1편에서 JVM의 전체 동작 과정을 살펴봤다면, 이번 2편에서는 런타임 데이터 영역의 메모리 구조와 실전 성능 최적화 기법을 심도 있게 다뤄보겠습니다.
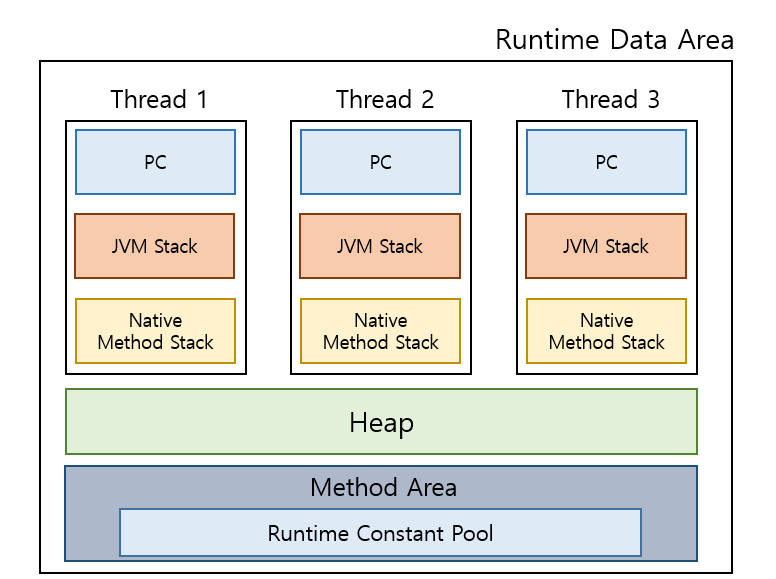
🧠 런타임 데이터 영역 (Runtime Data Area) 완전 분석
런타임 데이터 영역은 JVM이 프로그램을 실행하면서 사용하는 메모리 공간입니다. 각 영역의 특성과 역할을 정확히 이해하는 것이 성능 최적화의 핵심입니다.
메모리 영역 분류
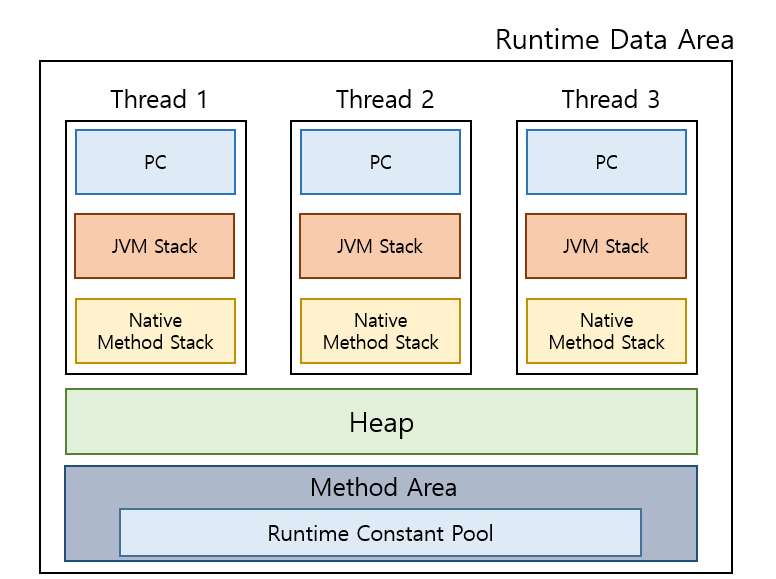
📚 Method Area (메서드 영역)
메서드 영역은 클래스 레벨의 정보를 저장하는 공간으로, JVM 시작 시 생성되어 프로그램 종료까지 유지됩니다.
메서드 영역에 저장되는 정보
public class MethodAreaExample {
// 1. 클래스 정보
private static final String COMPANY_NAME = "TechCorp"; // static 변수
private static int employeeCount = 0; // static 변수
// 2. 메서드 정보 (바이트코드)
public static void hireEmployee() { // static 메서드
employeeCount++;
}
// 3. 상수 풀
public String getWelcomeMessage() {
return "안녕하세요, " + COMPANY_NAME + "입니다!"; // 문자열 리터럴
}
}메서드 영역의 구성 요소:
-
클래스 메타데이터
- 클래스명, 부모 클래스, 인터페이스 정보
- 접근 제어자, 클래스 타입 정보
-
런타임 상수 풀 (Runtime Constant Pool)
- 문자열 리터럴, 숫자 상수
- 클래스와 메서드 참조
-
메서드 바이트코드
- 메서드의 실행 가능한 코드
- 지역 변수 테이블, 피연산자 스택 정보
-
Static 변수
- 클래스 변수 저장 공간
Runtime Constant Pool 심화
public class ConstantPoolExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 문자열 리터럴은 상수 풀에 저장됨
String str1 = "Hello";
String str2 = "Hello";
String str3 = new String("Hello");
System.out.println(str1 == str2); // true (같은 상수 풀 참조)
System.out.println(str1 == str3); // false (str3는 힙에 새로 생성)
System.out.println(str1.equals(str3)); // true (내용은 같음)
// intern() 메서드로 상수 풀에 추가 가능
String str4 = str3.intern();
System.out.println(str1 == str4); // true (상수 풀의 동일한 객체)
}
}🏠 Heap Area (힙 영역) 심화 분석
힙 영역은 객체 인스턴스와 배열이 저장되는 공간으로, 가비지 컬렉션의 주요 대상입니다.
힙 영역의 세대별 구조
Heap Memory
├─ Young Generation
│ ├─ Eden Space (새로운 객체 생성)
│ ├─ Survivor 0 (S0) (GC에서 살아남은 객체)
│ └─ Survivor 1 (S1) (GC에서 살아남은 객체)
└─ Old Generation (Tenured)
└─ Long-lived objects (오래 살아있는 객체)객체 생성과 생명 주기
public class HeapLifecycleExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. Eden 영역에 객체 생성
List<String> shortLivedList = new ArrayList<>();
shortLivedList.add("임시 데이터");
// shortLivedList는 메서드 종료 시 참조 해제 → Young GC 대상
// 2. 오래 살아있는 객체
GlobalCache.getInstance().put("key", "오래 유지될 데이터");
// 계속 참조되므로 Old Generation으로 이동
}
}
class GlobalCache {
private static GlobalCache instance = new GlobalCache();
private Map<String, String> cache = new HashMap<>();
public static GlobalCache getInstance() { return instance; }
public void put(String key, String value) { cache.put(key, value); }
}가비지 컬렉션 과정
Minor GC (Young Generation)
1. Eden 영역이 가득 참
2. 살아있는 객체를 Survivor 영역으로 이동
3. Eden 영역 정리
4. Survivor 영역 간 객체 이동 (age 증가)
5. age가 임계값에 도달하면 Old Generation으로 승격Major GC (Old Generation)
1. Old Generation이 가득 참
2. 전체 힙에 대한 GC 수행
3. 더 오랜 시간 소요 (Stop-the-World)public class GCExample {
private static List<byte[]> memoryConsumer = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Young Generation 압박 상황 시뮬레이션
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
// 1MB 크기의 배열을 반복적으로 생성
byte[] data = new byte[1024 * 1024];
if (i % 10 == 0) {
// 10번에 한 번씩 장기 보관 (Old Generation으로 이동)
memoryConsumer.add(data);
}
// Minor GC가 발생하여 임시 객체들 정리
// -verbose:gc 옵션으로 GC 로그 확인 가능
}
}
}📚 Stack Area (스택 영역) 상세 분석
스택 영역은 메서드 호출과 지역 변수를 관리하는 스레드별 메모리 공간입니다.
스택 프레임 구조
public class StackFrameExample {
public static void main(String[] args) { // 메인 스택 프레임
int mainVariable = 10;
System.out.println("메인 메서드 시작");
methodA(mainVariable); // methodA 스택 프레임 생성
System.out.println("메인 메서드 종료");
} // 메인 스택 프레임 제거
static void methodA(int param) { // methodA 스택 프레임
int localVar = param * 2;
String message = "Method A";
methodB(localVar); // methodB 스택 프레임 생성
System.out.println(message);
} // methodA 스택 프레임 제거
static void methodB(int value) { // methodB 스택 프레임
int result = value + 5;
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
} // methodB 스택 프레임 제거
}스택 프레임의 구성 요소
Stack Frame
├─ Local Variable Array (지역 변수 저장)
├─ Operand Stack (연산을 위한 스택)
├─ Frame Data (메서드 정보)
│ ├─ Constant Pool Reference
│ ├─ Method Return Address
│ └─ Exception Table기본 타입 vs 참조 타입의 저장 방식
public class MemoryStorageExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 기본 타입: 스택에 실제 값 저장
int number = 42; // 스택: [42]
double price = 19.99; // 스택: [19.99]
boolean flag = true; // 스택: [true]
// 참조 타입: 스택에 주소값, 힙에 실제 객체
String name = "김개발자"; // 스택: [주소값] → 힙: ["김개발자"]
List<String> skills = new ArrayList<>(); // 스택: [주소값] → 힙: [ArrayList 객체]
// 메서드 매개변수 전달 방식
modifyPrimitive(number); // 값 복사 (Call by Value)
modifyReference(skills); // 주소값 복사 (Call by Reference)
System.out.println(number); // 42 (변경되지 않음)
System.out.println(skills.size()); // 1 (변경됨)
}
static void modifyPrimitive(int value) {
value = 100; // 복사된 값만 변경
}
static void modifyReference(List<String> list) {
list.add("Java"); // 힙의 실제 객체 변경
}
}🎯 PC Register와 Native Method Stack
PC Register (Program Counter Register)
- 현재 실행 중인 JVM 명령어의 주소를 저장
- 스레드별로 독립적으로 관리
public class PCRegisterExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { // PC Register가 루프의 현재 위치 추적
sum += i; // 각 연산의 명령어 주소 저장
}
System.out.println(sum); // PC Register가 다음 실행할 명령어 가리킴
}
}Native Method Stack
- JNI(Java Native Interface)를 통해 호출되는 C/C++ 코드를 위한 스택
- Java 외부 라이브러리 호출 시 사용
public class NativeMethodExample {
// native 키워드로 선언된 메서드
public native void nativeMethod();
static {
// 네이티브 라이브러리 로드
System.loadLibrary("nativeLib");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NativeMethodExample example = new NativeMethodExample();
example.nativeMethod(); // Native Method Stack 사용
}
}🔧 실전 JVM 성능 최적화
1. 힙 메모리 튜닝
적절한 힙 크기 설정
# 기본 힙 설정
java -Xms2g -Xmx4g MyApplication
# Young Generation 크기 조정
java -Xms2g -Xmx4g -Xmn800m MyApplication
# New Ratio 설정 (Old:Young = 3:1)
java -Xms2g -Xmx4g -XX:NewRatio=3 MyApplication힙 크기 결정 가이드라인
public class HeapSizingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 메모리 사용량 모니터링
MemoryMXBean memoryBean = ManagementFactory.getMemoryMXBean();
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
long maxMemory = runtime.maxMemory(); // -Xmx 설정값
long totalMemory = runtime.totalMemory(); // 현재 할당된 메모리
long freeMemory = runtime.freeMemory(); // 사용 가능한 메모리
System.out.println("최대 메모리: " + (maxMemory / 1024 / 1024) + "MB");
System.out.println("할당된 메모리: " + (totalMemory / 1024 / 1024) + "MB");
System.out.println("사용 가능 메모리: " + (freeMemory / 1024 / 1024) + "MB");
// 힙 사용량 정보
MemoryUsage heapUsage = memoryBean.getHeapMemoryUsage();
System.out.println("힙 사용량: " + (heapUsage.getUsed() / 1024 / 1024) + "MB");
}
}2. 가비지 컬렉터 선택과 튜닝
다양한 GC 알고리즘
# Serial GC (단일 스레드, 소규모 애플리케이션)
java -XX:+UseSerialGC MyApp
# Parallel GC (멀티스레드, 처리량 중심)
java -XX:+UseParallelGC MyApp
# G1 GC (낮은 지연시간, 대용량 힙)
java -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=100 MyApp
# ZGC (매우 낮은 지연시간, Java 11+)
java -XX:+UseZGC MyApp
# Shenandoah GC (낮은 지연시간)
java -XX:+UseShenandoahGC MyAppGC 모니터링과 분석
public class GCMonitoringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// GC 정보 수집
List<GarbageCollectorMXBean> gcBeans = ManagementFactory.getGarbageCollectorMXBeans();
for (GarbageCollectorMXBean gcBean : gcBeans) {
System.out.println("GC 이름: " + gcBean.getName());
System.out.println("GC 횟수: " + gcBean.getCollectionCount());
System.out.println("GC 소요 시간: " + gcBean.getCollectionTime() + "ms");
}
// 메모리 풀 정보
List<MemoryPoolMXBean> poolBeans = ManagementFactory.getMemoryPoolMXBeans();
for (MemoryPoolMXBean poolBean : poolBeans) {
MemoryUsage usage = poolBean.getUsage();
System.out.println("풀 이름: " + poolBean.getName());
System.out.println("사용률: " + (usage.getUsed() * 100.0 / usage.getMax()) + "%");
}
}
}3. 메모리 누수 방지
일반적인 메모리 누수 패턴과 해결책
public class MemoryLeakExamples {
// ❌ 나쁜 예: Static 컬렉션에 계속 추가
private static List<String> staticList = new ArrayList<>();
public void badExample1() {
staticList.add("계속 추가되는 데이터"); // 메모리 누수!
}
// ✅ 좋은 예: 적절한 크기 제한
private static final int MAX_SIZE = 1000;
private static List<String> limitedList = new ArrayList<>();
public void goodExample1(String data) {
if (limitedList.size() >= MAX_SIZE) {
limitedList.remove(0); // 오래된 데이터 제거
}
limitedList.add(data);
}
// ❌ 나쁜 예: 리스너 등록 후 해제하지 않음
public class BadListener {
private SomeComponent component;
public BadListener(SomeComponent component) {
this.component = component;
component.addListener(this::onEvent); // 등록 후 해제하지 않음
}
private void onEvent(Event event) {
// 이벤트 처리
}
}
// ✅ 좋은 예: 적절한 리스너 해제
public class GoodListener implements AutoCloseable {
private SomeComponent component;
private EventListener listener;
public GoodListener(SomeComponent component) {
this.component = component;
this.listener = this::onEvent;
component.addListener(listener);
}
@Override
public void close() {
if (component != null && listener != null) {
component.removeListener(listener); // 명시적 해제
}
}
private void onEvent(Event event) {
// 이벤트 처리
}
}
// ❌ 나쁜 예: ThreadLocal 정리하지 않음
private static ThreadLocal<ExpensiveObject> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
public void badThreadLocalUsage() {
threadLocal.set(new ExpensiveObject());
// 정리하지 않으면 메모리 누수 발생
}
// ✅ 좋은 예: ThreadLocal 적절히 정리
public void goodThreadLocalUsage() {
try {
threadLocal.set(new ExpensiveObject());
// 작업 수행
} finally {
threadLocal.remove(); // 명시적 정리
}
}
}
class SomeComponent {
private List<EventListener> listeners = new ArrayList<>();
public void addListener(EventListener listener) {
listeners.add(listener);
}
public void removeListener(EventListener listener) {
listeners.remove(listener);
}
}
interface EventListener {
void onEvent(Event event);
}
class Event {}
class ExpensiveObject {}4. JIT 컴파일러 최적화
메서드 인라이닝 최적화
public class JITOptimizationExample {
// ✅ 인라이닝에 적합한 메서드
private static final int THRESHOLD = 100;
public final int simpleCalculation(int x) { // final 키워드로 인라이닝 촉진
return x * 2 + 1;
}
public int optimizableLoop(int[] array) {
int sum = 0;
for (int value : array) {
sum += simpleCalculation(value); // 인라이닝 대상
}
return sum;
}
// ❌ 인라이닝에 부적합한 메서드
public int complexMethod(int x) {
// 너무 복잡한 로직 (35바이트 이상)
if (x > THRESHOLD) {
return expensiveCalculation(x);
} else {
return anotherExpensiveCalculation(x);
}
}
// JIT 컴파일러 정보 확인을 위한 플래그
// -XX:+PrintCompilation -XX:+UnlockDiagnosticVMOptions -XX:+PrintInlining
}컴파일 임계값 조정
# 컴파일 임계값 설정
java -XX:CompileThreshold=1000 MyApp # 기본값: 10000 (Server VM)
# Tiered Compilation 설정
java -XX:+TieredCompilation \
-XX:Tier3CompileThreshold=2000 \
-XX:Tier4CompileThreshold=15000 MyApp5. 스택 최적화
스택 오버플로우 방지
public class StackOptimizationExample {
// ❌ 나쁜 예: 깊은 재귀 호출
public int factorialRecursive(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return 1;
return n * factorialRecursive(n - 1); // 스택 오버플로우 위험
}
// ✅ 좋은 예: 반복문으로 변환
public int factorialIterative(int n) {
int result = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
result *= i;
}
return result;
}
// ✅ 좋은 예: 꼬리 재귀 최적화 스타일
public long factorialTailRecursive(int n) {
return factorialHelper(n, 1);
}
private long factorialHelper(int n, long accumulator) {
if (n <= 1) return accumulator;
return factorialHelper(n - 1, n * accumulator);
}
}스택 크기 조정
# 스택 크기 설정
java -Xss512k MyApp # 기본값: 1MB (64-bit), 512KB (32-bit)
# 큰 스택이 필요한 경우
java -Xss2m MyApp📊 JVM 모니터링 도구와 실전 활용
1. 내장 모니터링 도구
jstat - GC 통계 정보
# GC 통계 5초마다 출력
jstat -gc <pid> 5s
# 힙 영역별 용량 정보
jstat -gccapacity <pid>
# 컴파일 통계
jstat -compiler <pid>jmap - 힙 덤프 분석
# 힙 덤프 생성
jmap -dump:format=b,file=heap.hprof <pid>
# 힙 히스토그램 출력
jmap -histo <pid>
# 클래스별 인스턴스 수 확인
jmap -histo <pid> | head -20jstack - 스레드 덤프 분석
# 스레드 덤프 생성
jstack <pid> > thread_dump.txt
# 데드락 감지
jstack -l <pid>2. 애플리케이션 내 모니터링
@Component
@Slf4j
public class JVMMonitor {
private final MemoryMXBean memoryMXBean;
private final List<GarbageCollectorMXBean> gcMXBeans;
private final ThreadMXBean threadMXBean;
public JVMMonitor() {
this.memoryMXBean = ManagementFactory.getMemoryMXBean();
this.gcMXBeans = ManagementFactory.getGarbageCollectorMXBeans();
this.threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean();
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 60000) // 1분마다 실행
public void monitorJVM() {
logMemoryUsage();
logGCStatistics();
logThreadInformation();
}
private void logMemoryUsage() {
MemoryUsage heapUsage = memoryMXBean.getHeapMemoryUsage();
MemoryUsage nonHeapUsage = memoryMXBean.getNonHeapMemoryUsage();
double heapUsedPercentage = (double) heapUsage.getUsed() / heapUsage.getMax() * 100;
log.info("힙 메모리 사용률: {:.2f}% ({}/{})",
heapUsedPercentage,
formatBytes(heapUsage.getUsed()),
formatBytes(heapUsage.getMax()));
log.info("Non-힙 메모리 사용량: {}", formatBytes(nonHeapUsage.getUsed()));
// 메모리 사용률이 80% 이상이면 경고
if (heapUsedPercentage > 80) {
log.warn("⚠️ 힙 메모리 사용률이 높습니다: {:.2f}%", heapUsedPercentage);
}
}
private void logGCStatistics() {
for (GarbageCollectorMXBean gcBean : gcMXBeans) {
long collections = gcBean.getCollectionCount();
long time = gcBean.getCollectionTime();
if (collections > 0) {
log.info("GC [{}]: 횟수={}, 총 시간={}ms, 평균={}ms",
gcBean.getName(), collections, time, time / collections);
}
}
}
private void logThreadInformation() {
int threadCount = threadMXBean.getThreadCount();
int peakThreadCount = threadMXBean.getPeakThreadCount();
log.info("스레드 정보: 현재={}, 최대={}", threadCount, peakThreadCount);
// 데드락 감지
long[] deadlockedThreads = threadMXBean.findDeadlockedThreads();
if (deadlockedThreads != null) {
log.error("🚨 데드락 감지됨! 스레드 수: {}", deadlockedThreads.length);
}
}
private String formatBytes(long bytes) {
String[] units = {"B", "KB", "MB", "GB"};
int unitIndex = 0;
double size = bytes;
while (size >= 1024 && unitIndex < units.length - 1) {
size /= 1024;
unitIndex++;
}
return String.format("%.2f %s", size, units[unitIndex]);
}
}3. 성능 튜닝 체크리스트
메모리 최적화 체크리스트
public class PerformanceTuningChecklist {
// ✅ 1. 적절한 컬렉션 선택
private List<String> frequentRead = new ArrayList<>(); // 빈번한 읽기
private Set<String> uniqueItems = new HashSet<>(); // 중복 제거
private Map<String, String> fastLookup = new HashMap<>(); // 빠른 조회
// ✅ 2. 초기 용량 설정
private List<String> knownSizeList = new ArrayList<>(1000);
private Map<String, String> knownSizeMap = new HashMap<>(256);
// ✅ 3. StringBuilder 사용
public String buildString(List<String> items) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(items.size() * 20); // 예상 크기 설정
for (String item : items) {
sb.append(item).append(", ");
}
return sb.toString();
}
// ✅ 4. 객체 풀 패턴 (필요한 경우)
private final Queue<ExpensiveObject> objectPool = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
public ExpensiveObject borrowObject() {
ExpensiveObject obj = objectPool.poll();
return obj != null ? obj : new ExpensiveObject();
}
public void returnObject(ExpensiveObject obj) {
obj.reset(); // 상태 초기화
objectPool.offer(obj);
}
// ✅ 5. 캐시 활용
@Cacheable("expensiveOperations")
public String expensiveOperation(String input) {
// 비용이 많이 드는 연산
return processHeavyCalculation(input);
}
private String processHeavyCalculation(String input) {
// 실제 계산 로직
return "result";
}
}🎯 실전 트러블슈팅 가이드
OutOfMemoryError 해결
// 1. 힙 공간 부족 (java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space)
// 해결책: 힙 크기 증가, 메모리 누수 제거
java -Xmx4g -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError MyApp
// 2. 메타스페이스 부족 (java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Metaspace)
// 해결책: 메타스페이스 크기 증가
java -XX:MetaspaceSize=256m -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=512m MyApp
// 3. 스택 오버플로우 (java.lang.StackOverflowError)
// 해결책: 스택 크기 증가, 재귀 로직 개선
java -Xss2m MyAppGC 튜닝 실전 예제
# 처리량 중심 애플리케이션
java -XX:+UseParallelGC \
-XX:ParallelGCThreads=8 \
-XX:+UseParallelOldGC \
-Xms4g -Xmx4g MyApp
# 응답 시간 중심 애플리케이션
java -XX:+UseG1GC \
-XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=100 \
-XX:G1HeapRegionSize=16m \
-Xms4g -Xmx4g MyApp
# 매우 큰 힙 (32GB+)
java -XX:+UseZGC \
-Xmx32g MyApp💡 마무리
JVM의 메모리 구조를 이해하고 적절한 튜닝을 수행하면 애플리케이션의 성능을 크게 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
핵심 포인트 요약
- 메모리 영역별 특성 이해: Method Area, Heap, Stack 각각의 역할과 최적화 포인트
- GC 알고리즘 선택: 애플리케이션 특성에 맞는 가비지 컬렉터 선택
- 지속적인 모니터링: JVM 메트릭을 통한 성능 추이 관찰
- 메모리 누수 방지: 일반적인 메모리 누수 패턴 인지와 예방
- 실전 튜닝: 운영 환경에서의 체계적인 성능 튜닝 접근법
Java 개발자로서 JVM에 대한 깊은 이해는 단순히 이론적 지식이 아닌, 실제 문제 해결 능력을 크게 향상시키는 실용적인 기술입니다. 지속적인 모니터링과 개선을 통해 더 나은 애플리케이션을 만들어 나가시길 바랍니다!