, 우선순위가 높은 순으로 나감
- 우선 순위가 같은 경우는 FIFO
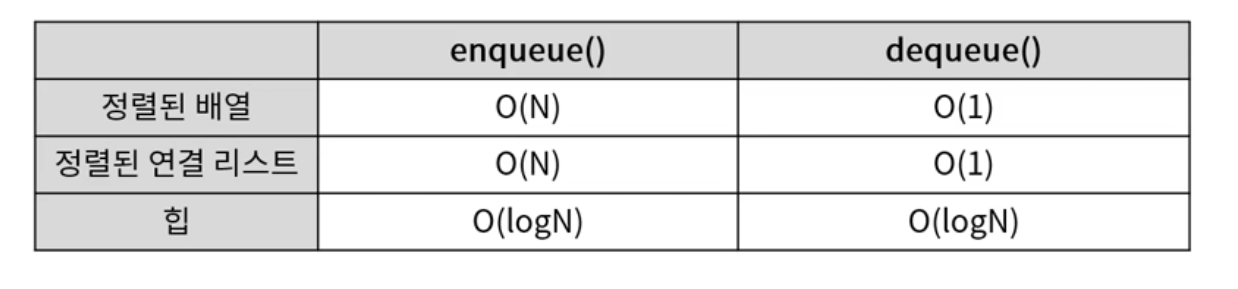
enqueue, dequeue
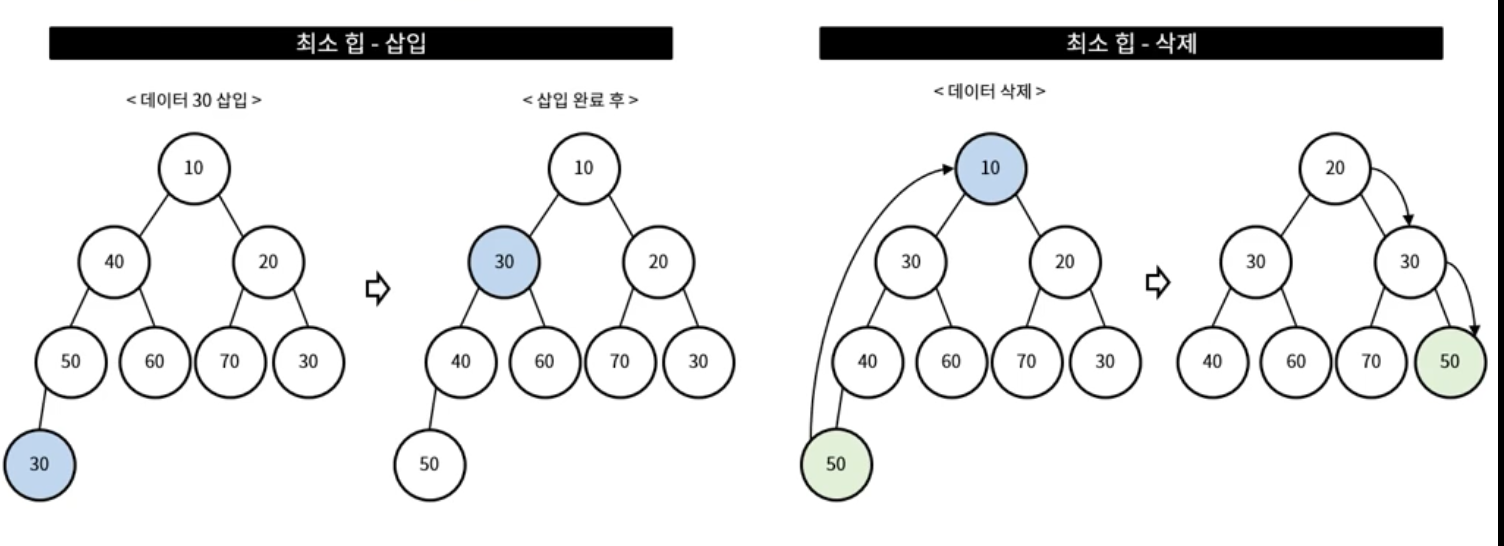
최소 힙 및 최대 힙의 삽입 삭제 방법과 같음!
구현
여러 방법으로 가능
- 배열
- 연결리스트
- 힙
자바에서 기본적으로 제공하는 우선순위 큐는 힙으로 되어있음
정렬되지 않은 배열의 경우엔 인큐와 디큐의 시간복잡도가 바뀜
LinkedList를 통한 우선순위 큐 구현
// 자바의 Priority Queue는 내부적으로 Heap으로 되어있다
// 밑의 코드는 연결리스트로 PriorityQueue 구현
public class Practice2 {
public static void enqueue(LinkedList<Integer> list, int data){
int idx = list.size();
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
if(list.get(i) > data){
idx = i;
break;
}
}
list.add(idx, data);
}
public static Integer dequeue(LinkedList<Integer> list){
if(list.size() == 0){
return null;
}
int data = list.get(0);
list.remove(0);
return data;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연결리스트를 이용한 우선순위 큐
System.out.println("== 연결리스트 방식의 우선순위 큐 ==");
LinkedList<Integer> pqList = new LinkedList<>();
// 값이 작을수록 우선순위 높은 상태
enqueue(pqList, 5);enqueue(pqList, 7);enqueue(pqList, 3);
enqueue(pqList, 1);enqueue(pqList, 9);
System.out.println(pqList);
System.out.println(dequeue(pqList));
System.out.println(dequeue(pqList));
System.out.println(pqList);
System.out.println();
// 자바 기본 PriorityQueue 사용
// 우선순위: 낮은 순자 순
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add(5);pq.add(7);pq.add(3);
pq.add(1);pq.add(9);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(pq.toArray())); // 13579 순 출력
// 우선순위 : 높은 숫자 순
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq2 = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
pq.add(5);pq.add(7);pq.add(3);
pq.add(1);pq.add(9);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(pq2.toArray()));
}
}숫자를 기준으로 내림차순 오름차순
class Person2{
String name;
int age;
public Person2(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
// 1 : 변경 안함
// -1 : 변경
// 새롭게 추가하는 데이터가 더 적을때 변경(적은 값이 위로 올라가고, 오름차순)
// this.age가 방금 들어오는 데이터, o.age는 기존에 있던 데이터
return this.age >= o.age ? 1: -1;
// 내림 차순 경우
// return this.age >= o.age ? -1 : 1;
}
}
public class Practice3 {
// 나이 순으로 오름차순 또는 내림차순 출력
public static void solution(String[] name, int[] age){
PriorityQueue<Person> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
for(int i = 0; i < name.length; i++){
pq.offer(new Person(name[i], age[i]));
}
// 위 for문 진행하고 프린트 시 에러 발생 -> Comparable
// Person에 Comparable 구현
System.out.println("== 실제 출력 순서 == ");
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
Person p = pq.poll();
System.out.println(p.name + " " + p.age);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] name = {"A", "B", "C", "D", "E"};
int[] age = {30,20,45,62,35};
solution(name,age);
// 다른 방법(인터페이스 상속 없이)
PriorityQueue<Person2> pq2 = new PriorityQueue<>(
(Person2 p1, Person2 p2) -> p1.age >= p2.age? 1: -1);
for(int i = 0; i < name.length; i++){
pq2.offer(new Person2(name[i], age[i]));
}
while(!pq2.isEmpty()){
Person2 p = pq2.poll();
System.out.println(p.name + " " + p.age);
}
}
}문자열 사전식 오름차순
public static void solution(String[] name, int[] age) {
PriorityQueue<Person4> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(
(Person4 p1, Person4 p2) -> p1.name.compareTo(p2.name)
);
for(int i = 0; i < name.length; i++){
pq.offer(new Person4(name[i], age[i]));
}
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
Person4 p = pq.poll();
System.out.println(p.name + " " + p.age);
}
}연습문제
문제 1
// Practice1
// nums 배열에 주어진 정수들 중에서 k 번째로 큰 수를 반환한는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
// 입력 예시
// 입력: 3, 1, 2, 7, 6, 4
// k: 2
// 출력: 6
// 입력: 1, 3, 7, 4, 2, 8, 9
// k: 7
// 출력: 1
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Practice1 {
public static int solution1(int[] nums, int k) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(); // 오름 차순으로
for(int num : nums){
// minHeap으로 푸는 경우
pq.offer(num);
if(pq.size() > k){
pq.poll();
}
}
return pq.peek();
}
public static int solution2(int[] nums, int k) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length - k];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] nums = {3, 1, 2, 7, 6, 4};
System.out.println(solution1(nums, 2));
System.out.println(solution2(nums, 2));
System.out.println();
nums = new int[]{1, 3, 7, 4, 2, 8, 9};
System.out.println(solution1(nums, 7));
System.out.println(solution2(nums, 7));
}
}문제 2
// Practice2
// 돌의 무게 데이터로 이루어진 정수형 stones 배열이 주어졌을 때 다음의 내용에 따라 프로그램을 작성하세요.
// 해당 배열로부터 가장 무게가 많이 나가는 돌 두개를 꺼내세요.
// 두 개의 돌을 충돌시키는데, 무게가 같으면 둘다 소멸,
// 무게가 다르면 남은 무게만큼의 돌은 다시 추가합니다.
// 이 과정을 반복하며 가장 마지막의 돌의 무게를 출력하세요.
// 입출력 예시
// 입력: 2, 7, 4, 1, 8, 1
// 출력: 1
// 입력: 5, 3, 5, 3, 4
// 출력: 2
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Practice2 {
public static void solution(int[] stones) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(
(x,y) -> y - x // 양수인 경우 즉 y값이 더 작을 경우 서로 change
);
for(int stone: stones){
pq.offer(stone);
}
while(pq.size() > 1){
int stone1 = pq.poll();
int stone2 = pq.poll();
int diff = Math.abs(stone1 - stone2);
if(diff != 0){
pq.offer(diff);
}
}
System.out.println(pq.poll());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] stones = {2, 7, 4, 1, 8, 1};
solution(stones);
stones = new int[]{5, 3, 5, 3, 4};
solution(stones);
}
}문제 3
// Practice3
// nums 배열에 주어진 정수들 중에서 가장 많이 발생한 숫자들 순으로 k 번째 까지 출력하세요.
// 빈도가 같은 경우에는 값이 작은 숫자가 먼저 출력되도록 구현하세요.
// 입출력 예시
// 입력: 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3
// k: 2
// 출력: 1, 2
// 입력: 3, 1, 5, 5, 3, 3, 1, 2, 2, 1, 3
// k: 3
// 출력: 3, 1, 2
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Practice3 {
public static void solution1(int[] nums, int k) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int num : nums){
map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
}
PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> pq =
new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> y.getValue() == x.getValue()?
x.getKey() - y.getKey() : y.getValue() - x.getValue());
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> item : map.entrySet()){
pq.add(item);
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> cur = pq.poll();
System.out.print(cur.getKey() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
class Num implements Comparable<Num> {
int key;
int freq;
public Num(int key, int freq) {
this.key = key;
this.freq = freq;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Num o) {
if(this.freq == o.freq){
return this.key - o.key;
}else{
return o.freq - this.freq;
}
}
}
public static void solution2(int[] nums, int k) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int num : nums){
map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
}
PriorityQueue<Num> pq = new PriorityQueue();
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> item: map.entrySet()){
pq.add(new Practice3().new Num(item.getKey(), item.getValue()));
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
Num cur = pq.poll();
System.out.print(cur.key + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] nums = {1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3};
solution1(nums, 2);
solution2(nums, 2);
System.out.println();
nums = new int[]{3, 1, 4, 4, 3, 3, 1, 2, 2, 1, 3};
solution1(nums, 3);
solution2(nums, 3);
}
}문제 4
// Practice4
// 문자열 s 가 주어졌을 때, 문자열 내에 동일한 알파벳이 연속적으로 배치되지 않도록 재배치 하세요.
// 재배치가 가능한 경우 재정렬한 문자열을 반환하고 불가능한 경우 null 을 반환하세요.
// 입출력 예시
// 입력: "aabb"
// 출력: "abab"
// 입력: "aaca"
// 출력: null
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Practice4 {
public static String solution(String s) {
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(String item : s.split("")){
map.put(item, map.getOrDefault(item, 0) + 1);
}
PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> pq =
new PriorityQueue<>((x,y) -> y.getValue() - x.getValue());
for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> item : map.entrySet()){
pq.offer(item);
}
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
Map.Entry<String, Integer> prev = null;
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
Map.Entry<String, Integer> cur = pq.poll();
if(prev != null && prev.getValue() > 0){
pq.offer(prev);
}
sb.append(cur.getKey());
cur.setValue(cur.getValue() - 1);
prev = cur;
if(pq.isEmpty() && prev.getValue() > 0){
return null;
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
System.out.println(solution("aabb"));
System.out.println(solution("aaaaabccd"));
System.out.println(solution("aaca"));
}
}
