2.1) Truthy와 Falsy
Truthy & Falsy란?
- 참이나 거짓을 의미하지 않는 값도, 조건문 내에서 참이나 거짓으로 평가하는 특징
- 이를 이용하면 조건문을 간단히 만들 수 있음
if(123) ---- Truthy
if(undefined) ---- Falsy1. Falsy한 값
let f1 = undefined;
let f2 = null;
let f3 = 0;
let f4 = -0;
let f5 = NaN;
Slet f6 = "";
let f7 = 0n; // Big Integer라는 특수한 자료형. 잘 사용되지 않는다.2. Truthy 한 값
// -> 7가지 Falsy 한 값들 제외한 나머지 모든 값
let t1 = "hello";
let t2 = 123;
let t3 = [];
let t4 = {};
let t5 = () => {};3. 활용 사례
// 객체를 받을 것이라고 생각했는데 undefined인 값이 넘어오는 경우가 정말 많음
function printName(person) {
if (!person) {
console.log("person의 값이 없음");
return;
}
console.log(person.name);
}
let person = { name: "이정환" };
printName(person);
2.2) 단락 평가
단락 평가(Short-circuit Evaluation)
- 논리 연산식에서 첫번째 피연산자의 값으로 결과값이 확정된다면, 두번째 피연산자의 값에 아예 접근하지 않는 것
// 기존 코드
function printNameOld(person) {
if(!person) {
console.log("person의 값이 없음");
return;
}
console.log(person.name);
}
// 단락 평가 활용 사례
// && = And = 하나라도 false이면 false
function printName(person) {
const name = person && person.name;
console.log(name || "person의 값이 없음");
}
printName();
printName({ name: "이정환" });
2.3) 구조분해할당
배열의 구조 분해 할당
let arr = [1, 2, 3];
let [one, two, three, four = 4] = arr;객체의 구조 분해 할당
- 중괄호 사용
- key를 바탕으로 할당된다.
let person = {
name: "이정환",
age: 27,
hobby: "테니스",
};
let {
age: myAge,
hobby,
name,
extra = "hello",
} = person;객체 구조 분해 할당을 이용해서 함수의 매개변수를 받는 방법
const func = ({ name, age, hobby, extra }) => {
console.log(name, age, hobby, extra);
};
func(person);2.4) Spread 연산자와 Rest 매개변수
Spread 연산자
...- Spread : 흩뿌리다, 펼치다 라는 뜻
- 객체나 배열에 저장된 여러개의 값을 개별로 흩뿌려주는 역할
let arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
let arr2 = [4, ...arr1, 5, 6];
let obj1 = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
};
let obj2 = {
...obj1,
c: 3,
d: 4,
};
function funcA(p1, p2, p3) {
// console.log(p1, p2, p3);
}
funcA(...arr1);Rest 매개변수
- Rest는 나머지, 나머지 매개변수
- rest 매개변수 뒤에 추가적인 매개변수가 오면 안된다.
function funcB(one, two, ...ds) {
console.log(ds); // 3
}
funcB(...arr1);
2.5) 원시타입 vs 객체타입
- 값이 저장되거나 복사되는 과정이 다름
- 원시-값 / 객체-참조값
- 객체 = 가변값 (메모리값 수정 O)
- 주의점
- 의도치 않게 값이 수정될 수 있다.
// 얕은 복사 - 참조값 복사 => 원본 객체가 수정될 수 있음
let o1 = {name : "이정환"};
let o2 = o1;
// 깊은 복사 - 새로운 객체 생성, 프로퍼티만 따로 복사
let o3 = { ...o1 };- 객체간의 비교는 기본적으로 참조값을 기준으로 이루어진다.
// 얕은 비교
console.log(o1 == o2); // true
console.log(o1 == o3); // false
// 깊은 비교 - 프로퍼티의 값을 비교
// JSON.stringify : 객체를 문자열로 변환하는 기능
console.log(
JSON.stringify(o1) == JSON.stringify(o3) // true
);- 배열과 함수도 사실 객체이다
- 추가적인 프로퍼티나 메서드를 가질 수 있다.
- 함수(Function) : 객체 + 추가 기능(호출, 선언, ...)
- 배열(Array) : 객체 + 추가 기능(순차 저장, 순회, ...)
2.6) 반복문으로 배열과 객체 순회하기
순회(Iteration)이란?
- 배열, 객체에 저장된 여러개의 값에 순서대로 하나씩 접근하는 것을 말함
- 주의점
for of는 Array에만 사용할 수 있음.for in은 객체에만 사용할 수 있음
1. 배열 순회
1.1 배열 인덱스
let arr = [1, 2, 3];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
console.log(arr[i]);
}1.2 for of 배열 순회
for (let item of arr) {
console.log(item);
}2. 객체 순회
2.1 Object.keys 내장함수
- 객체에서 key값들만 뽑아서 새로운 배열로 반환
let person = {
name: "이정환",
age: 27,
hobby: "테니스",
};
let keys = Object.keys(person); // ['name', 'age', 'hobby']
for (let key of keys) {
const value = person[key];
console.log(key, value);
}2.2 Object.values 내장함수
- 객체에서 value 값들만 뽑아서 새로운 배열로 반환
let values = Object.values(person); // ['이정환', 27, '테니스']
for (let value of values) {
console.log(value);
}2.3 for in 객체 순회
for (let key in person) {
const value = person[key];
console.log(key, value);
}
2.7) 배열 메서드 1. 요소 조작
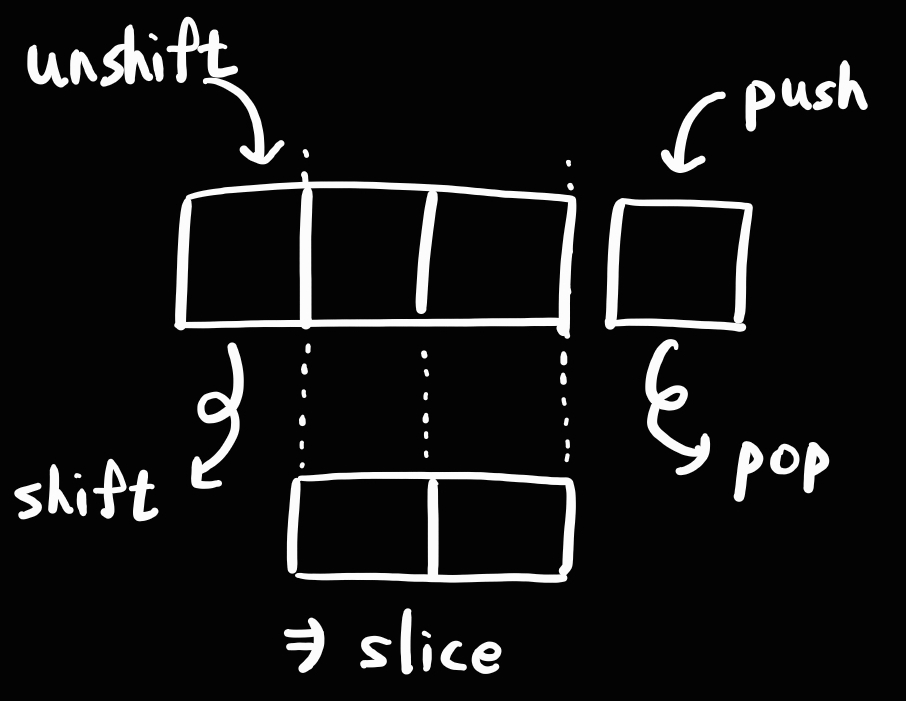
6가지의 요소 조작 메서드
 |  |
|---|
push
- 배열의 맨 뒤에 새로운 요소 추가
- 추가 후 변경된 배열의 길이 return
pop
- 배열의 맨 뒤에 있는 요소를 제거하고, 반환
shift
- 배열의 맨 앞에 있는 요소를 제거, 반환
unshift
- 배열의 맨 앞에 새로운 요소를 추가하는 메서드
- 추가 후 변경된 배열의 길이 return
slice
- 배열의 특정 범위를 잘라내서 새로운 배열로 반환
- 원본 배열에는 영향 X
slice(startIndex, endIndex):startIndex~endIndex-1에 해당하는 배열 반환
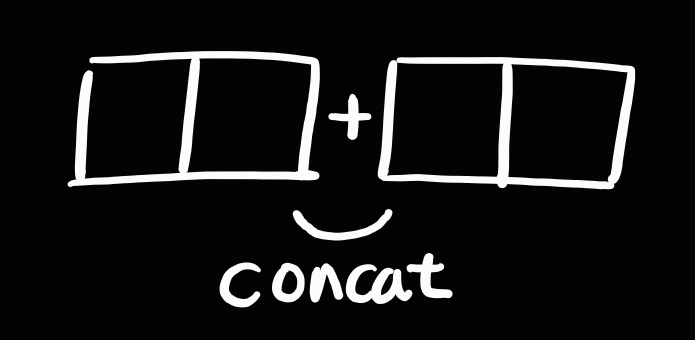
concat
- 두 개의 서로 다른 배열을 이어 붙여서 새로운 배열을 반환
2.8) 배열 메서드 2. 순회와 탐색
5가지의 요소 순회 및 탐색 메서드
forEach
- 모든 요소를 순회하면서, 각각의 요소에 특정 동작을 수행시키는 메서드
- Array 객체에서만 사용 가능한 메서드
- function 파라미터
- 첫번째 인수는 각각의 item- 두번째 인수는 배열의 index
- 세번째 인수는 배열 그 자체
let arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
arr1.forEach(function (item, idx, arr) {
console.log(idx, item*2);
});include
- 배열에 특정 요소가 있는지 확인하는 메서드
indexOf
- 특정 요소의 인덱스(위치)를 찾아서 반환하는 메서드
- 여러개라면 첫번째 위치를 반환
- 없다면
-1을 반환
findIndex
- 모든 요소를 순회하면서, 콜백함수를 만족하는 그런 특정 요소의 인덱스(위치)를 반환하는 메서드
- 객체 타입의 배열에서 유용함
- 없다면
-1을 반환
let objectArr = [
{ name: "이정환" },
{ name: "홍길동" },
];
console.log(
objectArr.indexOf({ name: "이정환" }) // -1
);
console.log(
objectArr.findIndex(
(item) => item.name === "이정환"
)
); // 02.9 배열 메서드 3. 배열 변형
5가지 배열 변형 메서드
filter
- 기존 배열에서 조건을 만족하는 요소들만 필터링하여 새로운 배열로 반환
let arr1 = [
{ name: "이정환", hobby: "테니스" },
{ name: "김효빈", hobby: "테니스" },
{ name: "홍길동", hobby: "독서" },
];
const tennisPeople = arr1.filter(
(item) => item.hobby === "테니스"
); // [{...}, {...}]map
- 배열의 모든 요소를 순회하면서, 각각 콜백함수를 실행하고 그 결과값들을 모아서 새로운 배열로 반환
let arr2 = [1, 2, 3];
const mapResult1 = arr2.map((item, idx, arr) => {
return item * 2;
});
let names = arr1.map((item) => item.name);sort
- 배열을 사전순으로 정렬하는 메서드
- sort의 매개변수로 sort의 기준이 될 콜백함수를 넘겨줄 수 있음
let arr3 = [10, 3, 5];
// 내림차순 정렬
arr3.sort((a, b) => {
if (a > b) {
// a가 b 앞에 와라
return -1;
} else if (a < b) {
// b가 a 앞에 와라
return 1;
} else {
// 두 값의 자리를 바꾸지 마라
return 0;
}
});toSorted (가장 최근에 추가된 최신 함수)
- 정렬된 새로운 배열을 반환하는 메서드, 원본 배열은 영향 없음
let arr5 = ["c", "a", "b"];
const sorted = arr5.toSorted();
console.log(arr5);
console.log(sorted);join
- 배열의 모든 요소를 하나의 문자열로 합쳐서 반환하는 메서드
let arr6 = ["hi", "im", "winterlood"];
const joined = arr6.join(" ");
console.log(joined); // hi im winterlood2.10) Date 객체와 날짜
- 월은 0부터 시작함
- Date객체 다루는 법 중요
Date 객체 생성 방법
1. Date 객체를 생성하는 방법
let date1 = new Date(); // 생성자. 현재시간.
let date2 = new Date(1997, 1, 7, 23, 59, 59);2. 타임 스탬프
- 협정 세계시(UTC) 기준
- 특정 시간이 "1970.01.01 00시 00분 00초"로 부터 몇 ms가 지났는지를 의미하는 숫자값
let ts1 = date1.getTime();
let date4 = new Date(ts1);3. 시간 요소들을 추출하는 방법
let year = date1.getFullYear();
let month = date1.getMonth() + 1;
let date = date1.getDate();
let hour = date1.getHours();
let minute = date1.getMinutes();
let seconds = date1.getSeconds();4. 시간 수정하기
date1.setFullYear(2023);
date1.setMonth(2);
date1.setDate(30);
date1.setHours(23);
date1.setMinutes(59);
date1.setSeconds(59);5. 시간을 여러 포맷으로 출력하기
console.log(date1.toDateString()); // Thu Mar 30 2023
console.log(date1.toLocaleString()); // 2023. 3. 30. 오후 11:59:592.11) 동기와 비동기
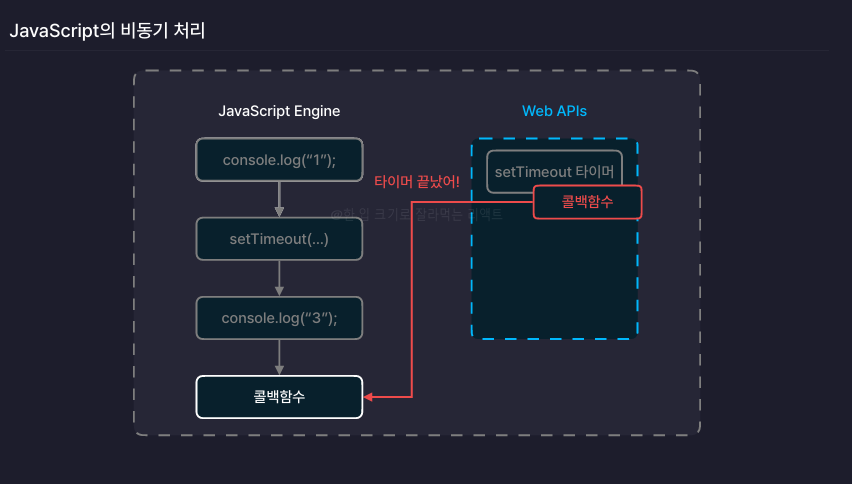
동가와 비동기
-
여러 개의 작업(쓰레드)을 하나씩 처리하는 흐름
-
Javascript는 기본적으로 동기적으로 실행된다.
-
다른 언어는 멀티스레드 방식을 지원하나, Javascript 엔진에는 스레드가 하나
-
비동기로 구성하되, 결과값을 이용하고 싶다면 callback함수를 호출하는 방식으로 구성할 수 있다.
-
비동기 작업들은 자바스크립트 엔진이 아닌 Web APIs에서 실행됨

-
Web APIs는 웹 브라우저가 직접 관리하는 별도의 영역
2.12) 비동기 작업 처리하기 1. 콜백 함수
- 비동기 함수의 결과값을 함수 외부에서 사용하고 싶다면, 콜백 함수를 호출하도록 설정해주면 된다.
function add(a, b, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
const sum = a + b;
callback(sum);
}, 3000);
}
add(1, 2, (value) => {
console.log(value);
});callback 지옥
// 음식을 주문하는 상황
function orderFood(callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
const food = "떡볶이";
callback(food);
}, 3000);
}
function cooldownFood(food, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
const cooldownedFood = `식은 ${food}`;
callback(cooldownedFood);
}, 2000);
}
function freezeFood(food, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
const freezedFood = `냉동된 ${food}`;
callback(freezedFood);
}, 1500);
}
// indent가 깊어진 상황
orderFood((food) => {
console.log(food);
cooldownFood(food, (cooldownedFood) => {
console.log(cooldownedFood);
freezeFood(cooldownedFood, (freezedFood) => {
console.log(freezedFood);
});
});
});
2.13) 비동기 작업 처리하기 2. Promise
Promise
- 비동기 작업을 효율적으로 처리할 수 있도록 도와주는 자바스크립트의 내장 객체

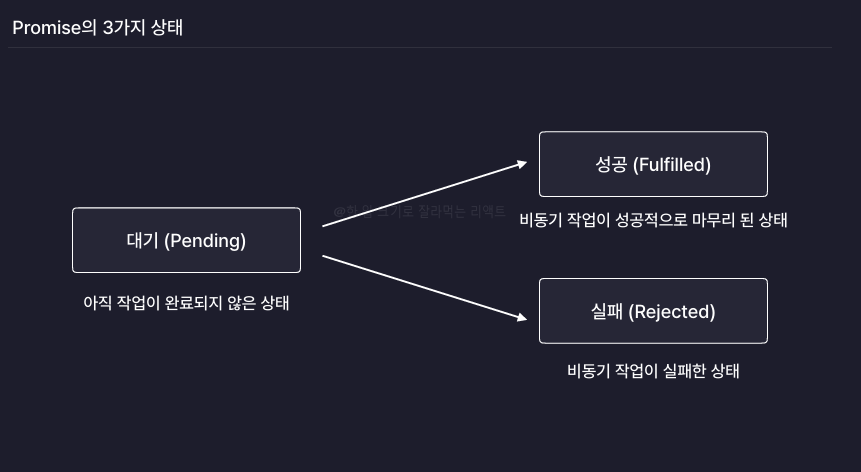
- 대기 -> 성공 : 해결(resolve)
- 대기 -> 실패 : 거부(reject)
Promise 객체 사용 예제⭐️⭐️⭐️
executor 함수: 프로미스 객체를 생성하면서 인수로 전달되는 콜백 함수- executor 함수에는 두 가지 매개변수가 전달됨
- 각각
PromiseState를fulfilled혹은rejected로 바꾸며, 함수의 인수로 결과값을 전달해줘야Promise객체의PromiseResult의 값이 바뀐다. resolve: 프로미스 작업(비동기 작업)을 성공 상태로 바꾸는 함수reject: 프로미스가 관리하는 비동기 작업을 실패 상태로 바꾸는 함수
- 각각
Promise.then(): fulfilled 상태일때 실행Promise.catch(): reject 상태일때 실행- Promise Chaining :
then()과catch()는 별도의 return문이 없으면 원본Promise객체를 반환함. 또한 필요에 따라 새로운 Promise 객체를 반환하도록 구성할 수 있음. 따라서Promise.then().catch()와 같은 식으로 연결하여 표현이 가능함.
function add10(num) {
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 비동기 작업 실행하는 함수
// executor
setTimeout(() => {
if (typeof num === "number") {
resolve(num + 10);
} else {
reject("num이 숫자가 아닙니다");
}
}, 2000);
});
return promise;
}
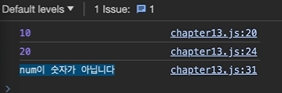
add10(0)
.then((result) => { // then : fulfilled 상태일때 실행
console.log(result);
return add10(result);
})
.then((result) => {
console.log(result);
return add10(undefined);
})
.then((result) => {
console.log(result);
})
.catch((error) => { // catch : rejected 상태일 때 실행
console.log(error);
});
2.14) 비동기 작업 처리하기 3. Async & Await
- 비동기 작업을 동기 작업을 처리하듯이 간결한 코드로 작성할 수 있음
Async
- 어떤 함수를 비동기 함수로 만들어주는 키워드
- 함수가 프로미스를 반환하도록 변환해주는 그런 키워드
- 함수가 프로미스 객체를 반환한다면 별도의 처리 없이 그대로 반환
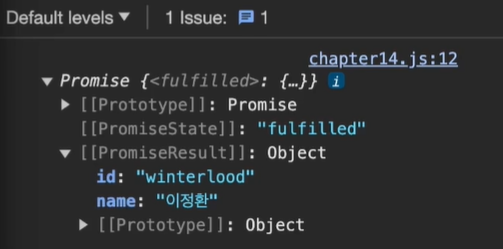
async function getData() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve({
name: "이정환",
id: "winterlood",
});
}, 1500);
});
}
Await
- Async 함수 내부에서만 사용이 가능한 키워드
- 비동기 함수가 다 처리되기를 기다리는 역할
// await를 안쓸경우
async function pringData() {
getData().then((result) => {
console.log(result);
});
}
// await를 쓸 경우
async function printData() {
const data = await getData();
console.log(data);
}
printData();