스프링의 대표적인 특성
- 제어의 역전 (Inversion Of Control)
- 의존성 주입 (Dependency Injection)
- 관점 지향 프로그래밍 (Aspect Oriented Programming)
- 제어의 역전 (Inversion Of Control)
: 스프링 컨테이너가 필요에 따라 개발자 대신 Bean들을 관리(제어)해주는 행위
- 확장 가능하고 모듈화된 프로그램을 구성하는 느슨한 결합을 달성하기 위해 다양한 종류의 컨트롤을 반전하는 것
- 제어의 역전은 클래스간의 결합을 느슨하게 설계하여 테스트가 가능하고 유지보수가 용이하게 만드는데 도움
- 의존성 주입 (Dependency Injection)
: 의존 관계를 외부에서 결정(주입)해주는 것 (인터페이스 + 다형성)
- 코드의 재사용성, 유연성이 높아지고 객체간 결합도가 낮기 때문에 한 클래스를 수정했을 때 다른 클래스도 수정해야 하는 상황을 막아준다는 장점
ex. CoffeeShop이라는 클래스에 CoffeeMachine을 담는 경우
: coffeeMachine의 종류에 상관없이 커피를 내리는 메소드를 정의해놓은 인터페이스를 만들고 각각의 클래스들이 그것을 구현
interface CoffeeMachine {
int getCoffeeShot();
}
class CoffeeMachinePremium implements CoffeeMachine {
String brand;
String name;
@Override
public int getCoffeeShot() {
// 커피 뽑는 과정.. 머신만의 특성..
// 프리미엄 과정....고급 과정....
return 1; // 에스프레소 1샷
}
}
class CoffeeMachineNormal implements CoffeeMachine {
String brand;
String name;
@Override
public int getCoffeeShot() {
// 커피 뽑는 과정.. 머신만의 특성..
return 1; // 에스프레소 1샷
}
}: CoffeeShop 클래스에는 CoffeeMachine이라는 인터페이스를 구현한 구현체를 담아서, 구현체 안에 있는 getCoffeeShot을 불러오는 createCoffee라는 메소드를 만든다
class CoffeeShop {
// 인터페이스인 CoffeeMachine을 구현한 구현체를 담는 필드변수 선언
CoffeeMachine coffeeMachine;
public CoffeeShop(CoffeeMachine coffeeMachine) {
this.coffeeMachine = coffeeMachine;
}
public int createCoffee() {
// 커피 제조에 필요한 과정
// 컵 꺼내고
// 물 따라놓고
// 샷 뽑고.
int shot = coffeeMachine.getCoffeeShot();
// 컵에다가 샷 붓고..
// 뚜껑 닫고
return 1; // 커피 한잔
}
}: CoffeeShop 클래스를 불러오는 곳에서는 coffeeMachine의 종류에 구애받지 않고 createCoffee 메소드를 불러와서 활용하면 끝!
package com.app.controller;
//인터페이스 다형성 개념 적용
public class DIConcept {
public void main() {
CoffeeMachineNormal cm = new CoffeeMachineNormal();
CoffeeMachinePremium cmp = new CoffeeMachinePremium();
// normal이든 premium이든 만들어서 coffeeShop에 넣어준다 -> 외부에서 뭘 주입할지만 바꿔주면 됨
// -> 인터페이스 다형성을 활용하여, 객체(bean)을 주입시키는 과정
CoffeeShop myShop = new CoffeeShop(cm);
int resultCoffee = myShop.createCoffee(); // 커피만든다.
System.out.println(resultCoffee); // 만든 커피 활용
}
}- 관점 지향 프로그래밍
: 여러 객체에서 공통적으로 사용하고 있는 기능을 분리해서 모듈화하고 재사용하는 프로그래밍 기법 (참고 : [Spring] AOP(관점 지향 프로그래밍))
bean 등록 방법
- xml
spring 폴더 밑에 있는 root-context.xml에 bean 객체 등록, bean들을 관리해주는 applicationContext에 접근해서 id로 불러와서 활용 가능
root-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="sampleBean1" class="com.app.beans.SampleBean1" />
<bean id="sampleBean2" class="com.app.beans.SampleBean2" />
<!-- lazy-init 기본 : 서버 시작 시, xml 로딩 과정에서 Bean 생성 -->
<!-- lazy-init true : 실제 Bean에 접근해서 사용하려고 할 때 생성 -->
<bean id="sampleBean3" class="com.app.beans.SampleBean3" lazy-init="true" />
<!-- scope 기본 : 싱글톤 (전체에서 1개만) -->
<!-- scope prototype : 일반적인 객체로 활용 (new 생성) -->
<bean id="sampleBean4" class="com.app.beans.SampleBean4" scope="prototype" />
</beans>ex.
SampleBean1, SampleBean2 클래스
package com.app.beans;
public class SampleBean1 {
public SampleBean1() {
System.out.println("SampleBean1 생성자");
}
}package com.app.beans;
public class SampleBean2 {
public SampleBean2() {
System.out.println("SampleBean2 생성자");
}
}BeanController
@Controller
public class BeanController {
@Autowired
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
//@Autowired
//BeanFactory beanFactory;
//IOC Container <- Bean을 관리하는 주체
// 1. ApplicationContext
// 2. BeanFactory
@RequestMapping("/sb1")
public String sb1() {
SampleBean1 sb1 = (SampleBean1) applicationContext.getBean("sampleBean1");
System.out.println("/sb1 - " + sb1);
return "checkBean";
}
@RequestMapping("/sb1_2")
public String sb1_2() {
SampleBean1 sb1 = (SampleBean1) applicationContext.getBean("sampleBean1");
System.out.println("/sb1_2 - " + sb1);
return "checkBean";
}
@RequestMapping("/sb2")
public String sb2() {
SampleBean2 sb = (SampleBean2) applicationContext.getBean("sampleBean2");
System.out.println("/sb2 - " + sb);
return "checkBean";
}
@RequestMapping("/sb2_2")
public String sb2_2() {
SampleBean2 sb = (SampleBean2) applicationContext.getBean("sampleBean2");
System.out.println("/sb2_2 - " + sb);
return "checkBean";
}
}서버 시작시에 SampleBean1, SampleBean2 객체가 생성되어서 콘솔에 찍히는 모습
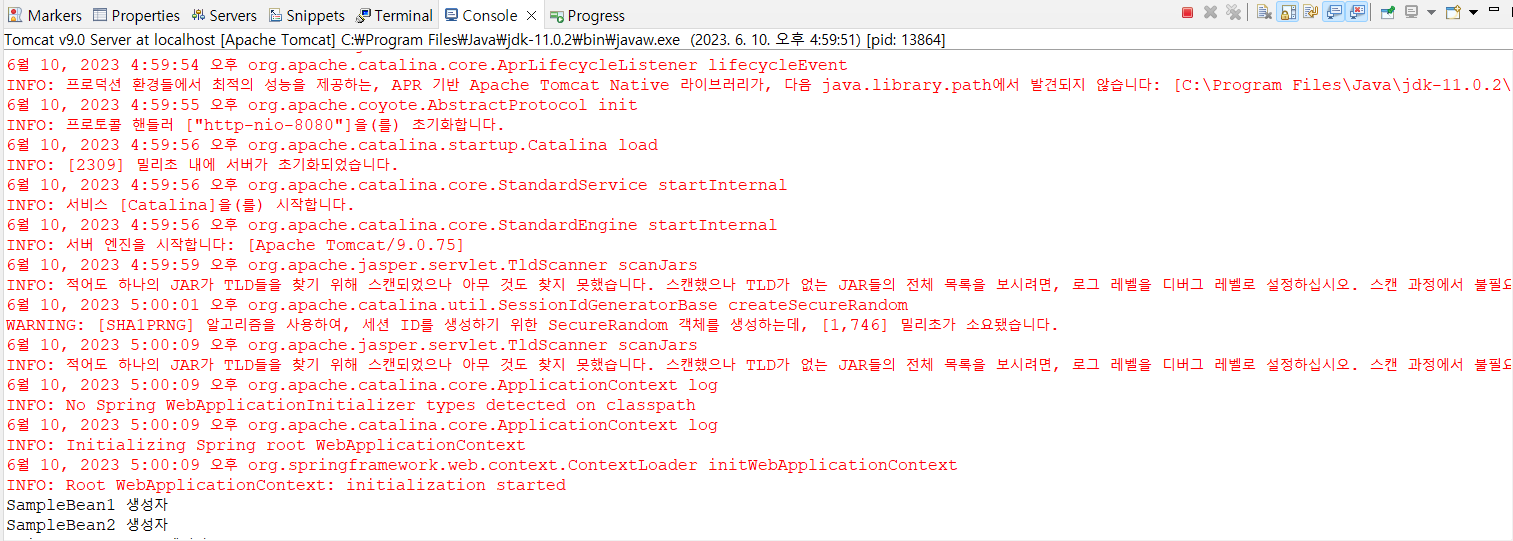
싱글톤이어서 여러번 불러도 똑같은 주소가 출력되는 모습
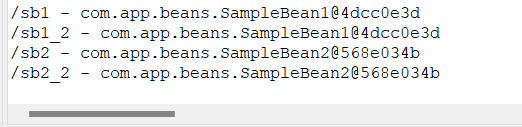
lazy-init 속성을 true로 설정하면 서버 시작시에 bean 객체가 만들어지는 것이 아니라 그 객체를 활용하려고 접근할 때 생성됨
ex.
SampleBean3 클래스
package com.app.beans;
public class SampleBean3 {
int check;
public SampleBean3() {
System.out.println("SampleBean3 생성자");
}
public int getCheck() {
return check;
}
public void setCheck(int check) {
this.check = check;
}
}BeanController
@Controller
public class BeanController {
@Autowired
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@RequestMapping("/sb3")
public String sb3() {
SampleBean3 sb = (SampleBean3) applicationContext.getBean("sampleBean3");
System.out.println("/sb3 - " + sb);
sb.setCheck(100);
System.out.println(sb.getCheck());
return "checkBean";
}
@RequestMapping("/sb3_2")
public String sb3_2() {
SampleBean3 sb = (SampleBean3) applicationContext.getBean("sampleBean3");
System.out.println("/sb3_2 - " + sb);
System.out.println(sb.getCheck());
return "checkBean";
}
}객체를 활용하려고 할 때 생성되고 그 이후에는 생성자가 호출되지 않는 모습
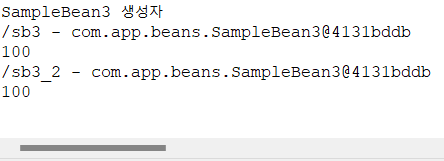
scope 속성을 prototype으로 설정하면 bean에 접근할 때 마다 새로운 객체가 만들어짐 (싱글톤 X)
ex.
SampleBean4 클래스
package com.app.beans;
public class SampleBean4 {
int check;
public SampleBean4() {
System.out.println("SampleBean4 생성자");
}
public int getCheck() {
return check;
}
public void setCheck(int check) {
this.check = check;
}
}
BeanController
@Controller
public class BeanController {
@Autowired
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@RequestMapping("/sb4")
public String sb4() {
SampleBean4 sb = (SampleBean4) applicationContext.getBean("sampleBean4");
System.out.println("/sb4 - " + sb);
sb.setCheck(100);
System.out.println(sb.getCheck());
return "checkBean";
}
@RequestMapping("/sb4_2")
public String sb4_2() {
SampleBean4 sb = (SampleBean4) applicationContext.getBean("sampleBean4");
System.out.println("/sb4_2 - " + sb);
System.out.println(sb.getCheck());
return "checkBean";
}
}객체를 활용하려고 호출할 때 마다 새로운 객체가 생성되고, 다른 주소가 호출되는 모습
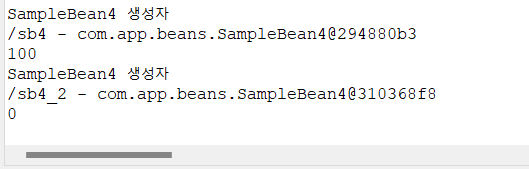
bean이 생성될 때의 메소드와 소멸될 때의 메소드를 정해줄 수 있음
root-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- InitDestroyBean 클래스 안에 bean_init 메소드를 만들고, init-method에 이름을 설정해주면 bean이 생성되는 초기에 호출됨 -->
<bean id="initDestroyBean" class="com.app.beans.InitDestroyBean" init-method="bean_init" destroy-method="bean_destroy"/>
</beans>InitDestroyBean 클래스
package com.app.beans;
public class InitDestroyBean {
public InitDestroyBean() {
System.out.println("InitDestroyBean 생성자");
}
public void bean_init() {
System.out.println("bean_init 생성시점에 부르는 초기 설정");
}
public void bean_destroy() {
System.out.println("bean_destroy 죽는 시점에 부르는 마지막 설정");
}
}생성 초기에 init-method가 실행된 모습
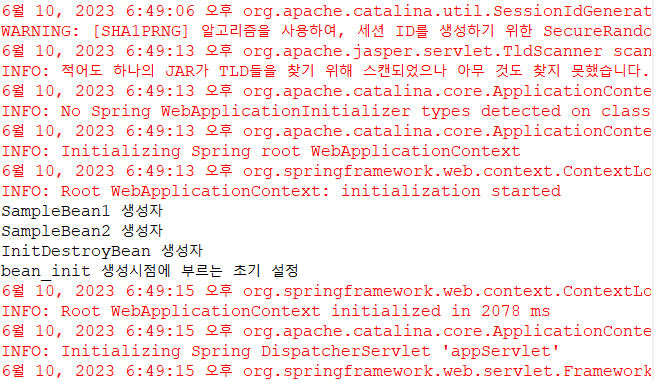
소멸될 때 destroy-method가 실행된 모습
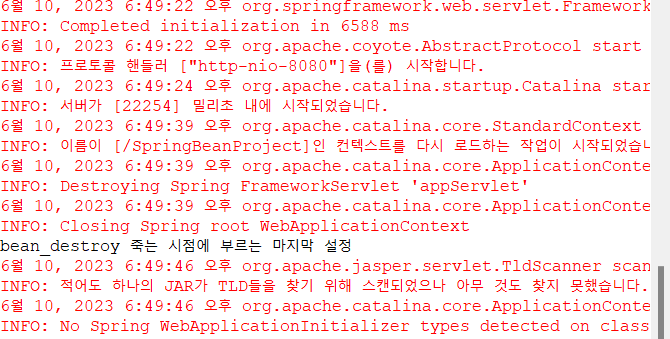
출처
의존성 주입(Dependency Injection) 의 개념과 방법 및 장단점
[Spring] 의존성 주입, 제어의 역전
