1. HTTPS 사설 인증서 발급 및 구현
1) 인증서 생성
- 아래 명령어를 통해 로컬을 인증된 발급기관으로 추가해야 한다.
- 설치 명령어
$ mkcert -install
- 다음으로 로컬 환경에 대한 인증서를 만들어야 한다.
localhost로 대표되는 로컬 환경에 대한 인증서를 만들기 위해 아래 명령어를 입력한다.
- 인증서 생성 명령어
$ mkcert -key-file key.pem -cert-file cert.pem localhost 127.0.0.1 ::1
-
이제 옵션으로 추가한
localhost,127.0.0.1(IPv4),::1(IPv6)에서 사용할 수 있는 인증서가 완성되었으며,cert.pem,key.pem이라는 파일이 생성된 것을 확인할 수 있다. -
인증서는 공개키, 그리고 인증기관의 서명을 포함하고 있으므로 공개되어도 상관이 없지만, key.pem의 경우 개인 키이므로 git에 커밋하지 않고, 암호처럼 다루어야 한다.
2) HTTPS 서버 작성
2-1. Node.js https 모듈 이용
- 서버를 실행한 후
https://localhost:3001로 접속하면 브라우저의 url 창 왼쪽에 자물쇠가 잠겨있는HTTPS프로토콜을 이용하는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.

const https = require('https');
const fs = require('fs');
https
.createServer(
{
key: fs.readFileSync(__dirname + '/key.pem', 'utf-8'),
cert: fs.readFileSync(__dirname + '/cert.pem', 'utf-8'),
},
function (req, res) {
res.write('Congrats! You made https server now :)');
res.end();
}
)
.listen(3001);2-2. express.js 이용
- 만약 express.js 를 사용하는 경우, 다음과 같이
https.createServer의 두 번째 파라미터에 들어갈 callback 함수를 Express 미들웨어로 교체해준다.
const https = require('https');
const fs = require('fs');
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
https
.createServer(
{
key: fs.readFileSync(__dirname + '/key.pem', 'utf-8'),
cert: fs.readFileSync(__dirname + '/cert.pem', 'utf-8'),
},
app.use('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Congrats! You made https server now :)');
})
)
.listen(3001);2. ngrok
-
ngrok이란 HTTP로 만들어진 서버를 HTTPS 프로토콜로 터널링 해주는 프로그램이다.
-
ngrok을 사용하면 로컬 개발환경인 localhost에서 구동 중인 웹 서비스를 외부 인터넷 환경에서 접근할 수 있도록 만들어준다.
- 터널링 명령어
$ ngrok http '본인의 로컬 서버 포트'
- 하지만 기본적으로 ngrok는 기본 세션 유효기간이 존재한다. 이 세션은 만료되어 다시 ngrok를 실행해줘야 하며, 재실행 시 접속 URL이 바뀌게 된다. 그래서 세션 제한없이 사용하기 위해서 authtoken을 등록해줘야 한다.
- authtoken 등록 명령어
ngrok authtoken '본인의 authtoken 코드'
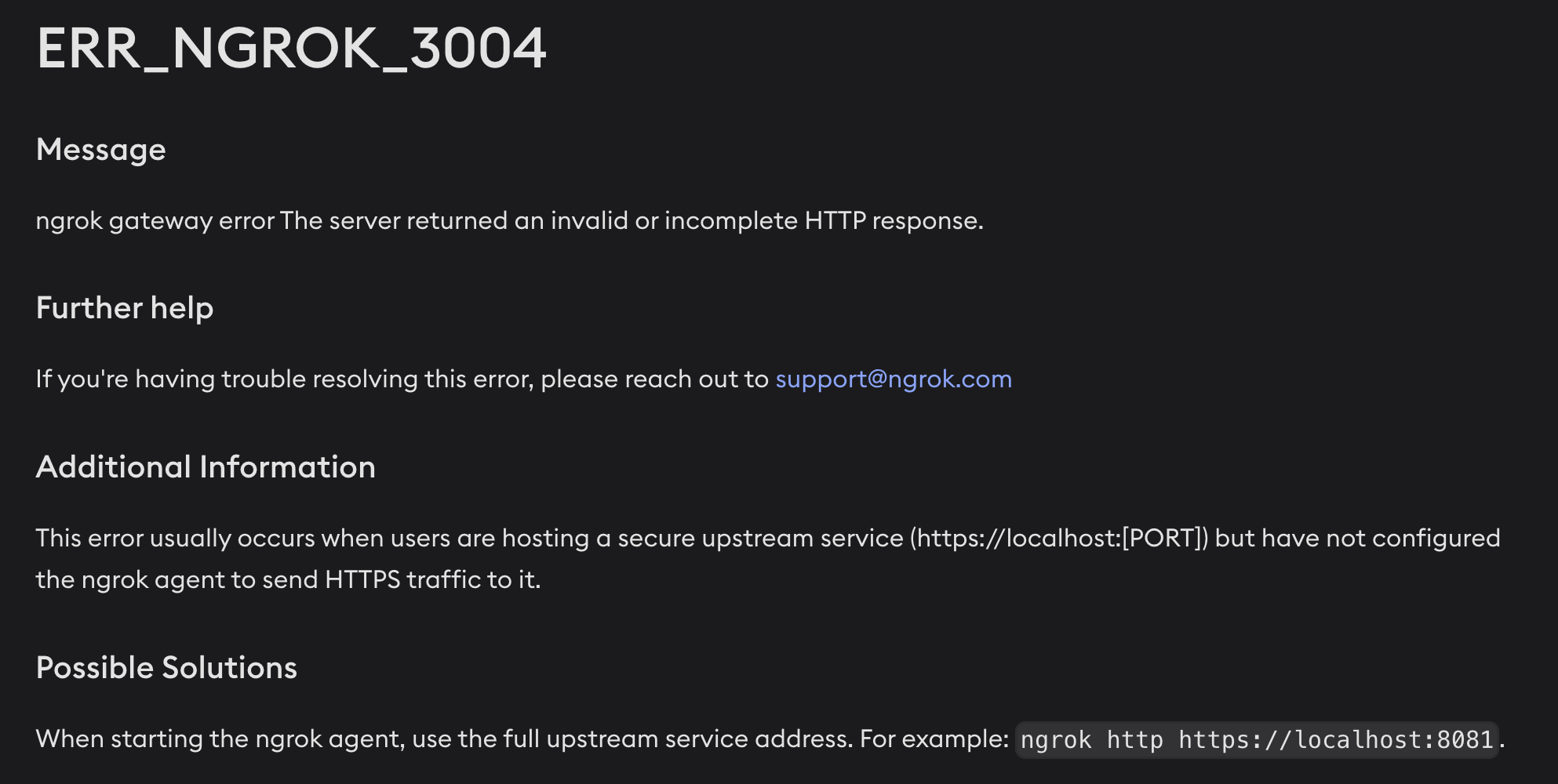
ngrok http 3001와 같이 로컬 포트 번호만 입력 후 실행했을 때 아래와 같은 오류가 난다면ngrok http https://localhost:3001/와 같이 포트 번호 입력 부분에 전체 주소를 입력해줘야 한다.
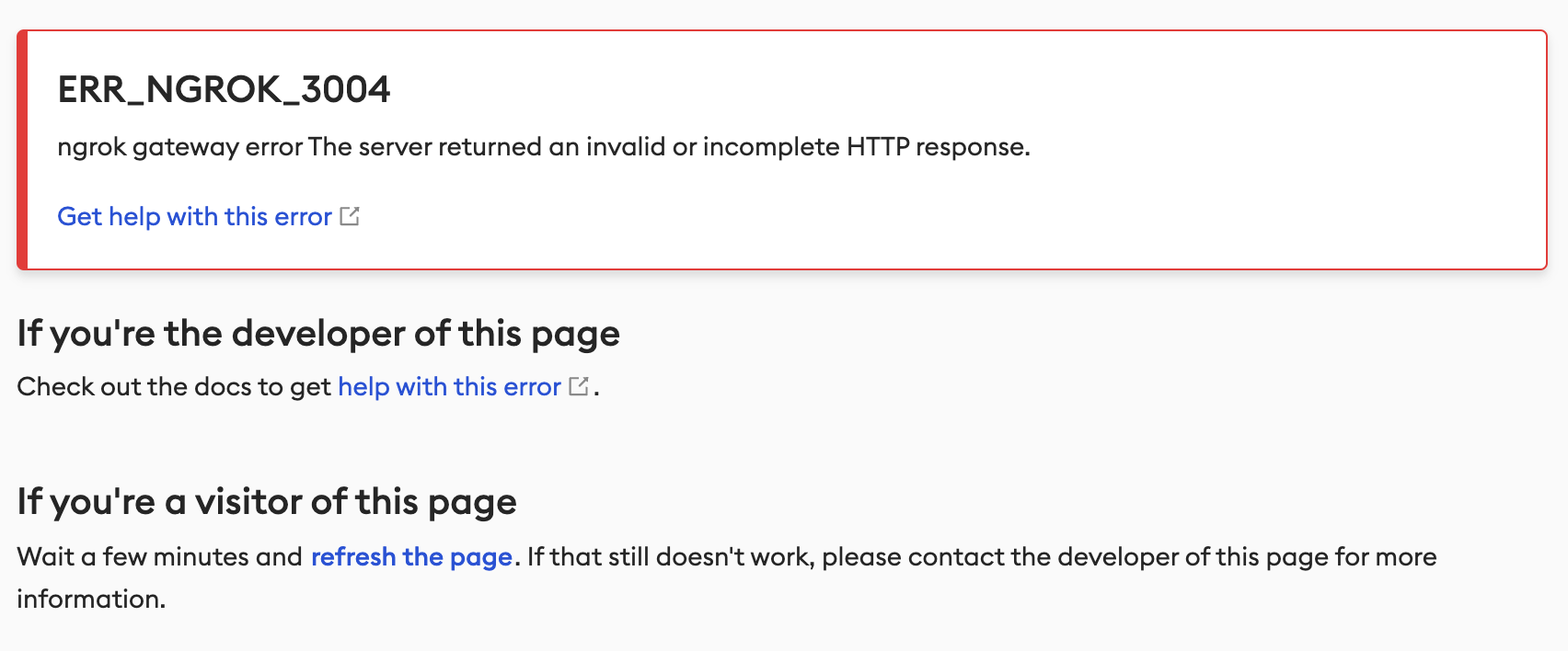
full upstream service address 주소를 입력하라는 가이드
-
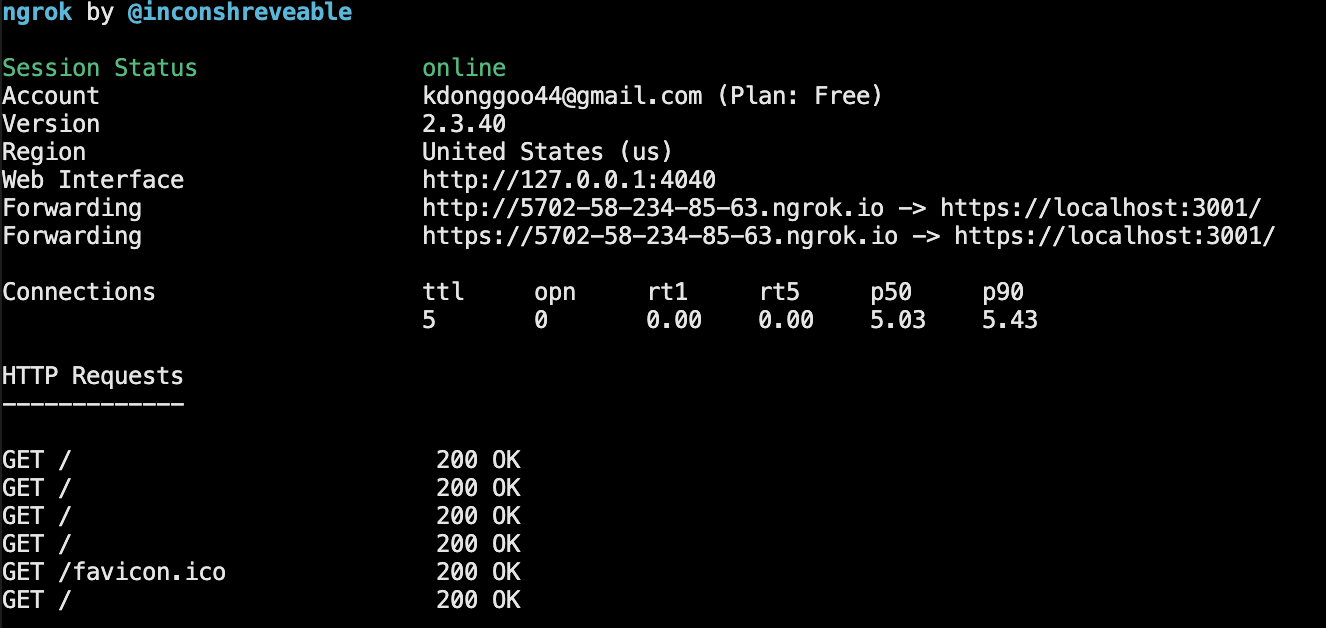
정상적으로 터널링이 완료되면 아래와 같은 창이 터미널에 뜨게 되고 이제 외부에서
https://5702-58-234-85-63.ngrok.io주소로 접속하면 나의 로컬 서버인https://localhost:3001/에 접속(포워딩)된다. -
포워딩이란
https://5702-58-234-85-63.ngrok.io주소로 요청(Request)을 하면 그 요청을 다른 도메인(localhost)으로 보내는 것을 말한다.