https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/
📕 문제 설명
정수 배열과 목표 값이 주어진다. 정수 배열 내에서 합으로 목표 값이 만들어 지는 두 숫자의 index를 반환해야 한다. (반환 순서는 상관 x)
정답은 하나로 고정되어 있다. 즉, 2가지 수로 해당 target을 만들 수 있는 경우의 수 자체가 1가지
-
Input
integer array, target value -
Output
integer array내에서 sum으로 target 만들 수 있는 two number의 인덱스 값
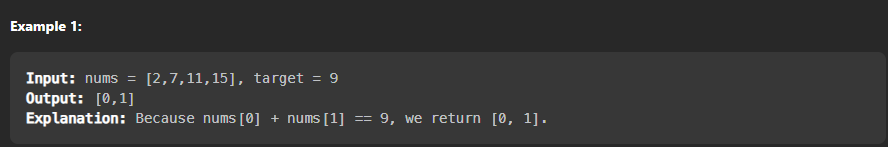
예제
정수 배열 : [2, 7, 11, 15]
목표 값: 9
해당 배열에서는 2와 7의 합으로 9를 만들 수 있으므로 [0, 1]을 반환한다.
풀이
1. 이중 for문으로 한 숫자 기준으로 두고 다른 숫자들 돌면서 합들 구하는 방식 -> 같은 값이 되는 경우 stop (O(N^2))
public class Solution {
public int[] TwoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] answer = new int[2]; // 정답 배열
for(int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < nums.Length; j++)
{
if (i != j && nums[i] + nums[j] == target)
{
answer = new int[] {i, j};
break;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
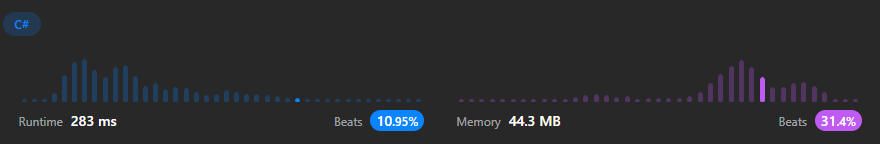
}풀이 1번 결과
2. target과의 차이값을 계산 후 해당 값이 존재하는 지 확인 (O(N))
O(N^2)보다 좋은 방법이 있다는 내용이 Follow Up Question으로 있다. Dictionary를 활용해 target과의 차를 nums가 가지고 있는지 확인하면 시간을 더 개선 가능하다.
- 현재 index의 값과 target과의 차 구하기
- 해당 차의 값 자체가 dictionary에 존재하는 지 확인
- 존재한다면 현재 index와 dictionary에서 해당 값의 index를 불러와 반환
Dictionary의 경우 key로는 현재 값을 넣고, value로 해당 값의 index를 넣는다.
결국 답은 한 쌍이 나오게 된다. 한 쌍 중 앞의 것을 먼저 보게 되면 해당 값이 dictionary에 담겨있게 되고, 뒤에 다른 값을 볼때는 target과의 차가 결국 앞에 담긴 값이 되기 때문에 답이 구해지는 방식이다.
public class Solution {
public int[] TwoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Dictionary<int, int> diffDict = new Dictionary<int, int>();
int[] answer = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
{
if (diffDict.TryGetValue(target - nums[i], out int index))
{
answer = new int[] {i, index};
break;
}
diffDict[nums[i]] = i;
}
return answer;
}
}풀이 2번 결과
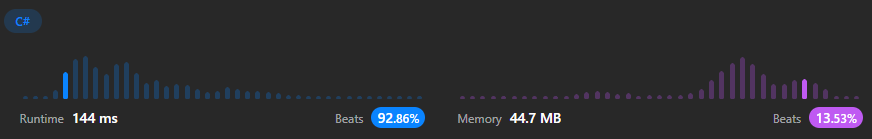
메모리는 dictionary 정의하면서 좀 더 사용되었지만 시간이 많이 개선된 것을 볼 수 있다.