이진 탐색(Binary Search)
정렬된 상태의 데이터에서 특정 값을 빠르게 탐색하는 방법
- 찾고자 하는 값과 (정렬된)데이터 중앙에 있는 값을 비교
- 찾고자 하는 값이 더 작으면 데이터 왼쪽 부분에서 이진 탐색
- 찾고자 하는 값이 더 크면 데이터 오른쪽 부분에서 이진 탐색
알고리즘 시간 복잡도 : O(logn)
찾고자 하는 데이터가 30일 경우
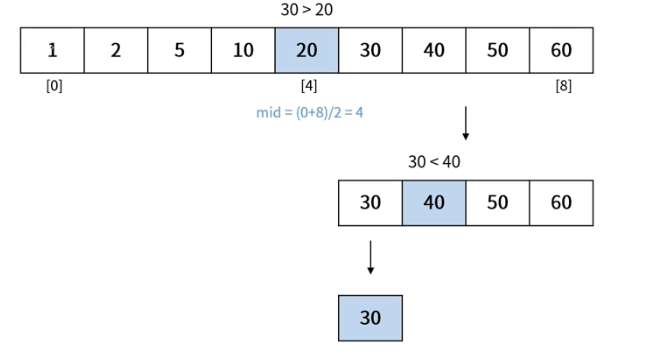
위 경우는 worst case
-> log 8 -> 3
구현
public class Main {
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target){
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length-1;
while(left<=right){
int mid = (left+right) / 2;
if(arr[mid] == target){
return mid;
}else if(arr[mid] < target){
left = mid + 1;
}else{
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static int binarySearch2(int[] arr, int target, int left, int right){
if(left > right){
return -1;
}
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(arr[mid] == target){
return mid;
}else if(target < arr[mid]){
return binarySearch2(arr,target, left, mid-1);
}else{
return binarySearch2(arr,target,mid+1, right);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,5,10,20,30,40,50,60};
System.out.println("Index: " + binarySearch(arr, 30));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Index: " + binarySearch2(arr, 30, 0, arr.length));
}
}자바에서 제공하는 이진 탐색
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,5,10,20,30,40,50,60};
System.out.println("데이터가 있는 경우");
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr,1)); // 해당 값에 위치 반환
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr,10));
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr,30));
System.out.println("데이터가 없는 경우");
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr,3)); // -3
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr,11)); // -5
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr,35)); // -7
// 이 위치중에 있었다면 이 인덱스에 있었을 것이다 -> 원래라면 2 위치 이것을 플러스 1 한후 마이너스 값 반환
}
}이진 탐색 연습 문제
문제 1
// Practice1
// 이진 탐색 추가 구현
// target 값이 arr 내에 있으면 해당 인덱스 반환
// 없으면 해당 값이 있을 경우의 위치에 -1을 곱하고 1을 뺀 값을 반환
// 입출력 예시
// 입력 arr: 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60
// target: 30
// 출력: 5
// target: 3
// 출력: -3
public class Practice1 {
public static int solution(int[] arr, int target) {
if(arr == null || arr.length == 0){
return -1;
}
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length-1;
while(left <= right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(target == arr[mid]){
return mid;
}else if(target < arr[mid]){
right = mid - 1;
}else{
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return -left-1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] arr = {1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60};
System.out.println(solution(arr, 30)); // 5
System.out.println(solution(arr, 3)); // -3
System.out.println(solution(arr, 11)); // -5
System.out.println(solution(arr, 35)); // -7
}
}문제2
// Practice
// 원형 정렬 상태 배열에서의 이진 탐색
// nums 배열에 원형 상태로 데이터가 정렬되어 있을 때,
// 이진 탐색으로 데이터를 찾는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
// O(log n) 유지
// 배열을 재 정렬하지 않고 풀기
// 입출력 예시
// arr: 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 0, 1, 2
// target: 0
// 출력: 5
// target: 3
// 출력: -1
public class Practice2 {
public static int solution(int[] arr, int target) {
if(arr == null || arr.length == 0){
return -1;
}
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length-1;
while(left <= right){
int mid = left + (right-left)/2;
if(target == arr[mid]){
return mid;
}
// 4 5 6 7 0 1 2
if(arr[left] <= arr[mid]){
if(target >= arr[left] && target < arr[mid]){
right = mid - 1;
}else{
left = mid + 1;
}
}else{
// 11 5 6 7 8 9 10
if(target > arr[mid] && target <= arr[right]) {
left = mid + 1;
}else{
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] nums = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 0, 1, 2};
System.out.println(solution(nums, 0)); // 5
System.out.println(solution(nums, 3)); // -1
}
}문제 3
// Practice3
// 2차원 행렬에서 이진 탐색으로 데이터 찾기
// row x col 행렬 데이터가 주어졌을 때, target 을 이진 탐색으로 찾는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
// 각 행의 데이터는 오름차순으로 정렬 상태
// 입출력 예시
// 행렬: {{1, 3, 7, 8}, {10, 11, 15, 20}, {21, 30, 35, 60}}
// target: 3
// 출력: true
// target: 13
// 출력: false
public class Practice3 {
public static boolean solution(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if(matrix == null || matrix.length == 0){
return false;
}
int left = 0;
int rows = matrix.length;
int cols = matrix[0].length;
int right = rows * cols - 1;
while(left <= right){
int mid = (left + right) /2;
if(matrix[mid/cols][mid % cols] == target){
return true;
}else if(matrix[mid / cols][mid % cols] < target){
left = mid+1;
}else{
right = mid-1;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[][] matrix = {{1, 3, 7, 8}, {10, 11, 15, 20}, {21, 30, 35, 60}};
System.out.println(solution(matrix, 3)); // true
System.out.println(solution(matrix, 13)); // false
System.out.println(solution(matrix, 35)); // true
}
}문제 4
// Practice4
// 정수형 배열 weights 와 정수 days 가 주어졌다.
// weights 에는 각 상품의 무게들의 정보가 들어있고, days 는 운송 납기일이다.
// 상품들은 weights 에 적혀있는 순서대로 실어서 운송해야 하는데,
// days 이내에 운송을 하기 위한 차량의 최소한의 적재량을 계산하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
// 입출력 예시
// weights: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
// days: 5
// 출력: 15
// weights: 3, 2, 2, 4, 1, 4
// days: 3
// 출력: 6
public class Practice4 {
public static int solution(int[] weights, int days) {
// 위 weights 에서 나온 최소한의 적재량의 최소는 10, 최대는 다 한번에 보내는 55
// 10과 55의 중앙은 32(이 경우엔 2일 만에 다 가능 : 더 좌측에서 찾아봄)
// 10과 32의 중앙 -> 21(이 경우 3일만에 가능)
// 이렇게 쭉하다가 최종적으로 선택된 최소 적재량이 출력
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
for(int w : weights){
left = Math.max(left,w);
right += w;
}
while(left <= right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
int cnt = 1;
int cur = 0;
for(int w : weights){
if (cur + w > mid){
cnt+= 1;
cur = 0;
}
cur += w;
}
if(cnt > days){
left = mid + 1;
}else{
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return left;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] weights = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
System.out.println(solution(weights, 5)); // 15
weights = new int[]{3, 2, 2, 4, 1, 4};
System.out.println(solution(weights, 3)); // 6
}
}// Practice5
// 정수형 배열 nums 와 정수 m 이 주어졌다.
// nums 에는 양의 정수 값들이 들어 있고, m 은 배열을 부분 배열로 분리할 수 있는 수이다.
// nums 배열을 m 개의 부분 배열로 분리할 때,
// 각 부분 배열의 합중 가장 큰 값이 최소가 되도록 분리했을 때의 합을 출력하세요.
// 입출력 예시
// nums: 7, 2, 5, 10, 8 -> left의 최솟값 : 10, right의 최대값 32
// m: 2
// 출력: 18
// nums: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
// m: 2
// 출력: 9
public class Practice5 {
public static int solution(int[] nums, int m) {
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
for(int num: nums){
left = Math.max(num, left);
right += num;
}
if(m == 1){
return right;
}
while(left<=right){
int mid = (left+right) / 2;
int cnt = 1;
int total = 0;
for(int num : nums){
total += num;
if(total > mid){
total = num;
cnt++;
}
}
if(cnt <= m){
right = mid - 1;
}else{
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] nums = {7, 2, 5, 10, 8};
System.out.println(solution(nums, 2)); // 18
nums = new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
System.out.println(solution(nums, 2)); // 9
nums = new int[] {1, 4, 4};
System.out.println(solution(nums, 3)); // 4
}
}
