개요
- Nestjs CQRS 패턴의 Event 주도 개발 방식 적용해본다
CQRS 패턴이란
- Command and Query Responsibility Segregation의 약자로, 읽기 작업을 분리하여 성능과 확장성 향상을 도모
Saga란
- EDA(Event Driven Architecture) 애플리케이션 반응성과 확장성을 향상시키기 위한 패턴
- 단일 saga는 N개의 이벤트를 수신할 수 있으며 각 saga는 명령을 포함하는 Observable을 반환 (비동기)
Event 주도 개발 + Saga
- Nestjs CQRS의 EventBus로 EDA(Event Driven Architecture) 구현하기
- Saga 패턴 도표
(https://velog.velcdn.com/images/dobecom/post/8bae2c35-b852-453a-9166-9512a5ad81c9/image.png)
- Compensation Transaction에 대한 내용은 예시나 가이드가 없어서 리서치를 해본 결과는 다음과 같다.
- 여러 이벤트가 수행되다가 중간에 실패한 경우, 이전 이벤트에 대한 보상 트랜잭션은 직접 처리하는 이벤트를 만들어줘야 한다
[예시]
1) 특정 비즈니스 로직에 대해 서로 다른 이벤트 A, B, C가 수행 될 예정
2) 이벤트 A 수행
3) 이벤트 B 수행 중 에러 발생
4) "B 실패 이벤트"를 구현하여 이벤트 A (또는 이벤트 C) 에 대한 보상 트랜잭션 로직을 처리하도록 함
문제점) 이벤트 간 의존성 발생? -> 트랜잭션 idx?를 옵저버 패턴으로 구현하면 가능? (확인 중)
* 내용 추가 : 애그리거트 패턴 : 메시지큐로 이벤트 던져놓고 비동기로 각각 처리된 후 이벤트의 결과를 이벤트스토어로 다시 돌려주게 되어 "결과적일관성"(<->ACID)를 갖게 됨 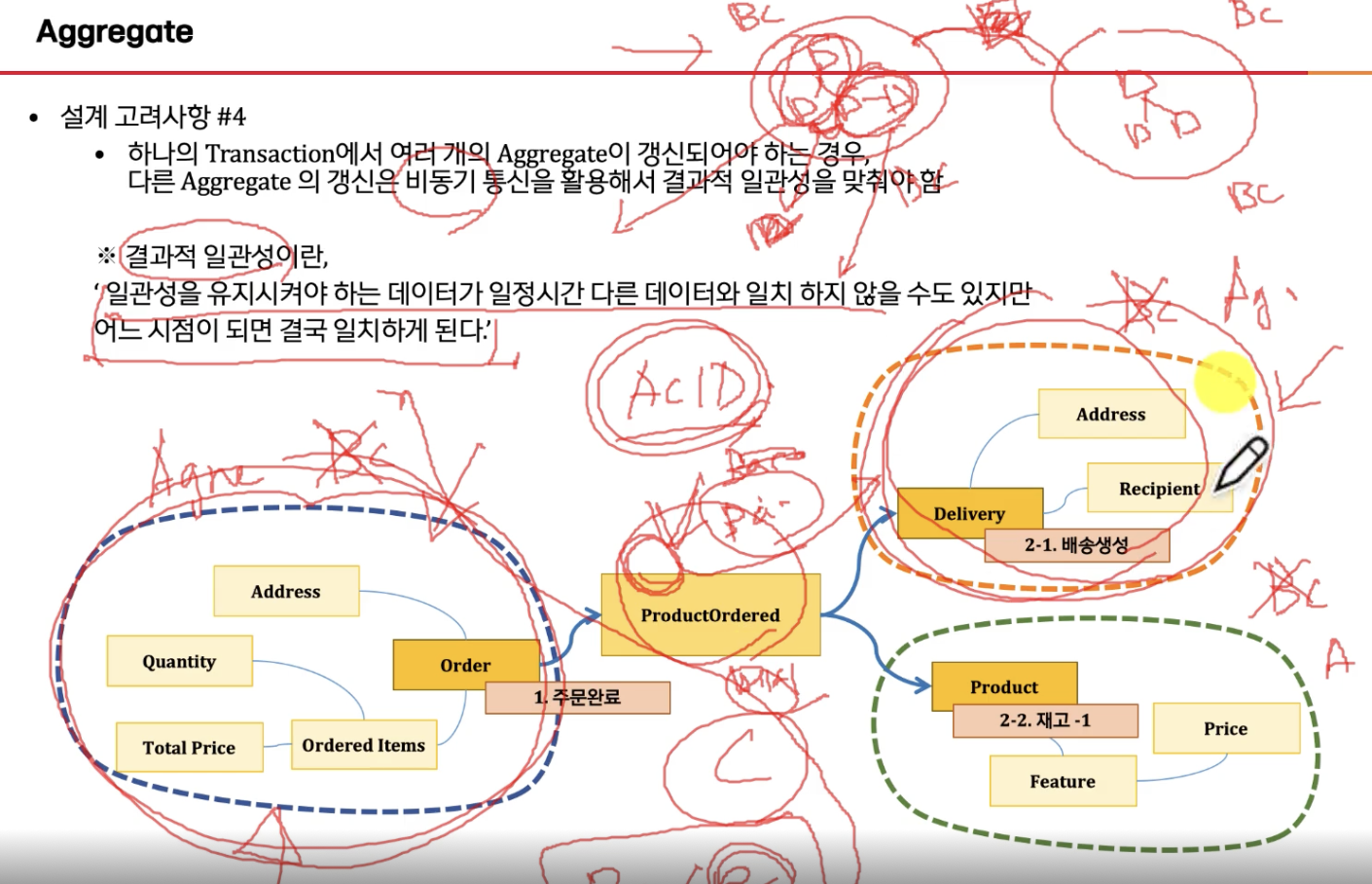
구현한 예시 코드 설명
// Controller - Command Bus로 삭제 명령 전달
@Delete('delete')
@HttpCode(HttpStatus.OK)
async deleteAccount(
@CurrentUser() user: any,
) {
return await this.commandBus.execute(
new DeleteAccountCommand(user.idx)
);
}// Command Handler - 구현된 User 도메인 모델을 통해 이벤트 호출
// user.commit()이 실행 될 때가 이벤트가 실제로 처리되는 시점이다.
@CommandHandler(DeleteAccountCommand)
export class DeleteAccountHandler
implements ICommandHandler<DeleteAccountCommand>
{
constructor(
private readonly publisher: EventPublisher
) {}
async execute(command: DeleteAccountCommand) {
const { idx } = command;
try {
const user = this.publisher.mergeObjectContext(new User(idx));
user.deleteProjectManagementInfo();
user.deleteUser();
user.commit();
return { result: 'Success' };
} catch (err) {
throw new InternalServerErrorException(err);
}
}
}
// User Model - User 도메인에 대한 이벤트 구현
export class User extends AggregateRoot {
constructor(private readonly idx: number) {
super();
}
data: UserDto;
setData(data) {
this.data = data;
}
deleteProjectManagementInfo() {
this.apply(new DeleteProjectManagementInfoEvent(this.idx));
}
deleteUser = async () => {
this.apply(new DeleteUserEvent(this.idx));
}
}
// Saga - 이벤트는 Saga를 통해 호출이 감지되고 해당 이벤트에 수반되는 Command Handler를 호출한다
@Injectable()
export class UserSagas {
@Saga()
deleteRequested = (events$: Observable<any>): Observable<ICommand> => {
return events$
.pipe(
ofType(DeleteUserEvent),
delay(1000),
map(event => {
return new DeleteUserCommand(event.idx);
}),
);
}
@Saga()
userDeleted = (events$: Observable<any>): Observable<ICommand> => {
return events$
.pipe(
ofType(DeleteProjectManagementInfoEvent),
delay(1000),
map(event => {
return new DeleteProjectCommand(event.idx);
}),
);
}
}
// 이벤트 A에 대한 Command Handler - 성공 / 실패에 따른 이벤트 별도 처리 필요
@CommandHandler(DeleteProjectCommand)
export class DeleteProjectHandler
implements ICommandHandler<DeleteProjectCommand>
{
constructor(private readonly userRepo: UserRepository,
private readonly publisher: EventPublisher,
) {}
async execute(command: DeleteProjectCommand) {
const { idx } = command;
try {
// 트랜잭션 처리
await this.userRepo.deleteProjectInfo(command.userId);
// 성공 시 "DeleteSuccessEvent" emit
this.eventBus.publish(new DeleteProjectInfoSuccessEvent(command.orderId));
} catch (error) {
// 에러 발생 시 관련된 트랜잭션 롤백
this.eventBus.publish(new DeleteProjectInfoFailedEvent(command.orderId, command.orderDetails));
this.eventBus.publish(new DeleteUserFailedEvent(event.userId, command.userDetails));
}
}
}마치며
- 개발 환경은 MSA가 아닌 Monolithic Nestjs CQRS 패턴의 이벤트 개발 방식으로 진행함
- 이벤트 주도 개발은 확장성, 비동기 처리, 성능(경우에 따라..)에 유리한 만큼 위와 같은 보상트랜잭션 문제가 걸릴 경우 복잡해 질 수 있다
- EDA, DDD, MSA, Saga에 대해 좀 더 스터디 필요