참고 자료
https://referencesource.microsoft.com/#mscorlib/system/collections/generic/list.cs,cf7f4095e4de7646
https://learn.microsoft.com/ko-kr/dotnet/api/system.collections.generic.list-1.capacity?view=net-7.0
C# List는 Array로 구현되어 있다.
공식 문서를 살펴보면 리스트는 내부적으로 배열로 구현되어 있고 크기가 늘어남에 따라 더 큰 배열을 만들어 기존의 요소들을 복사하고 삭제하는 과정을 거친다.
// Implements a variable-size List that uses an array of objects to store the
// elements. A List has a capacity, which is the allocated length
// of the internal array. As elements are added to a List, the capacity
// of the List is automatically increased as required by reallocating the
// internal array.리스트 기본 동작 방식
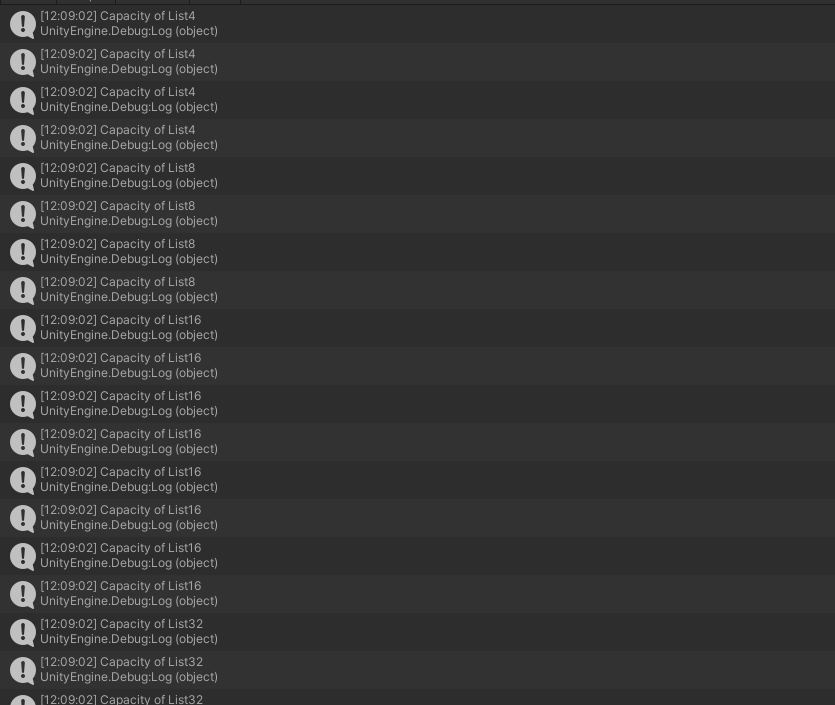
리스트에 값을 넣어보면서 capacity를 확인해보면 다음과 같이 2^n 형태로 크기가 늘어나는 것을 볼 수 있다.
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class ListTest : MonoBehaviour
{
private void Start()
{
List<int> intList = new List<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i ++)
{
intList.Add(i);
Debug.Log("Capacity of List" + intList.Capacity);
}
}
}
리스트 생성
생성자 - None
생성자가 없는 경우 리스트는 빈 array를 할당받는다.
static readonly T[] _emptyArray = new T[0];
// Constructs a List. The list is initially empty and has a capacity
// of zero. Upon adding the first element to the list the capacity is
// increased to 16, and then increased in multiples of two as required.
public List() {
_items = _emptyArray;
}생성자 - int
생성자로 int를 주는 경우 리스트를 만들면서 바로 capacity를 설정하는 것이다. 초기에 capacity 크기의 배열로 리스트를 설정하는 것이다.
public List(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 0) ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.capacity, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNum);
Contract.EndContractBlock();
if (capacity == 0)
_items = _emptyArray;
else
_items = new T[capacity];
}생성자 - IEnumerable
즉, 다음과 같이 요소들이 추가될 때 더 큰 배열을 만들고 값들을 복사한다.
기본적으로 제공하는 default capacity는 4이다. 즉, 새로 추가된 값이 4가 넘어가면 더 큰 배열을 만들어 값을 복사한다.
초기에 바로 capacity 값을 넘겨주어 리스트를 만들 수 있다. 아니면 (list).Capacity로 property setter를 통해 값을 설정할 수 있다.
그 다음 처음 생성할 때 값들을 넣은 케이스를 살펴보자.
// Constructs a List, copying the contents of the given collection. The
// size and capacity of the new list will both be equal to the size of the
// given collection.
//
public List(IEnumerable<T> collection) {
if (collection==null)
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.collection);
Contract.EndContractBlock();
ICollection<T> c = collection as ICollection<T>;
if( c != null) {
int count = c.Count;
if (count == 0)
{
_items = _emptyArray;
}
else {
_items = new T[count];
c.CopyTo(_items, 0);
_size = count;
}
}
else {
_size = 0;
_items = _emptyArray;
// This enumerable could be empty. Let Add allocate a new array, if needed.
// Note it will also go to _defaultCapacity first, not 1, then 2, etc.
using(IEnumerator<T> en = collection.GetEnumerator()) {
while(en.MoveNext()) {
Add(en.Current);
}
}
}
}Capacity
Capacity 프로퍼티는 다음과 같다. Capacity를 설정하면 처음 지정된 사이즈의 array로 리스트를 만들게 된다. 즉 capacity를 미리 설정해준다면 매번 copy를 하며 발생하는 가비지를 줄일 수 있다.
// Gets and sets the capacity of this list. The capacity is the size of
// the internal array used to hold items. When set, the internal
// array of the list is reallocated to the given capacity.
//
public int Capacity {
get {
Contract.Ensures(Contract.Result<int>() >= 0);
return _items.Length;
}
set {
if (value < _size) {
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.value, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_SmallCapacity);
}
Contract.EndContractBlock();
if (value != _items.Length) {
if (value > 0) {
T[] newItems = new T[value];
if (_size > 0) {
Array.Copy(_items, 0, newItems, 0, _size);
}
_items = newItems;
}
else {
_items = _emptyArray;
}
}
}
}리스트 요소 추가
리스트는 다양한 함수를 가지고 있다. 그 중 추가와 삭제를 위주로 살펴보며 내부적으로 어떻게 요소들을 관리하는지에 대해 살펴보고자 한다.
Add
리스트에 요소를 추가하는 경우
// Adds the given object to the end of this list. The size of the list is
// increased by one. If required, the capacity of the list is doubled
// before adding the new element.
//
public void Add(T item) {
if (_size == _items.Length) EnsureCapacity(_size + 1);
_items[_size++] = item;
_version++;
}
현재 새 요소가 추가되었을 때 크기가 capacity 보다 크다면 capacity를 2의 배수로 늘린다.
// Ensures that the capacity of this list is at least the given minimum
// value. If the currect capacity of the list is less than min, the
// capacity is increased to twice the current capacity or to min,
// whichever is larger.
private void EnsureCapacity(int min) {
if (_items.Length < min) {
int newCapacity = _items.Length == 0? _defaultCapacity : _items.Length * 2;
// Allow the list to grow to maximum possible capacity (~2G elements) before encountering overflow.
// Note that this check works even when _items.Length overflowed thanks to the (uint) cast
if ((uint)newCapacity > Array.MaxArrayLength) newCapacity = Array.MaxArrayLength;
if (newCapacity < min) newCapacity = min;
Capacity = newCapacity;
}
}리스트 요소 삭제
내부적으로 Array.Clear()를 사용하여 모든 요소들을 삭제한다.
Array.Clear(array, index, length): index부터 시작해서 length 만큼 array의 요소들 삭제
Clear
// Clears the contents of List.
public void Clear() {
if (_size > 0)
{
Array.Clear(_items, 0, _size); // Don't need to doc this but we clear the elements so that the gc can reclaim the references.
_size = 0;
}
_version++;
}RemoveAt
내부적으로 Array.Copy()를 사용하여 삭제한 요소 기준 뒤의 요소들을 한 칸씩 당겨서 복사한다. (+ Remove는 내부적으로 item의 index를 찾아서 RemoveAt을 호출하므로 따로 다루지 않는다.)
즉, Array.Copy를 하므로 O(N)이 소요된다. 삭제를 자주 불러야한다면 좋은 선택은 아니다..!
Array.Copy (sourceArray, sourceIndex, destinationArray, destinationIndex, length) : 지정한 소스 인덱스부터 복사하여 지정된 대상 인덱스부터 시작하는 다른 Array에 붙여 넣는다.
- source index: 복사가 시작되는 source array의 index
- destination index: 저장이 시작되는 destination array의 index
- length: 복사할 요소 개수
// Removes the element at the given index. The size of the list is
// decreased by one.
//
public void RemoveAt(int index) {
if ((uint)index >= (uint)_size) {
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException();
}
Contract.EndContractBlock();
_size--;
if (index < _size) {
Array.Copy(_items, index + 1, _items, index, _size - index);
}
_items[_size] = default(T);
_version++;
}RemoveAll
이건 추가로 clear과 어떤 차이를 보이는 지 궁금해서 넣었다.
// This method removes all items which matches the predicate.
// The complexity is O(n).
public int RemoveAll(Predicate<T> match) {
if( match == null) {
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.match);
}
Contract.Ensures(Contract.Result<int>() >= 0);
Contract.Ensures(Contract.Result<int>() <= Contract.OldValue(Count));
Contract.EndContractBlock();
int freeIndex = 0; // the first free slot in items array
// Find the first item which needs to be removed.
while( freeIndex < _size && !match(_items[freeIndex])) freeIndex++;
if( freeIndex >= _size) return 0;
int current = freeIndex + 1;
while( current < _size) {
// Find the first item which needs to be kept.
while( current < _size && match(_items[current])) current++;
if( current < _size) {
// copy item to the free slot.
_items[freeIndex++] = _items[current++];
}
}
Array.Clear(_items, freeIndex, _size - freeIndex);
int result = _size - freeIndex;
_size = freeIndex;
_version++;
return result;
}💬 정리
- C#의 리스트는 내부적으로 배열로 구현되어 있다.
- 리스트에서 요소를 추가할 때 설정된 크기를 넘어가면 더 큰 배열을 생성하고 copy하는 과정이 발생한다. -> 리스트 요소를 추가가 잦게 일어나는 상황이라면 이런 copy가 계속 이루어 진다고 보면 된다.
- 따라서, 가능하다면 list의 크기를 미리 잡을 수 있는 capacity를 사용하는 것도 도움이 될 수 있다!