그래프(Graph) 란?
그래프는 vertex(정점)와 edge(정점과 정점을 연결하는 간선)로 구성된 한정된 자료구조를 의미한다.
그래프 종류
- 무방향 그래프 (간선에 방향이 따로 없음)
- 방향 그래프 (간선에 방향이 있음)
- 가중치 그래프 (간선에 가중치가 있음)
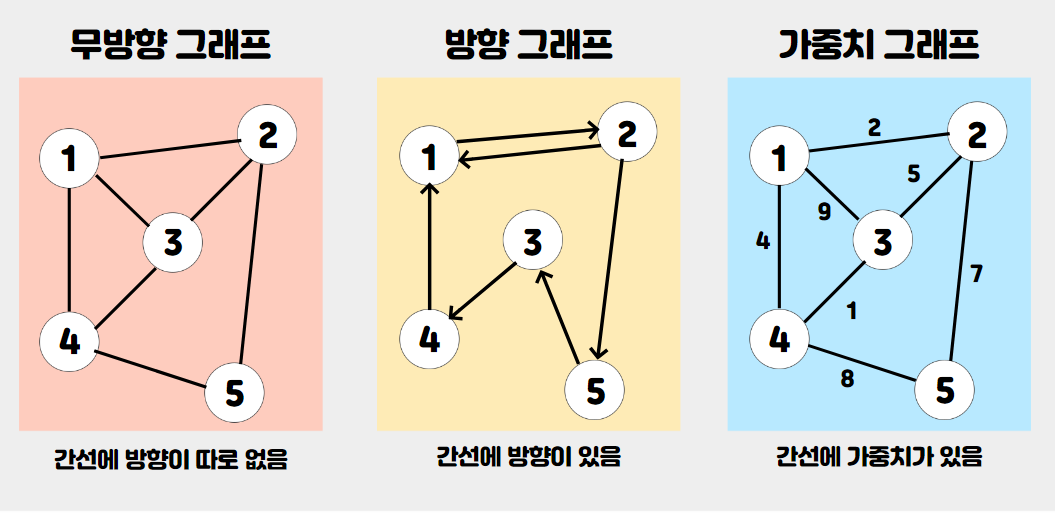
https://born2bedeveloper.tistory.com/42
그래프 구현
행렬로 구현하기
- 무방향 그래프
정점 a와 정점 b를 잇는 간선이 있을 경우, 행렬(a,b)에 1을 표기한다.
만약 가중치가 있는 그래프라면 1 대신 가중치를 넣을 수 있다.
기본적으로 무방향 그래프의 경우는 (a,b) (b,a)에 모두 간선 값을 넣지만, 방향 그래프같은 경우는 위의 표와 같이 방향에 맞는 간선만 표기한다.
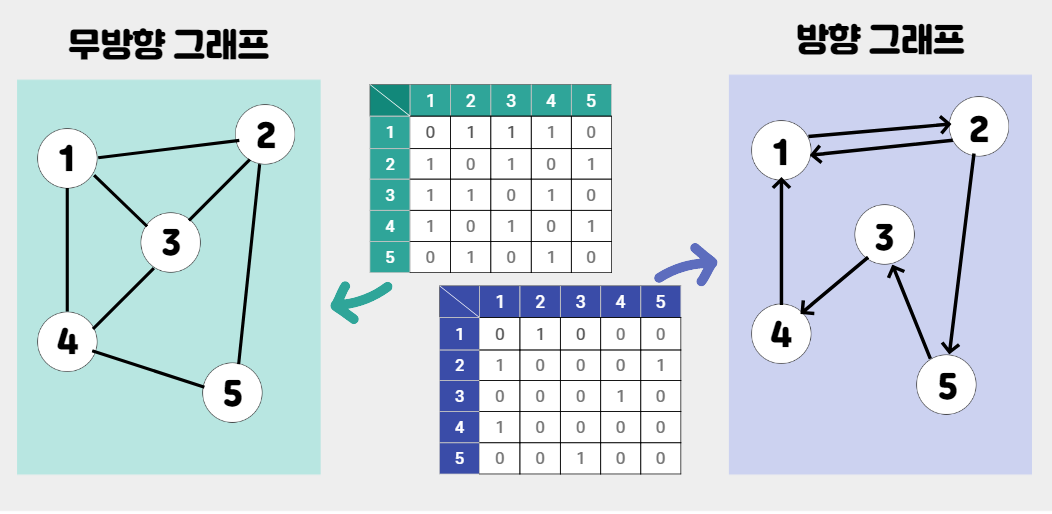
https://born2bedeveloper.tistory.com/42
- 무방향 그래프 코드 구현
public class Main {
public static void print(int[][] graph) {
for (int i = 1; i < graph.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < graph.length; j++)
System.out.print(graph[i][j]+ " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void putEdge(int[][] graph, int x, int y) {
graph[x][y] = 1;
graph[y][x] = 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 5; //그래프 정점의 개수
int[][] graph = new int[n+1][n+1]; //index를 1부터 맞추기 위해 n+1
putEdge(graph, 1, 2);
putEdge(graph, 1, 3);
putEdge(graph, 1, 4);
putEdge(graph, 2, 3);
putEdge(graph, 2, 5);
putEdge(graph, 3, 4);
putEdge(graph, 4, 5);
print(graph);
}
}인접 리스트로 구현하기
해당 노드와 연결되어있는 노드들을 리스트로 쭉 붙이는 방식이다.
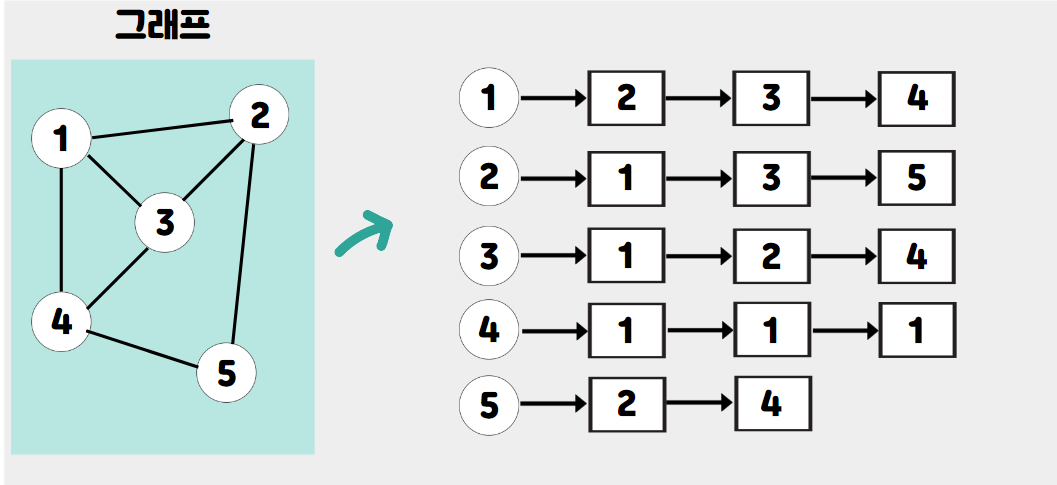
https://born2bedeveloper.tistory.com/42
- ArrayList 사용하여 코드로 구현
public class Main {
public static void print(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph) {
for (int i = 1; i < graph.size(); i++) {
ArrayList<Integer> node = graph.get(i);
System.out.print("node"+"["+i+"] : ");
for (int j = 0; j < node.size(); j++)
System.out.print(node.get(j)+ "->");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void putEdge(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph, int x, int y) {
graph.get(x).add(y);
graph.get(y).add(x);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 5; //그래프 정점의 개수
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
graph.add(new ArrayList<>()); //각 노드 별 리스트를 만들어준다.
putEdge(graph, 1, 2);
putEdge(graph, 1, 3);
putEdge(graph, 1, 4);
putEdge(graph, 2, 3);
putEdge(graph, 2, 5);
putEdge(graph, 3, 4);
putEdge(graph, 4, 5);
print(graph);
}
}| 인접 행렬 | 인접 리스트 | |
| 시간 복잡도 | O(N^2) 정점 N*N만큼 필요 | O(N) N : 간선의 개수 |
| 두 정점의 연결 여부 | graph[x][y] 의 값으로 한번에 확인 | graph\ 의 원소에서 y가 나올때까지 탐색 |
| 인접 노드 파악 여부 | N * N만큼 반복문을 돌아 확인 | 각 리스트에 담겨있는 원소를 확인 |
👉 간선이 많은 그래프의 경우, 인접 행렬을 통해 빠르게 연결 여부를 확인할 수 있음.
👉 반면 간선이 적은 그래프의 경우는, 인접 리스트를 통해 인접 노드를 빠르게 확인할 수 있음.
